c-Fms and the alphavbeta3 integrin collaborate during osteoclast differentiation
- PMID: 12618529
- PMCID: PMC151897
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI16924
c-Fms and the alphavbeta3 integrin collaborate during osteoclast differentiation
Abstract
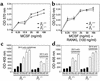
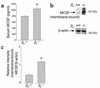
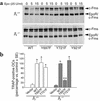
beta(3) integrin-null osteoclasts are dysfunctional, but their numbers are increased in vivo. In vitro, however, the number of beta(3)(-/-) osteoclasts is reduced because of arrested differentiation. This paradox suggests cytokine regulation of beta(3)(-/-) osteoclastogenesis differs in vitro and in vivo. In vitro, additional MCSF, but not receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL), completely rescues beta(3)(-/-) osteoclastogenesis. Similarly, activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) and expression of c-Fos, both essential for osteoclastogenesis, are attenuated in beta(3)(-/-) preosteoclasts, but completely restored by additional MCSF. In fact, circulating and bone marrow cell membrane-bound MCSFs are enhanced in beta(3)(-/-) mice, correlating with the increase in the osteoclast number. To identify components of the MCSF receptor that is critical for osteoclastogenesis in beta(3)(-/-) cells, we retrovirally transduced authentic osteoclast precursors with chimeric c-Fms constructs containing various cytoplasmic domain mutations. Normalization of osteoclastogenesis and ERK activation, in beta(3)(-/-) cells, uniquely requires c-Fms tyrosine 697. Finally, like high-dose MCSF, overexpression of c-Fos normalizes the number of beta(3)(-/-) osteoclasts in vitro, but not their ability to resorb dentin. Thus, while c-Fms and alpha(v)beta(3) collaborate in the osteoclastogenic process via shared activation of the ERK/c-Fos signaling pathway, the integrin is essential for matrix degradation.
Figures


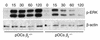


Similar articles
-
Tyrosines 559 and 807 in the cytoplasmic tail of the macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor play distinct roles in osteoclast differentiation and function.Endocrinology. 2002 Dec;143(12):4868-74. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-220467. Endocrinology. 2002. PMID: 12446614
-
Caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxy-phenethyl ester suppresses receptor activator of NF-κB ligand–induced osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase/activator protein 1 and Ca2+–nuclear factor of activated T-cells cytoplasmic 1 signaling pathways.J Bone Miner Res. 2012 Jun;27(6):1298-1308. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1576. J Bone Miner Res. 2012. PMID: 22337253
-
Association of sustained ERK activity with integrin beta3 induction during receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL)-directed osteoclast differentiation.Exp Cell Res. 2003 Oct 1;289(2):368-77. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(03)00288-x. Exp Cell Res. 2003. PMID: 14499638
-
alphavbeta3 and macrophage colony-stimulating factor: partners in osteoclast biology.Immunol Rev. 2005 Dec;208:88-105. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00331.x. Immunol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16313343 Review.
-
Avβ3 integrin: Pathogenetic role in osteotropic tumors.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015 Oct;96(1):183-93. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.05.018. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015. PMID: 26126493 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of a human peripheral blood monocyte subset that differentiates into osteoclasts.Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(5):R152. doi: 10.1186/ar2046. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006. PMID: 16987426 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoclasts and the immune system.J Bone Miner Metab. 2009;27(5):519-29. doi: 10.1007/s00774-009-0089-z. Epub 2009 May 20. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009. PMID: 19455385 Review.
-
Osteoblast Role in Rheumatic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 15;18(6):1272. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061272. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28617323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD44 and beta3 integrin organize two functionally distinct actin-based domains in osteoclasts.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Dec;18(12):4899-910. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-04-0378. Epub 2007 Sep 26. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17898081 Free PMC article.
-
Role of DC-STAMP in cellular fusion of osteoclasts and macrophage giant cells.J Bone Miner Metab. 2006;24(5):355-8. doi: 10.1007/s00774-006-0697-9. J Bone Miner Metab. 2006. PMID: 16937266 Review.
References
-
- Hamilton JA. CSF-1 signal transduction. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1997;62:145–155. - PubMed
-
- Felix R, et al. Impairment of macrophage colony-stimulating factor production and lack of resident bone marrow macrophages in the osteopetrotic op/op mouse. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1990;5:781–789. - PubMed
-
- Feng X, et al. Tyrosines 559 and 807 in the cytoplasmic tail of the m-csf receptor play distinct roles in osteoclast differentiation and function. Endocrinology. 2002;143:4868–4874. - PubMed
-
- van der Flier A, Sonnenberg A. Function and interactions of integrins. Cell Tissue Res. 2001;305:285–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AR32788/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR-46852/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR046523/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR-48812/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AR046523/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR046852/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR-48853/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR032788/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR048812/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR048853/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR-46523/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK-56341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

