Lysosomal membrane permeabilization induces cell death in a mitochondrion-dependent fashion
- PMID: 12756268
- PMCID: PMC2193790
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20021952
Lysosomal membrane permeabilization induces cell death in a mitochondrion-dependent fashion
Abstract
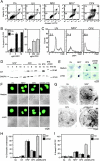
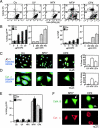
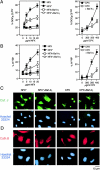
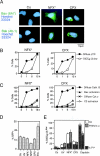
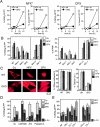
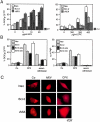
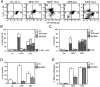
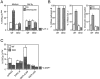
A number of diseases are due to lysosomal destabilization, which results in damaging cell loss. To investigate the mechanisms of lysosomal cell death, we characterized the cytotoxic action of two widely used quinolone antibiotics: ciprofloxacin (CPX) or norfloxacin (NFX). CPX or NFX plus UV light (NFX*) induce lysosomal membrane permeabilization (LMP), as detected by the release of cathepsins from lysosomes. Inhibition of the lysosomal accumulation of CPX or NFX suppresses their capacity to induce LMP and to kill cells. CPX- or NFX-triggered LMP results in caspase-independent cell death, with hallmarks of apoptosis such as chromatin condensation and phosphatidylserine exposure on the plasma membrane. LMP triggers mitochondrial membrane permeabilization (MMP), as detected by the release of cytochrome c. Both CPX and NFX* cause Bax and Bak to adopt their apoptotic conformation and to insert into mitochondrial membranes. Bax-/- Bak-/- double knockout cells fail to undergo MMP and cell death in response to CPX- or NFX-induced LMP. The single knockout of Bax or Bak (but not Bid) or the transfection-enforced expression of mitochondrion-targeted (but not endoplasmic reticulum-targeted) Bcl-2 conferred protection against CPX (but not NFX*)-induced MMP and death. Altogether, our data indicate that mitochondria are indispensable for cell death initiated by lysosomal destabilization.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization is a critical step of lysosome-initiated apoptosis induced by hydroxychloroquine.Oncogene. 2003 Jun 19;22(25):3927-36. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206622. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12813466
-
Involvement of proapoptotic molecules Bax and Bak in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced mitochondrial disruption and apoptosis: differential regulation of cytochrome c and Smac/DIABLO release.Cancer Res. 2003 Apr 1;63(7):1712-21. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12670926
-
Cathepsin-cleaved Bid promotes apoptosis in human neutrophils via oxidative stress-induced lysosomal membrane permeabilization.J Leukoc Biol. 2007 May;81(5):1213-23. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0506359. Epub 2007 Jan 30. J Leukoc Biol. 2007. PMID: 17264306
-
Lysosomal membrane permeabilization in cell death.Oncogene. 2008 Oct 27;27(50):6434-51. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.310. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18955971 Review.
-
Bax and other pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family "killer-proteins" and their victim the mitochondrion.Cell Tissue Res. 2001 Dec;306(3):347-61. doi: 10.1007/s00441-001-0472-0. Epub 2001 Oct 30. Cell Tissue Res. 2001. PMID: 11735035 Review.
Cited by
-
Remote Actuation of Magnetic Nanoparticles For Cancer Cell Selective Treatment Through Cytoskeletal Disruption.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 20;6:33560. doi: 10.1038/srep33560. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27644858 Free PMC article.
-
Light induces NLRP3 inflammasome activation in retinal pigment epithelial cells via lipofuscin-mediated photooxidative damage.J Mol Med (Berl). 2015 Aug;93(8):905-16. doi: 10.1007/s00109-015-1275-1. Epub 2015 Mar 18. J Mol Med (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25783493 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte death: a clear and present danger.Physiol Rev. 2010 Jul;90(3):1165-94. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00061.2009. Physiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20664081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantification of Efferocytosis by Single-cell Fluorescence Microscopy.J Vis Exp. 2018 Aug 18;(138):58149. doi: 10.3791/58149. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 30176011 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans functional orthologue of human protein h-mucolipin-1 is required for lysosome biogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Mar 30;101(13):4483-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400709101. Epub 2004 Mar 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15070744 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Green, D.R., and G. Kroemer. 1998. The central executioner of apoptosis: mitochondria or caspases? Trends Cell Biol. 8:267–271. - PubMed
-
- Kroemer, G., and J.C. Reed. 2000. Mitochondrial control of cell death. Nat. Med. 6:513–519. - PubMed
-
- Wang, X. 2002. The expanding role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev. 15:2922–2933. - PubMed
-
- Ferri, K.F., and G.K. Kroemer. 2001. Organelle-specific initiation of cell death pathways. Nat. Cell Biol. 3:E255–E263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

