Cellular responses to cytomegalovirus in immunosuppressed patients: circulating CD8+ T cells recognizing CMVpp65 are present but display functional impairment
- PMID: 12653843
- PMCID: PMC1808671
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02098.x
Cellular responses to cytomegalovirus in immunosuppressed patients: circulating CD8+ T cells recognizing CMVpp65 are present but display functional impairment
Abstract
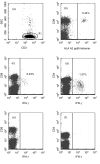
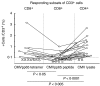
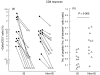
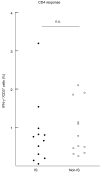
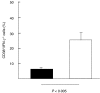
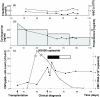
The availability of tetrameric complexes of HLA class I molecules folded with immunodominant peptides makes it possible to utilize flow cytometry for rapid and highly specific visualization of virus specific CD8+ T cells. An alternate technique is to incubate whole blood with specific antigens and to subsequently detect and characterize responding T cells (e.g. by performing intracellular staining of interferon-gamma). By using an HLA-A2 tetramer construct folded with the same immunodominant CMV-peptide as that used for peptide pulsing, we monitored both the presence and functional capacity of CMV-specific CD8+ T cells. In addition T cell activation was assayed by determination of CD38 and CD69 expression. Twelve organ transplant patients and 31 healthy blood donors with latent CMV infection were investigated using CMV pp65 tetramer staining and intracellular staining of interferon-gamma after CMV pp65 peptide pulsing or CMV lysate pulsing. CMV-specific T cells were detected in similar absolute numbers as well as frequencies of T cells in the two groups investigated. However, the CMV-specific CD8+ T cells in immunosuppressed individuals showed a decreased functional response to the CMV-peptide, as evidenced by reduced interferon-gamma production when compared to healthy blood donors (19%; 42%, P < 0.005). In addition, CD38 expression was markedly higher in immunosuppressed patients compared to healthy blood donors (24%; 6%, P < 0.005). In a case report we demonstrate that reactivation of CMV can occur in an immunosuppressed patient with high number of CMV-specific T cells, but without functional capacity. Hence, these findings reflect impaired activation of cytotoxic T cells controlling latent CMV infection in immunosuppressed patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of CMVpp65-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes using MHC tetramers in kidney transplant patients and healthy participants.Transplantation. 2000 Jun 15;69(11):2243-50. doi: 10.1097/00007890-200006150-00005. Transplantation. 2000. PMID: 10868621
-
Rapid monitoring of immune reconstitution after allogeneic stem cell transplantation--a comparison of different assays for the detection of cytomegalovirus-specific T cells.Eur J Haematol. 2013 Dec;91(6):534-45. doi: 10.1111/ejh.12187. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Eur J Haematol. 2013. PMID: 23952609
-
Co-ordinated isolation of CD8(+) and CD4(+) T cells recognizing a broad repertoire of cytomegalovirus pp65 and IE1 epitopes for highly specific adoptive immunotherapy.Cytotherapy. 2010 Nov;12(7):933-44. doi: 10.3109/14653240903505822. Cytotherapy. 2010. PMID: 20078388
-
CD8(+) T-cell immunity to cytomegalovirus.Hum Immunol. 2004 May;65(5):456-64. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2004.02.014. Hum Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15172445 Review.
-
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific CD8+ T cells in individuals with HIV infection: correlation with protection from CMV disease.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006 Apr;57(4):585-8. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl049. Epub 2006 Feb 27. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16504998 Review.
Cited by
-
Viral findings in adult hematological patients with neutropenia.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36543. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036543. Epub 2012 May 3. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22570724 Free PMC article.
-
The hallmarks of CMV-specific CD8 T-cell differentiation.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2019 Aug;208(3-4):365-373. doi: 10.1007/s00430-019-00608-7. Epub 2019 Apr 13. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30989333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T cell control of primary and latent cytomegalovirus infections in healthy subjects.J Clin Immunol. 2005 Sep;25(5):473-81. doi: 10.1007/s10875-005-5372-8. J Clin Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16160916
-
Single-cell T-cell receptor-β analysis of HLA-A*2402-restricted CMV- pp65-specific cytotoxic T-cells in allogeneic hematopoietic SCT.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014 Jan;49(1):87-94. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2013.122. Epub 2013 Aug 12. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014. PMID: 23933763
-
Monitoring of pathogen-specific T-cell immune reconstitution after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Front Immunol. 2013 Sep 17;4:276. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00276. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24062744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Reusser P, Cathomas G, Attenhofer R, Tamm M, Thiel G. Cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific T cell immunity after renal transplantation mediates protection from CMV disease by limiting the systemic virus load. J Infect Dis. 1999;180:247–53. - PubMed
-
- Lee PP, Yee C, Savage PA, et al. Characterization of circulating T cells specific for tumor-associated antigens in melanoma patients. Nat Med. 1999;5:677–85. - PubMed
-
- Komanduri KV, Viswanathan MN, Wieder ED, et al. Restoration of cytomegalovirus-specific CD4+ T-lymphocyte responses after ganciclovir and highly active antiretroviral therapy in individuals infected with HIV-1. Nat Med. 1998;4:953–6. - PubMed
-
- Li CR, Greenberg PD, Gilbert MJ, Goodrich JM, Riddell SR. Recovery of HLA-restricted cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific T cell responses after allogeneic bone marrow transplant: correlation with CMV disease and effect of ganciclovir prophylaxis. Blood. 1994;83:1971–9. - PubMed
-
- Engstrand M, Tournay C, Peyrat MA, et al. Characterization of CMVpp65-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes using MHC tetramers in kidney transplant patients and healthy participants. Transplantation. 2000;69:2243–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

