Reductive genome evolution in Buchnera aphidicola
- PMID: 12522265
- PMCID: PMC141039
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0235981100
Reductive genome evolution in Buchnera aphidicola
Abstract
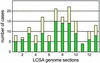
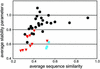
We have sequenced the genome of the intracellular symbiont Buchnera aphidicola from the aphid Baizongia pistacea. This strain diverged 80-150 million years ago from the common ancestor of two previously sequenced Buchnera strains. Here, a field-collected, nonclonal sample of insects was used as source material for laboratory procedures. As a consequence, the genome assembly unveiled intrapopulational variation, consisting of approximately 1,200 polymorphic sites. Comparison of the 618-kb (kbp) genome with the two other Buchnera genomes revealed a nearly perfect gene-order conservation, indicating that the onset of genomic stasis coincided closely with establishment of the symbiosis with aphids, approximately 200 million years ago. Extensive genome reduction also predates the synchronous diversification of Buchnera and its host; but, at a slower rate, gene loss continues among the extant lineages. A computational study of protein folding predicts that proteins in Buchnera, as well as proteins of other intracellular bacteria, are generally characterized by smaller folding efficiency compared with proteins of free living bacteria. These and other degenerative genomic features are discussed in light of compensatory processes and theoretical predictions on the long-term evolutionary fate of symbionts like Buchnera.
Figures


Similar articles
-
New clues about the evolutionary history of metabolic losses in bacterial endosymbionts, provided by the genome of Buchnera aphidicola from the aphid Cinara tujafilina.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Jul;77(13):4446-54. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00141-11. Epub 2011 May 13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21571878 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Evolution of the Obligate Endosymbiont Buchnera aphidicola.Mol Biol Evol. 2019 Jul 1;36(7):1481-1489. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msz082. Mol Biol Evol. 2019. PMID: 30989224
-
Extreme genome reduction in Buchnera spp.: toward the minimal genome needed for symbiotic life.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Apr 2;99(7):4454-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.062067299. Epub 2002 Mar 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11904373 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic analysis of the symbiotic function of Buchnera aphidicola, the primary endosymbiont of the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum.C R Biol. 2009 Nov;332(11):1034-49. doi: 10.1016/j.crvi.2009.09.007. Epub 2009 Oct 14. C R Biol. 2009. PMID: 19909925 Review.
-
Chromosomal stasis versus plasmid plasticity in aphid endosymbiont Buchnera aphidicola.Heredity (Edinb). 2005 Nov;95(5):339-47. doi: 10.1038/sj.hdy.6800716. Heredity (Edinb). 2005. PMID: 16118664 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutation induced extinction in finite populations: lethal mutagenesis and lethal isolation.PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(8):e1002609. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002609. Epub 2012 Aug 2. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012. PMID: 22876168 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome-wide analysis of functional divergence in bacteria: exploring a host of ecological adaptations.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35659. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035659. Epub 2012 Apr 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22563391 Free PMC article.
-
A universal and constant rate of gene content change traces pangenome flux to LUCA.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2024 Jan 9;371:fnae068. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnae068. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39165128 Free PMC article.
-
The players in a mutualistic symbiosis: insects, bacteria, viruses, and virulence genes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Nov 22;102(47):16919-26. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507029102. Epub 2005 Sep 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16195380 Free PMC article.
-
Transitional genomes and nutritional role reversals identified for dual symbionts of adelgids (Aphidoidea: Adelgidae).ISME J. 2022 Mar;16(3):642-654. doi: 10.1038/s41396-021-01102-w. Epub 2021 Sep 10. ISME J. 2022. PMID: 34508228 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ochman H, Moran N A. Science. 2001;292:1096–1099. - PubMed
-
- Buchner P. Endosymbiosis of Animals with Plant Microorganisms. New York: Interscience; 1965. pp. 297–332.
-
- Baumann P, Baumann L, Lai C Y, Rouhbakhsh D, Moran N A, Clark M A. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1995;49:55–94. - PubMed
-
- Douglas A E. Annu Rev Entomol. 1998;43:17–37. - PubMed
-
- Moran N A, Munson M A, Baumann P, Ishikawa H. Proc R Soc London Ser B. 1993;253:167–171.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

