Lymphotoxin and lipopolysaccharide induce NF-kappaB-p52 generation by a co-translational mechanism
- PMID: 12524526
- PMCID: PMC1315810
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.embor710
Lymphotoxin and lipopolysaccharide induce NF-kappaB-p52 generation by a co-translational mechanism
Abstract
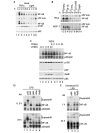
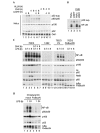
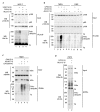
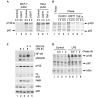
The 'classical' NF-kappaB activation pathway proceeds via IkappaB kinase (IKK)-beta/gamma-mediated phosphorylation, induced ubiquitination and the degradation of small IkappaBs. An alternative, NF-kappaB-inducing kinase and IKK-alpha-dependent pathway, which stimulates the processing of NF-kappaB2/p100, has recently been suggested. However, no physiological stimulus has been shown to trigger the activation of this pathway. Here we demonstrate that persistent stimulation with lymphotoxin beta (LT-beta) receptor agonists or lipopolysaccharide (LPS), but not with interleukin-1beta, tumour necrosis factor-alpha or 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate, induces the generation of p52 DNA-binding complexes by activating the processing of the p100 precursor. Induction of p52 DNA-binding activity is delayed in comparison with p50/p65 complexes and depends on de novo protein synthesis. p100 is constitutively and inducibly polyubiquitinated, and both ubiquitination and p52 generation are coupled to continuing p100 translation. Thus, both LT-beta receptor agonists and LPS induce NF-kappaB/p100 processing to p52 at the level of the ribosome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lymphotoxin beta receptor induces sequential activation of distinct NF-kappa B factors via separate signaling pathways.J Biol Chem. 2003 Apr 4;278(14):12006-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M210768200. Epub 2003 Jan 28. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12556537
-
RelB is required for Peyer's patch development: differential regulation of p52-RelB by lymphotoxin and TNF.EMBO J. 2003 Jan 2;22(1):121-30. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg004. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12505990 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus core protein enhances NF-kappaB signal pathway triggering by lymphotoxin-beta receptor ligand and tumor necrosis factor alpha.J Virol. 1999 Feb;73(2):1672-81. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.2.1672-1681.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 9882379 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
Functions of NF-kappaB1 and NF-kappaB2 in immune cell biology.Biochem J. 2004 Sep 1;382(Pt 2):393-409. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040544. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15214841 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Helicobacter pylori induces IkappaB kinase alpha nuclear translocation and chemokine production in gastric epithelial cells.Infect Immun. 2006 Mar;74(3):1452-61. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.3.1452-1461.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16495515 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in NFKB2 and potential genetic heterogeneity in patients with DAVID syndrome, having variable endocrine and immune deficiencies.BMC Med Genet. 2014 Dec 19;15:139. doi: 10.1186/s12881-014-0139-9. BMC Med Genet. 2014. PMID: 25524009 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen peroxide modulates immunoglobulin expression by targeting the 3'Igh regulatory region through an NFκB-dependent mechanism.Free Radic Res. 2011 Jul;45(7):796-809. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2011.581280. Epub 2011 May 20. Free Radic Res. 2011. PMID: 21599461 Free PMC article.
-
First Insight into the Modulation of Noncanonical NF-κB Signaling Components by Poxviruses in Established Immune-Derived Cell Lines: An In Vitro Model of Ectromelia Virus Infection.Pathogens. 2020 Oct 4;9(10):814. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9100814. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 33020446 Free PMC article.
-
The IkappaB kinase complex and NF-kappaB act as master regulators of lipopolysaccharide-induced gene expression and control subordinate activation of AP-1.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Jul;24(14):6488-500. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.14.6488-6500.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15226448 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bodmer J.L., Schneider P. & Tschopp J. (2002) The molecular architecture of the TNF superfamily. Trends Biochem. Sci., 27, 19–26. - PubMed
-
- Fong A. & Sun S.C. (2002) Genetic evidence for the essential role of β-transducin repeat-containing protein in the inducible processing of NF-κB2/p100. J. Biol. Chem., 277, 22111–22114. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh S. & Karin M. (2002) Missing pieces in the NF-κB puzzle. Cell, 109 (Suppl.), S81–S96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

