Immunocytochemical description of five bipolar cell types of the mouse retina
- PMID: 12508320
- PMCID: PMC2834891
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.10491
Immunocytochemical description of five bipolar cell types of the mouse retina
Abstract
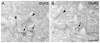
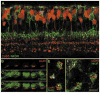
With the ever-growing number of transgenic mice being used in vision research, a precise knowledge of the cellular organization of the mouse retina is required. As with the cat, rabbit, rat, and primate retinae, as many as 10 cone bipolar types and one rod bipolar type can be expected to exist in the mouse retina; however, they still have to be defined. In the current study, several immunocytochemical markers were applied to sections of mouse retina, and the labeling of bipolar cells was studied using confocal microscopy and electron microscopy. By using antibodies against the neurokinin-3 receptor NK3R; the plasma membrane calcium ATPase1 (PMCA1); and the calcium (Ca)-binding proteins CaB1, CaB5, caldendrin, and recoverin, three different OFF-cone bipolar cells could be identified. One type of ON-cone bipolar cell was identified through its immunoreactivity for CaB5 and PMCA1. Rod bipolar cells, comparable in morphology to those of other mammalian retinae, expressed protein kinase Calpha and CaB5. It was also shown that putative OFF-cone bipolar cells receive light signals through flat contacts at the cone pedicle base, whereas ON-cone bipolar signaling involves invaginating contacts. The distribution of the kainate receptor subunit GluR5 was studied by confocal and electron microscopy. GluR5 was expressed at flat bipolar cell contacts; however, it appears to be involved with only certain types of OFF-cone bipolar cells. This suggests that different bipolar cell types receive their light signals through different sets of glutamate receptors.
Copyright 2002 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
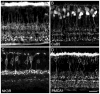
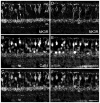
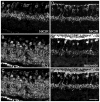


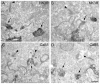
Similar articles
-
Localization of kainate receptors at the cone pedicles of the primate retina.J Comp Neurol. 2001 Aug 6;436(4):471-86. doi: 10.1002/cne.1081. J Comp Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11447590
-
Expression of genes encoding glutamate receptors and transporters in rod and cone bipolar cells of the primate retina determined by single-cell polymerase chain reaction.Mol Vis. 2007 Nov 28;13:2194-208. Mol Vis. 2007. PMID: 18087239
-
Types of bipolar cells in the mouse retina.J Comp Neurol. 2004 Jan 26;469(1):70-82. doi: 10.1002/cne.10985. J Comp Neurol. 2004. PMID: 14689473
-
Birth and death in the retina: more related than we thought?Neuron. 1999 Jul;23(3):411-2. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80790-4. Neuron. 1999. PMID: 10433249 Review. No abstract available.
-
Caldendrins in the inner retina.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;514:451-63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0121-3_27. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002. PMID: 12596938 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of connexin36 in cone pedicles and OFF-cone bipolar cells of the mouse retina.J Neurosci. 2004 Mar 31;24(13):3325-34. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5598-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15056712 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and cellular localization of the voltage-gated calcium channel α2δ3 in the rodent retina.J Comp Neurol. 2015 Jul 1;523(10):1443-60. doi: 10.1002/cne.23751. Epub 2015 Mar 10. J Comp Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25631988 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid precursor protein is required for normal function of the rod and cone pathways in the mouse retina.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29892. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029892. Epub 2012 Jan 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22279552 Free PMC article.
-
New Approach for Untangling the Role of Uncommon Calcium-Binding Proteins in the Central Nervous System.Brain Sci. 2021 May 14;11(5):634. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11050634. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34069107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrical synapses in retinal ON cone bipolar cells: subtype-specific expression of connexins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Sep 13;102(37):13313-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505067102. Epub 2005 Sep 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16150718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andressen C, Mai JK. Localization of the CD15 carbohydrate epitope in the vertebrate retina. Vis Neurosci. 1997;14:253–262. - PubMed
-
- Berrebi AS, Oberdick J, Sangameswaran L, Christakos S, Morgan JI, Mugnaini E. Cerebellar Purkinje cell markers are expressed in retinal bipolar neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1991;308:630–649. - PubMed
-
- Blumauer N, Brecha NC. Off-type of cone bipolar cells express neurokinin-3 (NK-3) receptors in the rat retina. Soc Neurosci Abstr. 1998:2091.
-
- Boycott BB, Wässle H. Morphological classification of bipolar cells in the macaque monkey retina. Eur J Neurosci. 1991;3:1069–1088. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

