LAGAN and Multi-LAGAN: efficient tools for large-scale multiple alignment of genomic DNA
- PMID: 12654723
- PMCID: PMC430158
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.926603
LAGAN and Multi-LAGAN: efficient tools for large-scale multiple alignment of genomic DNA
Abstract
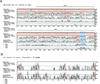
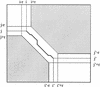
To compare entire genomes from different species, biologists increasingly need alignment methods that are efficient enough to handle long sequences, and accurate enough to correctly align the conserved biological features between distant species. We present LAGAN, a system for rapid global alignment of two homologous genomic sequences, and Multi-LAGAN, a system for multiple global alignment of genomic sequences. We tested our systems on a data set consisting of greater than 12 Mb of high-quality sequence from 12 vertebrate species. All the sequence was derived from the genomic region orthologous to an approximately 1.5-Mb region on human chromosome 7q31.3. We found that both LAGAN and Multi-LAGAN compare favorably with other leading alignment methods in correctly aligning protein-coding exons, especially between distant homologs such as human and chicken, or human and fugu. Multi-LAGAN produced the most accurate alignments, while requiring just 75 minutes on a personal computer to obtain the multiple alignment of all 12 sequences. Multi-LAGAN is a practical method for generating multiple alignments of long genomic sequences at any evolutionary distance. Our systems are publicly available at http://lagan.stanford.edu.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Glocal alignment: finding rearrangements during alignment.Bioinformatics. 2003;19 Suppl 1:i54-62. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg1005. Bioinformatics. 2003. PMID: 12855437
-
ABC: software for interactive browsing of genomic multiple sequence alignment data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2004 Dec 8;5:192. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-192. BMC Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15588288 Free PMC article.
-
Phylo-VISTA: interactive visualization of multiple DNA sequence alignments.Bioinformatics. 2004 Mar 22;20(5):636-43. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg459. Epub 2004 Jan 22. Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15033870
-
Computation and analysis of genomic multi-sequence alignments.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2007;8:193-213. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genom.8.080706.092300. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2007. PMID: 17489682 Review.
-
Differences between pair-wise and multi-sequence alignment methods affect vertebrate genome comparisons.Trends Genet. 2006 Apr;22(4):187-93. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2006.02.005. Epub 2006 Feb 24. Trends Genet. 2006. PMID: 16499991 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolutionary dynamics of the accessory genome of Listeria monocytogenes.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 25;8(6):e67511. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067511. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23825666 Free PMC article.
-
An independent genome duplication inferred from Hox paralogs in the American paddlefish--a representative basal ray-finned fish and important comparative reference.Genome Biol Evol. 2012;4(9):937-53. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evs067. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Genome Biol Evol. 2012. PMID: 22851613 Free PMC article.
-
GLADX: an automated approach to analyze the lineage-specific loss and pseudogenization of genes.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38792. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038792. Epub 2012 Jun 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22723889 Free PMC article.
-
Two Korean Endemic Clematis Chloroplast Genomes: Inversion, Reposition, Expansion of the Inverted Repeat Region, Phylogenetic Analysis, and Nucleotide Substitution Rates.Plants (Basel). 2021 Feb 19;10(2):397. doi: 10.3390/plants10020397. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33669616 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved Noncoding Sequences Regulate lhx5 Expression in the Zebrafish Forebrain.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 6;10(7):e0132525. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132525. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26147098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul S.F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E.W., and Lipman, D.J. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: 403-410. - PubMed
-
- Anson E.L. and Myers, E.W. 1997. Re-Aligner: A program for refining DNA sequence multialignments. J. Comp. Biol. 4: 369-383. - PubMed
-
- Barton G.J. and Sternberg, M.J.E. 1987. A strategy for the rapid multiple alignment of protein sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 198: 327-337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
