Human cytomegalovirus activates inflammatory cytokine responses via CD14 and Toll-like receptor 2
- PMID: 12663765
- PMCID: PMC152130
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.8.4588-4596.2003
Human cytomegalovirus activates inflammatory cytokine responses via CD14 and Toll-like receptor 2
Abstract
Human cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a ubiquitous opportunistic pathogen that causes significant morbidity and mortality in immunocompromised people. An understanding of how CMV induces and circumvents host immunity is of critical importance in efforts to design effective therapeutics. It was recently discovered that mere cell contact by CMV particles leads to profound modulation of cellular gene expression, including induction of inflammatory cytokines and interferon-stimulated genes characteristic of innate immune detection. These findings suggest that a membrane receptor recognizes a CMV envelope protein(s), leading to innate immune activation. Here, we show that the pattern recognition receptors Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and CD14 recognize CMV virions and trigger inflammatory cytokine production. Induction of inflammatory cytokines is mediated via TLR2-dependent activation of NF-kappa B. Since many of the pathological processes associated with CMV disease are facilitated or directly mediated by inflammatory cytokines, identification of the host membrane detection machinery may ultimately lead to improved therapeutics.
Figures
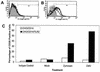
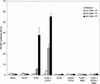
Similar articles
-
Dependence of bacterial protein adhesins on toll-like receptors for proinflammatory cytokine induction.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002 Mar;9(2):403-11. doi: 10.1128/cdli.9.2.403-411.2002. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11874886 Free PMC article.
-
Non-LPS components of Chlamydia pneumoniae stimulate cytokine production through Toll-like receptor 2-dependent pathways.Eur J Immunol. 2002 Apr;32(4):1188-95. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200204)32:4<1188::AID-IMMU1188>3.0.CO;2-A. Eur J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11932927
-
Acute alcohol inhibits the induction of nuclear regulatory factor kappa B activation through CD14/toll-like receptor 4, interleukin-1, and tumor necrosis factor receptors: a common mechanism independent of inhibitory kappa B alpha degradation?Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2002 Nov;26(11):1609-14. doi: 10.1097/01.ALC.0000036926.46632.57. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2002. PMID: 12436048
-
Toll-like receptors as sensors of pathogens.Pediatr Res. 2001 Sep;50(3):315-21. doi: 10.1203/00006450-200109000-00004. Pediatr Res. 2001. PMID: 11518816 Review.
-
Interactions of oral pathogens with toll-like receptors: possible role in atherosclerosis.Ann Periodontol. 2002 Dec;7(1):72-8. doi: 10.1902/annals.2002.7.1.72. Ann Periodontol. 2002. PMID: 16013219 Review.
Cited by
-
Viral infections in etiology of mental disorders: a broad analysis of cytokine profile similarities - a narrative review.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Aug 14;14:1423739. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1423739. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39206043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The battle between host antiviral innate immunity and immune evasion by cytomegalovirus.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Aug 9;81(1):341. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05369-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39120730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of Cytomegalovirus Ocular Diseases: Retinitis, Corneal Endotheliitis, and Iridocyclitis.Viruses. 2024 Jul 11;16(7):1110. doi: 10.3390/v16071110. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39066272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytomegalovirus-induced peroxynitrite promotes virus entry and contributes to pathogenesis in a murine model of infection.mBio. 2024 Aug 14;15(8):e0315223. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03152-23. Epub 2024 Jul 2. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38953361 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Transformation by Human Cytomegalovirus.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 22;16(11):1970. doi: 10.3390/cancers16111970. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AbuBakar, S., I. Boldogh, and T. Albrecht. 1990. Human cytomegalovirus stimulates arachidonic acid metabolism through pathways that are affected by inhibitors of phospholipase A2 and protein kinase C. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 166:953-959. - PubMed
-
- Akira, S.2001. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Adv. Immunol. 78:1-56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

