Identification of a receptor-binding domain of the spike glycoprotein of human coronavirus HCoV-229E
- PMID: 12551991
- PMCID: PMC141070
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.4.2530-2538.2003
Identification of a receptor-binding domain of the spike glycoprotein of human coronavirus HCoV-229E
Abstract
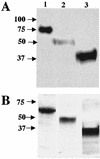
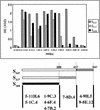
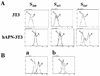
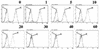
Human coronavirus HCoV-229E uses human aminopeptidase N (hAPN) as its receptor (C. L. Yeager et al., Nature 357:420-422, 1992). To identify the receptor-binding domain of the viral spike glycoprotein (S), we expressed soluble truncated histidine-tagged S glycoproteins by using baculovirus expression vectors. Truncated S proteins purified by nickel affinity chromatography were shown to be glycosylated and to react with polyclonal anti-HCoV-229E antibodies and monoclonal antibodies to the viral S protein. A truncated protein (S(547)) that contains the N-terminal 547 amino acids bound to 3T3 mouse cells that express hAPN but not to mouse 3T3 cells transfected with empty vector. Binding of S(547) to hAPN was blocked by an anti-hAPN monoclonal antibody that inhibits binding of virus to hAPN and blocks virus infection of human cells and was also blocked by polyclonal anti-HCoV-229E antibody. S proteins that contain the N-terminal 268 or 417 amino acids did not bind to hAPN-3T3 cells. Antibody to the region from amino acid 417 to the C terminus of S blocked binding of S(547) to hAPN-3T3 cells. Thus, the data suggest that the domain of the spike protein between amino acids 417 and 547 is required for the binding of HCoV-229E to its hAPN receptor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human coronavirus 229E: receptor binding domain and neutralization by soluble receptor at 37 degrees C.J Virol. 2003 Apr;77(7):4435-8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.7.4435-4438.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12634402 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular determinants of species specificity in the coronavirus receptor aminopeptidase N (CD13): influence of N-linked glycosylation.J Virol. 2001 Oct;75(20):9741-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.20.9741-9752.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11559807 Free PMC article.
-
Highly conserved regions within the spike proteins of human coronaviruses 229E and NL63 determine recognition of their respective cellular receptors.J Virol. 2006 Sep;80(17):8639-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00560-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16912312 Free PMC article.
-
Towards a coronavirus-based HIV multigene vaccine.Clin Dev Immunol. 2006 Jun-Dec;13(2-4):353-60. doi: 10.1080/17402520600579168. Clin Dev Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17162377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronavirus spike proteins in viral entry and pathogenesis.Virology. 2001 Jan 20;279(2):371-4. doi: 10.1006/viro.2000.0757. Virology. 2001. PMID: 11162792 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Potent Antiviral Activity of Vitamin B12 against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, and Human Coronavirus 229E.Microorganisms. 2023 Nov 15;11(11):2777. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11112777. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38004788 Free PMC article.
-
SCARF Genes in COVID-19 and Kidney Disease: A Path to Comorbidity-Specific Therapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 8;24(22):16078. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216078. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plausibility of natural immunomodulators in the treatment of COVID-19-A comprehensive analysis and future recommendations.Heliyon. 2023 Jun;9(6):e17478. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17478. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37366526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-organ system involvement in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A mega review.J Family Med Prim Care. 2022 Sep;11(9):5014-5023. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1570_21. Epub 2022 Oct 14. J Family Med Prim Care. 2022. PMID: 36505634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Candidate Multi-Epitope Vaccine against Corona B.1.617 Lineage: In Silico Approach.Life (Basel). 2022 Oct 27;12(11):1715. doi: 10.3390/life12111715. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36362871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker, K. A., R. E. Dutch, R. A. Lamb, and T. S. Jardetzky. 1999. Structural basis for paramyxovirus-mediated membrane fusion. Mol. Cell 3:309-319. - PubMed
-
- Beauchemin, N., P. Draber, G. Dveksler, P. Gold, S. Gray-Owen, F. Grunert, S. Hammarstrom, K. V. Holmes, A. Karlsson, M. Kuroki, S. H. Lin, L. Lucka, S. M. Najjar, M. Neumaier, B. Obrink, J. E. Shively, K. M. Skubitz, C. P. Stanners, P. Thomas, J. A. Thompson, M. Virji, S. von Kleist, C. Wagener, S. Watt, and W. Zimmermann. 1999. Redefined nomenclature for members of the carcinoembryonic antigen family. Exp. Cell Res. 252:243-249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

