WW domain sequence activity relationships identified using ligand recognition propensities of 42 WW domains
- PMID: 12592019
- PMCID: PMC2312455
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.0233203
WW domain sequence activity relationships identified using ligand recognition propensities of 42 WW domains
Abstract
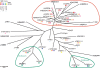
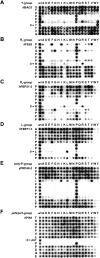
WW domains mediate protein-protein interactions in a number of different cellular functions by recognizing proline-containing peptide sequences. We determined peptide recognition propensities for 42 WW domains using NMR spectroscopy and peptide library screens. As potential ligands, we studied both model peptides and peptides based on naturally occurring sequences, including phosphorylated residues. Thirty-two WW domains were classified into six groups according to detected ligand recognition preferences for binding the motifs PPx(Y/poY), (p/phi)P(p,g)PPpR, (p/phi)PPRgpPp, PPLPp, (p/xi)PPPPP, and (poS/poT)P (motifs according to modified Seefeld Convention 2001). In addition to these distinct binding motifs, group-specific WW domain consensus sequences were identified. For PPxY-recognizing domains, phospho-tyrosine binding was also observed. Based on the sequences of the PPx(Y/poY)-specific group, a profile hidden Markov model was calculated and used to predict PPx(Y/poY)-recognition activity for WW domains, which were not assayed. PPx(Y/poY)-binding was found to be a common property of NEDD4-like ubiquitin ligases.
Figures
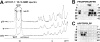


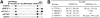
Similar articles
-
A novel pro-Arg motif recognized by WW domains.J Biol Chem. 2000 Apr 7;275(14):10359-69. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.14.10359. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10744724
-
Solution structures of the YAP65 WW domain and the variant L30 K in complex with the peptides GTPPPPYTVG, N-(n-octyl)-GPPPY and PLPPY and the application of peptide libraries reveal a minimal binding epitope.J Mol Biol. 2001 Dec 14;314(5):1147-56. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.5199. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11743730
-
Solution structure of a Nedd4 WW domain-ENaC peptide complex.Nat Struct Biol. 2001 May;8(5):407-12. doi: 10.1038/87562. Nat Struct Biol. 2001. PMID: 11323714
-
Characterization of a novel protein-binding module--the WW domain.FEBS Lett. 1995 Aug 1;369(1):67-71. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00550-s. FEBS Lett. 1995. PMID: 7641887 Review.
-
WW and SH3 domains, two different scaffolds to recognize proline-rich ligands.FEBS Lett. 2002 Feb 20;513(1):30-7. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)03290-2. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 11911877 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure-function-folding relationship in a WW domain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jul 11;103(28):10648-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600511103. Epub 2006 Jun 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16807295 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of binding interfaces of the human scaffold protein AXIN1 by peptide microarrays.J Biol Chem. 2018 Oct 19;293(42):16337-16347. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005127. Epub 2018 Aug 30. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30166345 Free PMC article.
-
Nedd4 mediates agonist-dependent ubiquitination, lysosomal targeting, and degradation of the beta2-adrenergic receptor.J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 8;283(32):22166-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709668200. Epub 2008 Jun 10. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18544533 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Nef impairs heterotrimeric G-protein signaling by targeting Gα(i2) for degradation through ubiquitination.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 30;287(49):41481-98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.361782. Epub 2012 Oct 15. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23071112 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIα function at endosomes is regulated by the ubiquitin ligase Itch.EMBO Rep. 2012 Dec;13(12):1087-94. doi: 10.1038/embor.2012.164. Epub 2012 Nov 13. EMBO Rep. 2012. PMID: 23146885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aasland, R., Abrams, C., Ampe, C., Ball, L.J., Bedford, M.T., Cesareni, G., Gimona, M., Hurley, J.H., Jarchau, T., Lehto, V.P., et al. 2002. Normalization of nomenclature for peptide motifs as ligands of modular protein domains. FEBS Lett. 513 141–144. - PubMed
-
- Bedford, M.T., Sarbassova, D., Xu, J., Leder, P., and Yaffe, M.B. 2000. A novel pro-Arg motif recognized by WW domains. J. Biol. Chem. 275 10359–10369. - PubMed
-
- Blom, N., Gammeltoft, S., and Brunak, S. 1999. Sequence and structure-based prediction of eukaryotic protein phosphorylation sites. J. Mol. Biol. 294 1351–1362. - PubMed
-
- Chang, A., Cheang, S., Espanel, X., and Sudol, M. 2000. Rsp5 WW domains interact directly with the carboxyl-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. J. Biol. Chem. 275 20562–20571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

