Hic-5 communicates between focal adhesions and the nucleus through oxidant-sensitive nuclear export signal
- PMID: 12631731
- PMCID: PMC151587
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.02-06-0099
Hic-5 communicates between focal adhesions and the nucleus through oxidant-sensitive nuclear export signal
Abstract
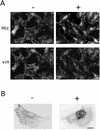
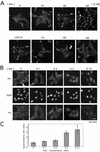
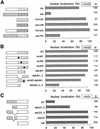
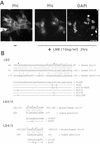
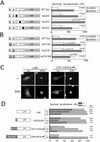
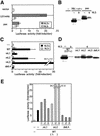
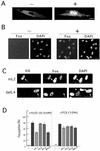
hic-5 was originally isolated as an H(2)O(2)-inducible cDNA clone whose product was normally found at focal adhesions. In this study, we found that Hic-5 accumulated in the nucleus in response to oxidants such as H(2)O(2). Other focal adhesion proteins including paxillin, the most homologous to Hic-5, remained in the cytoplasm. Mutation analyses revealed that the C- and N-terminal halves of Hic-5 contributed to its nuclear localization in a positive and negative manner, respectively. After the finding that leptomycin B (LMB), an inhibitor of nuclear export signal (NES), caused Hic-5 to be retained in the nucleus, Hic-5 was demonstrated to harbor NES in the N-terminal, which was sensitive to oxidants, thereby regulating the nuclear accumulation of Hic-5. NES consisted of a leucine-rich stretch and two cysteines with a limited similarity to Yap/Pap-type NES. In the nucleus, Hic-5 was suggested to participate in the gene expression of c-fos. Using dominant negative mutants, we found that Hic-5 was actually involved in endogenous c-fos gene expression upon H(2)O(2) treatment. Hic-5 was thus proposed as a focal adhesion protein with the novel aspect of shuttling between focal adhesions and the nucleus through an oxidant-sensitive NES, mediating the redox signaling directly to the nucleus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Involvement of FAK and PTP-PEST in the regulation of redox-sensitive nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of a LIM protein, Hic-5.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005 Mar-Apr;7(3-4):335-47. doi: 10.1089/ars.2005.7.335. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005. PMID: 15706082
-
Characterization of a focal adhesion protein, Hic-5, that shares extensive homology with paxillin.J Cell Sci. 1999 Jan;112 ( Pt 2):181-90. doi: 10.1242/jcs.112.2.181. J Cell Sci. 1999. PMID: 9858471
-
Specific decrease in the level of Hic-5, a focal adhesion protein, during immortalization of mouse embryonic fibroblasts, and its association with focal adhesion kinase.J Cell Biochem. 2000 Jan;76(3):411-9. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4644(20000301)76:3<411::aid-jcb9>3.0.co;2-j. J Cell Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10649439
-
[Regulation of cellular phenotypes by Hic-5 that localizes both in the focal adhesion and in the nucleus].Seikagaku. 2002 May;74(5):408-11. Seikagaku. 2002. PMID: 12073614 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Zyxin and paxillin proteins: focal adhesion plaque LIM domain proteins go nuclear.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003 Feb 17;1593(2-3):115-20. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(02)00349-x. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003. PMID: 12581855 Review.
Cited by
-
Paxillin family of focal adhesion adaptor proteins and regulation of cancer cell invasion.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2020;355:1-52. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2020.05.003. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32859368 Free PMC article.
-
Leupaxin is expressed in mammary carcinoma and acts as a transcriptional activator of the estrogen receptor α.Int J Oncol. 2015 Jul;47(1):106-14. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.2988. Epub 2015 May 6. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25955236 Free PMC article.
-
Cbl-c ubiquitin ligase activity is increased via the interaction of its RING finger domain with a LIM domain of the paxillin homolog, Hic 5.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49428. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049428. Epub 2012 Nov 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23145173 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular profiling of signalling proteins for effects induced by the anti-cancer compound GSAO with 400 antibodies.BMC Cancer. 2006 Jun 9;6:155. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-155. BMC Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16764713 Free PMC article.
-
The focal adhesion protein Hic-5 is highly expressed in the rat myometrium during late pregnancy and labour and co-localizes with FAK.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2007 Jun 5;5:22. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-5-22. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17550607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoto H, Sasaki H, Ishino M, Sasaki T. Nuclear translocation of cell adhesion kinase beta/praline-rich tyrosine kinase 2. Cell Struct Funct. 2002;27:47–61. - PubMed
-
- Brown MC, Curtis MS, Turner CE. Paxillin LD motifs may define a new family of protein recognition domains. Nature Struct Biol. 1998;5:677–678. - PubMed
-
- Crawford D, Zbinden I, Amstad P, Cerutti P. Oxidant stress induces the protooncogene c-fos and c-myc in mouse epidermal cells. Oncogene. 1988;3:27–32. - PubMed
-
- Dawid IB, Toyama R, Taira M. LIM domain proteins. CR Acad Sci Iii. 1995;318:295–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

