Phosphorylation of the Stat1 transactivating domain is required for the response to type I interferons
- PMID: 12671680
- PMCID: PMC1319158
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.embor802
Phosphorylation of the Stat1 transactivating domain is required for the response to type I interferons
Abstract
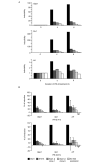
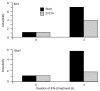
Stat1 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 1) regulates transcription in response to the type I interferons IFN-alpha and IFN-beta, either in its dimerized form or as a subunit of the interferon-stimulated gene factor 3 (Isgf3) complex (consisting of Stat1, Stat2 and interferon-regulating factor 9). Full-length Stat1-alpha and the splice variant Stat1-beta, which lacks the carboxyl terminus and the Ser727 phosphorylation site, are found in all cell types. IFN-induced phosphorylation of Stat1-alpha on Ser727 occurs in the absence of the candidate kinase, protein kinase C-delta. When expressed in Stat1-deficient cells, Stat1-beta and a Stat1-S727A mutant both restored the formation of Stat1 dimers and of the Isgf3 complex on treatment with IFN-beta. By contrast, only Stat1-alpha restored the ability of IFN-beta to induce high levels of transcription from target genes of Stat1 dimers and Isgf3 and to induce an antiviral state. Our data suggest an important contribution of the Stat1 C terminus and its phosphorylation at Ser727 to the transcriptional activities of the Stat1 dimer and the Isgf3 complex.
Figures



Similar articles
-
p38 MAP kinase is required for STAT1 serine phosphorylation and transcriptional activation induced by interferons.EMBO J. 1999 Oct 15;18(20):5601-8. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.20.5601. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 10523304 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired response to interferon-alpha/beta and lethal viral disease in human STAT1 deficiency.Nat Genet. 2003 Mar;33(3):388-91. doi: 10.1038/ng1097. Epub 2003 Feb 18. Nat Genet. 2003. PMID: 12590259
-
Resistance to interferons in melanoma cells does not correlate with the expression or activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (Stat1).J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002 May;22(5):603-13. doi: 10.1089/10799900252982089. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002. PMID: 12060499
-
Distinct STAT structure promotes interaction of STAT2 with the p48 subunit of the interferon-alpha-stimulated transcription factor ISGF3.J Biol Chem. 1997 Aug 8;272(32):20070-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.32.20070. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9242679
-
A Positive Feedback Amplifier Circuit That Regulates Interferon (IFN)-Stimulated Gene Expression and Controls Type I and Type II IFN Responses.Front Immunol. 2018 May 28;9:1135. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01135. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29892288 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired interferon response in senecavirus A infection and identification of 3Cpro as an antagonist.J Virol. 2024 Jul 23;98(7):e0058524. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00585-24. Epub 2024 Jun 13. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38869319 Free PMC article.
-
STAT1β enhances STAT1 function by protecting STAT1α from degradation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Oct 5;8(10):e3077. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.481. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28981100 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating cholesterol-rich lipid rafts to disrupt influenza A virus infection.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 13;13:982264. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.982264. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36177026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Programming Bordetella pertussis lipid A to promote adjuvanticity.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Sep 14;23(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02518-7. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 39272136 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon induction and function at the mucosal surface.Immunol Rev. 2013 Sep;255(1):25-39. doi: 10.1111/imr.12101. Immunol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23947345 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Darnell J.E., Kerr I.M. & Stark G.R. (1994) Jakstat pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science, 264, 1415–1421. - PubMed
-
- Decker T. & Kovarik P. (2000) Serine phosphorylation of Stats. Oncogene, 19, 2628–2637. - PubMed
-
- Durbin J.E., Hackenmiller R., Simon M.C. & Levy D.E. (1996) Targeted disruption of the mouse Stat1 gene results in compromised innate immunity to viral disease. Cell, 84, 443–450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

