Selective PDZ protein-dependent stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by the adenovirus E4-ORF1 oncoprotein
- PMID: 12569363
- PMCID: PMC3501958
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206151
Selective PDZ protein-dependent stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by the adenovirus E4-ORF1 oncoprotein
Abstract
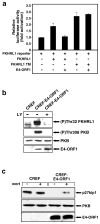
While PDZ domain-containing proteins represent cellular targets for several different viral oncoproteins, including human papillomavirus E6, human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax, and human adenovirus E4-ORF1, the functional consequences for such interactions have not been elucidated. Here we report that, at the plasma membrane of cells, the adenovirus E4-ORF1 oncoprotein selectively and potently stimulates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), triggering a downstream cascade of events that includes activation of both protein kinase B and p70S6-kinase. This activity of E4-ORF1 could be abrogated by overexpression of its PDZ-protein targets or by disruption of its PDZ domain-binding motif, which was shown to mediate complex formation between E4-ORF1 and PDZ proteins at the plasma membrane of cells. Furthermore, E4-ORF1 mutants unable to activate the PI3K pathway failed to transform cells in culture or to promote tumors in animals, and drugs that block either PI3K or p70S6-kinase inhibited E4-ORF1-induced transformation of cells. From these results, we propose that the transforming and tumorigenic potentials of the adenovirus E4-ORF1 oncoprotein depend on its capacity to activate PI3K through a novel PDZ protein-dependent mechanism of action.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interactions of the PDZ-protein MAGI-1 with adenovirus E4-ORF1 and high-risk papillomavirus E6 oncoproteins.Oncogene. 2000 Nov 2;19(46):5270-80. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203906. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11077444 Free PMC article.
-
Link of the unique oncogenic properties of adenovirus type 9 E4-ORF1 to a select interaction with the candidate tumor suppressor protein ZO-2.EMBO J. 2001 Oct 15;20(20):5578-86. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.20.5578. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11598001 Free PMC article.
-
A new crucial protein interaction element that targets the adenovirus E4-ORF1 oncoprotein to membrane vesicles.J Virol. 2007 May;81(9):4787-97. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02855-06. Epub 2007 Feb 21. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17314165 Free PMC article.
-
Cell polarity proteins: common targets for tumorigenic human viruses.Oncogene. 2008 Nov 24;27(55):7031-46. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.352. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 19029943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenovirus early E4 genes in viral oncogenesis.Oncogene. 2001 Nov 26;20(54):7847-54. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204914. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11753667 Review.
Cited by
-
E4orf1: A protein for enhancing glucose uptake despite impaired proximal insulin signaling.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 6;13(12):e0208427. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208427. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30521580 Free PMC article.
-
E4orf1 limits the oncolytic potential of the E1B-55K deletion mutant adenovirus.J Virol. 2009 Mar;83(6):2406-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01972-08. Epub 2009 Jan 7. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19129452 Free PMC article.
-
Doxycycline-regulated 3T3-L1 preadipocyte cell line with inducible, stable expression of adenoviral E4orf1 gene: a cell model to study insulin-independent glucose disposal.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e60651. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060651. Epub 2013 Mar 27. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23544159 Free PMC article.
-
Adipocyte commitment of 3T3-L1 cells is required to support human adenovirus 36 productive replication concurrent with altered lipid and glucose metabolism.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Sep 27;12:1016200. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1016200. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36237435 Free PMC article.
-
A specificity map for the PDZ domain family.PLoS Biol. 2008 Sep 30;6(9):e239. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060239. PLoS Biol. 2008. PMID: 18828675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blume-Jensen P, Hunter T. Nature. 2001;411:355–365. - PubMed
-
- Bowman T, Garcia R, Turkson J, Jove R. Oncogene. 2000;19:2474–2488. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME. Cell. 1999;96:857–868. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

