An experimental study of a Mediterranean diet intervention for patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 12594104
- PMCID: PMC1754463
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.62.3.208
An experimental study of a Mediterranean diet intervention for patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the efficacy of a Mediterranean diet (MD) versus an ordinary Western diet for suppression of disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
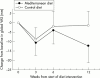
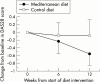
Methods: Patients with well controlled, although active RA of at least two years' duration, who were receiving stable pharmacological treatment, were invited to participate. All patients were randomly allocated to the MD or the control diet (CD). To achieve good compliance with prescribed diets all patients were for the first three weeks served the MD or the CD, respectively, for lunch and dinner at the outpatient clinic's canteen. Clinical examinations were performed at baseline, and again in the 3rd, 6th, and 12th week. A composite disease activity index (DAS28), a physical function index (Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ)), a health survey of quality of life (Short Form-36 (SF-36)), and the daily consumption of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs were used as primary efficacy variables.
Results: From baseline to the end of the study the patients in the MD group (n=26) showed a decrease in DAS28 of 0.56 (p<0.001), in HAQ of 0.15 (p=0.020), and in two dimensions of the SF-36 Health Survey: an increase in "vitality" of 11.3 (p=0.018) and a decrease in "compared with one year earlier" of 0.6 (p=0.016). For the control patients (n=25) no significant change was seen at the end of the study. This difference between the two treatment groups was notable only in the second half of the trial.
Conclusion: The results indicate that patients with RA, by adjusting to a Mediterranean diet, did obtain a reduction in inflammatory activity, an increase in physical function, and improved vitality.
Figures
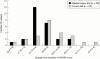
Similar articles
-
A randomized controlled cross-over trial investigating the effect of anti-inflammatory diet on disease activity and quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis: the Anti-inflammatory Diet In Rheumatoid Arthritis (ADIRA) study protocol.Nutr J. 2018 Apr 20;17(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12937-018-0354-x. Nutr J. 2018. PMID: 29678183 Free PMC article.
-
Adherence to Mediterranean diet and patient perception of rheumatoid arthritis.Complement Ther Med. 2020 Aug;52:102519. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2020.102519. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Complement Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32951762
-
The Mediterranean diet, and not dietary inflammatory index, is associated with rheumatoid arthritis disease activity, the impact of disease and functional disability.Eur J Nutr. 2023 Oct;62(7):2827-2839. doi: 10.1007/s00394-023-03196-8. Epub 2023 Jun 24. Eur J Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37355497
-
The effects of the Mediterranean diet on rheumatoid arthritis prevention and treatment: a systematic review of human prospective studies.Rheumatol Int. 2018 May;38(5):737-747. doi: 10.1007/s00296-017-3912-1. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Rheumatol Int. 2018. PMID: 29256100 Review.
-
Dietary interventions for rheumatoid arthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Jan 21;(1):CD006400. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006400.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 19160281 Review.
Cited by
-
Current nutritional status of patients with rheumatic diseases in the population of Poland.Reumatologia. 2015;53(1):26-33. doi: 10.5114/reum.2015.50554. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Reumatologia. 2015. PMID: 27407222 Free PMC article.
-
Diet, Microbiota, and Gut Permeability-The Unknown Triad in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Dec 14;5:349. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00349. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30619860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of nutrition and generally available products such as nicotine and alcohol on rheumatoid arthritis - review of the literature.Reumatologia. 2018;56(2):121-127. doi: 10.5114/reum.2018.75524. Epub 2018 May 9. Reumatologia. 2018. PMID: 29853728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide association study of self-reported food reactions in Japanese identifies shrimp and peach specific loci in the HLA-DR/DQ gene region.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 18;8(1):1069. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18241-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29348432 Free PMC article.
-
[Recommendations of the committee on complementary medicine and nutrition in ayurvedic medicine, homeopathy, nutrition and Mediterranean diet].Z Rheumatol. 2023 Aug;82(6):517-531. doi: 10.1007/s00393-023-01356-z. Epub 2023 May 22. Z Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37212842 Free PMC article. Review. German.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
