Rap1p and other transcriptional regulators can function in defining distinct domains of gene expression
- PMID: 12582242
- PMCID: PMC150219
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg200
Rap1p and other transcriptional regulators can function in defining distinct domains of gene expression
Abstract
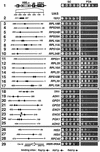
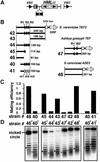
Barrier elements that are able to block the propagation of transcriptional silencing in yeast are functionally similar to chromatin boundary/insulator elements in metazoans that delimit functional chromosomal domains. We show that the upstream activating sequences of many highly expressed ribosome protein genes and glycolytic genes exhibit barrier activity. Analyses of these barriers indicate that binding sites for transcriptional regulators Rap1p, Abf1p, Reb1p, Adr1p and Gcn4p may participate in barrier function. We also present evidence suggesting that Rap1p is directly involved in barrier activity, and its barrier function correlates with local changes in chromatin structure. We further demonstrate that tethering the transcriptional activation domain of Rap1p to DNA is sufficient to recapitulate barrier activity. Moreover, targeting the activation domain of Adr1p or Gcn4p also establishes a barrier to silencing. These results support the notion that transcriptional regulators could also participate in delimiting functional domains in the genome.
Figures



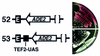
Similar articles
-
The different (sur)faces of Rap1p.Mol Genet Genomics. 2003 Mar;268(6):791-8. doi: 10.1007/s00438-002-0801-3. Epub 2003 Jan 25. Mol Genet Genomics. 2003. PMID: 12655405 Review.
-
Role of the N-terminal region of Rap1p in the transcriptional activation of glycolytic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Yeast. 2004 Jul 30;21(10):851-66. doi: 10.1002/yea.1123. Yeast. 2004. PMID: 15300680
-
The multifunctional transcription factors Abf1p, Rap1p and Reb1p are required for full transcriptional activation of the chromosomal PGK gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Gen Genet. 1996 Feb 25;250(3):348-56. doi: 10.1007/BF02174393. Mol Gen Genet. 1996. PMID: 8602150
-
The transcriptional repressor activator protein Rap1p is a direct regulator of TATA-binding protein.J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 28;283(13):8699-710. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709436200. Epub 2008 Jan 14. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18195009 Free PMC article.
-
Global regulators of ribosome biosynthesis in yeast.Biochem Cell Biol. 1995 Nov-Dec;73(11-12):825-34. doi: 10.1139/o95-090. Biochem Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 8721998 Review.
Cited by
-
A canonical promoter organization of the transcription machinery and its regulators in the Saccharomyces genome.Genome Res. 2009 Mar;19(3):360-71. doi: 10.1101/gr.084970.108. Epub 2009 Jan 5. Genome Res. 2009. PMID: 19124666 Free PMC article.
-
The Yaf9 component of the SWR1 and NuA4 complexes is required for proper gene expression, histone H4 acetylation, and Htz1 replacement near telomeres.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Nov;24(21):9424-36. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.21.9424-9436.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15485911 Free PMC article.
-
Global nucleosome occupancy in yeast.Genome Biol. 2004;5(9):R62. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-9-r62. Epub 2004 Aug 20. Genome Biol. 2004. PMID: 15345046 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of boundaries of transcriptionally silent chromatin by nucleosome-excluding structures.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Mar;24(5):2118-31. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.5.2118-2131.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14966290 Free PMC article.
-
Interacting models of cooperative gene regulation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Nov 16;101(46):16234-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407365101. Epub 2004 Nov 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15534222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grunstein M. (1998) Yeast heterochromatin: regulation of its assembly and inheritance by histones. Cell, 93, 325–328. - PubMed
-
- Braunstein M., Rose,A., Holmes,S.G., Allis,C.D. and Broach,J.R. (1993) Transcriptional silencing in yeast is associated with reduced nucleosome acetylation. Genes Dev., 7, 592–604. - PubMed
-
- Imai S., Armstrong,C.M., Kaeberlein,M. and Guarente,L. (2000) Transcriptional silencing and longevity protein Sir2 is an NAD-dependent histone deacetylase. Nature, 403, 795–800. - PubMed
-
- Moazed D. (2001) Common themes in mechanisms of gene silencing. Mol. Cell, 8, 489–498. - PubMed
-
- Carmen A.A., Milne,L. and Grunstein,M. (2001) Acetylation of the yeast histone H4 N terminus regulates its binding to heterochromatin protein SIR3. J. Biol. Chem., 277, 4778–4781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

