Defective CD8 T cell memory following acute infection without CD4 T cell help
- PMID: 12690202
- PMCID: PMC2778341
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1083317
Defective CD8 T cell memory following acute infection without CD4 T cell help
Abstract
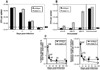
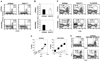
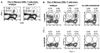
The CD8+ cytotoxic T cell response to pathogens is thought to be CD4+ helper T cell independent because infectious agents provide their own inflammatory signals. Mice that lack CD4+ T cells mount a primary CD8 response to Listeria monocytogenes equal to that of wild-type mice and rapidly clear the infection. However, protective memory to a challenge is gradually lost in the former animals. Memory CD8+ T cells from normal mice can respond rapidly, but memory CD8+ T cells that are generated without CD4 help are defective in their ability to respond to secondary encounters with antigen. The results highlight a previously undescribed role for CD4 help in promoting protective CD8 memory development.
Figures
Comment in
-
Immunology. CD8 T cells remember with a little help.Science. 2003 Apr 11;300(5617):263-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1084511. Science. 2003. PMID: 12690179 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Requirement for CD4 T cell help in generating functional CD8 T cell memory.Science. 2003 Apr 11;300(5617):337-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1082305. Science. 2003. PMID: 12690201
-
Simultaneous assessment of antigen-stimulated cytokine production and memory subset composition of memory CD8 T cells.J Immunol Methods. 2006 Jun 30;313(1-2):161-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2006.04.005. Epub 2006 May 26. J Immunol Methods. 2006. PMID: 16762359
-
Class Ia MHC-deficient BALB/c mice generate CD8+ T cell-mediated protective immunity against Listeria monocytogenes infection.J Immunol. 2003 Jul 1;171(1):291-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.1.291. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12817010
-
Primary and secondary immune responses to Listeria monocytogenes.Curr Opin Immunol. 1996 Aug;8(4):526-30. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(96)80041-0. Curr Opin Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8794012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding memory CD8+ T cells.Immunol Lett. 2017 May;185:32-39. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2017.02.012. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Immunol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28274794 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CD8+ T-Cell Memory: The Why, the When, and the How.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2021 May 3;13(5):a038661. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a038661. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2021. PMID: 33648987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MHC class Ib-restricted CD8 T cells differ in dependence on CD4 T cell help and CD28 costimulation over the course of mouse polyomavirus infection.J Immunol. 2012 Apr 1;188(7):3071-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103554. Epub 2012 Mar 5. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22393155 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosal immunology of HIV infection.Immunol Rev. 2013 Jul;254(1):10-33. doi: 10.1111/imr.12072. Immunol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23772612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate-like CD4 T cells selected by thymocytes suppress adaptive immune responses against bacterial infections.Open J Immunol. 2012 Mar;2(1):25-39. doi: 10.4236/oji.2012.21004. Epub 2011 Dec 30. Open J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23264931 Free PMC article.
-
The surprising kinetics of the T cell response to live antigenic cells.J Immunol. 2007 Oct 15;179(8):4988-95. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.8.4988. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17911583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bennett SR, et al. Nature. 1998;393:478. - PubMed
-
- Schoenberger SP, Toes RE, van der Voort EI, Offringa R, Melief CJ. Nature. 1998;393:480. - PubMed
-
- Ridge JP, Di Rosa F, Matzinger P. Nature. 1998;393:474. - PubMed
-
- Janeway CA, Jr, Medzhitov R. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002;20:197. - PubMed
-
- Gordon S. Cell. 2002;111:927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

