Negative regulation of BRCA1 gene expression by HMGA1 proteins accounts for the reduced BRCA1 protein levels in sporadic breast carcinoma
- PMID: 12640109
- PMCID: PMC150734
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.7.2225-2238.2003
Negative regulation of BRCA1 gene expression by HMGA1 proteins accounts for the reduced BRCA1 protein levels in sporadic breast carcinoma
Abstract
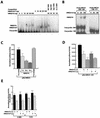
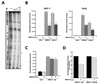
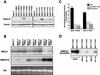
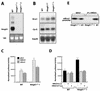
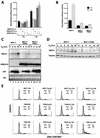
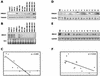
A drastic reduction in BRCA1 gene expression is a characteristic feature of aggressive sporadic breast carcinoma. However, the mechanisms underlying BRCA1 downregulation in breast cancer are not well understood. Here we report that both in vitro and in vivo HMGA1b protein binds to and inhibits the activity of both human and mouse BRCA1 promoters. Consistently, murine embryonic stem (ES) cells with the Hmga1 gene deleted display higher Brca1 mRNA and protein levels than do wild-type ES cells. Stable transfection of MCF-7 cells with the HMGA1b cDNA results in a decrease of BRCA1 gene expression and in a lack of BRCA1 induction after estrogen treatment. Finally, we found an inverse correlation between HMGA1 and BRCA1 mRNA and protein expression in human mammary carcinoma cell lines and tissues. These data indicate that HMGA1 proteins are involved in transcriptional regulation of the BRCA1 gene, and their overexpression may have a role in BRCA1 downregulation observed in aggressive mammary carcinomas.
Figures
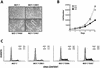
Similar articles
-
BRCA1/p220 loss triggers BRCA1-IRIS overexpression via mRNA stabilization in breast cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2012 Mar;3(3):299-313. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.462. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 22431556 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-proliferative effects of 1alpha,25(OH)2D3 on breast and prostate cancer cells are associated with induction of BRCA1 gene expression.Oncogene. 2000 Oct 19;19(44):5091-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203888. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11042697
-
Transactivation of the p21 promoter by BRCA1 splice variants in mammary epithelial cells: evidence for both common and distinct activities of wildtype and mutant forms.Oncogene. 2000 Dec 14;19(54):6351-60. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204025. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11175350
-
The role of epigenetic transcriptional regulation in BRCA1-mediated tumor suppression.Transcription. 2013 Jan-Feb;4(1):24-8. doi: 10.4161/trns.22600. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Transcription. 2013. PMID: 23131665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of BRCA1 expression and its relationship to sporadic breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2003;5(1):45-52. doi: 10.1186/bcr557. Epub 2002 Nov 13. Breast Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12559046 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Construction and analysis of cells lacking the HMGA gene family.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Sep 1;31(17):5025-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg684. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12930952 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profile of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes in premenopausal Mexican women with breast cancer: clinical and immunohistochemical correlates.Med Oncol. 2009;26(3):269-75. doi: 10.1007/s12032-008-9114-7. Epub 2008 Nov 15. Med Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19012002
-
Critical role of HMGA proteins in cancer cell chemoresistance.J Mol Med (Berl). 2017 Apr;95(4):353-360. doi: 10.1007/s00109-017-1520-x. Epub 2017 Mar 14. J Mol Med (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28293697 Review.
-
High mobility group A: a novel biomarker and therapeutic target in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Surgeon. 2009 Oct;7(5):297-306. doi: 10.1016/s1479-666x(09)80008-5. Surgeon. 2009. PMID: 19848064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HMGA2 directly mediates chromatin condensation in association with neuronal fate regulation.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 12;14(1):6420. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42094-9. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37828010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe, N., T. Watanabe, M. Sugiyama, H. Uchimura, G. Chiappetta, A. Fusco, and Y. Atomi. 1999. Determination of high mobility group I(Y) expression level in colorectal neoplasias: a potential diagnostic marker. Cancer Res. 59:1169-1174. - PubMed
-
- Abe, N., T. Watanabe, T. Masaki, T. Mori, M. Sugiyama, H. Uchimura, Y. Fujioka, G. Chiappetta, A. Fusco, and Y. Atomi. 2000. Pancreatic duct cell carcinomas express high levels of high mobility group I(Y) proteins. Cancer Res. 60:3117-3122. - PubMed
-
- Baldassarre, G., M. V. Barone, B. Belletti, C. Sandomenico, P. Bruni, S. Spiezia, A. Boccia, M. T. Vento, A. Romano, S. Pepe, A. Fusco, and G. Viglietto. 1999. Key role of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27kip1 for embryonal carcinoma cell survival and differentiation. Oncogene 18:6241-6251. - PubMed
-
- Baldassarre, G., M. Fedele, S. Battista, A. Vecchione, A. J. Klein-Szanto, M. Santoro, T. A. Waldmann, N. Azimi, C. M. Croce, and A. Fusco. 2001. Onset of natural killer cell lymphomas in transgenic mice carrying a truncated HMGI-C gene by the chronic stimulation of the IL-2 and IL-15 pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:7970-7975. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bandiera, A., D. Bonifacio, G. Manfioletti, F. Mantovani, A. Rustighi, F. Zanconati, A. Fusco, L. Di Bonito, and V. Giancotti. 1998. Expression of HMGI(Y) proteins in squamous intraepithelial and invasive lesions of the uterine cervix. Cancer Res. 58:426-431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
