Comparative analysis of ribosomal proteins in complete genomes: an example of reductive evolution at the domain scale
- PMID: 12490706
- PMCID: PMC140077
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkf693
Comparative analysis of ribosomal proteins in complete genomes: an example of reductive evolution at the domain scale
Abstract
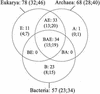
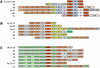
A comprehensive investigation of ribosomal genes in complete genomes from 66 different species allows us to address the distribution of r-proteins between and within the three primary domains. Thirty-four r-protein families are represented in all domains but 33 families are specific to Archaea and Eucarya, providing evidence for specialisation at an early stage of evolution between the bacterial lineage and the lineage leading to Archaea and Eukaryotes. With only one specific r-protein, the archaeal ribosome appears to be a small-scale model of the eukaryotic one in terms of protein composition. However, the mechanism of evolution of the protein component of the ribosome appears dramatically different in Archaea. In Bacteria and Eucarya, a restricted number of ribosomal genes can be lost with a bias toward losses in intracellular pathogens. In Archaea, losses implicate 15% of the ribosomal genes revealing an unexpected plasticity of the translation apparatus and the pattern of gene losses indicates a progressive elimination of ribosomal genes in the course of archaeal evolution. This first documented case of reductive evolution at the domain scale provides a new framework for discussing the shape of the universal tree of life and the selective forces directing the evolution of prokaryotes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ribosomal proteins: structure, function, and evolution.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2012 Jun;77(6):562-74. doi: 10.1134/S0006297912060028. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2012. PMID: 22817455 Review.
-
Protein Fold Usages in Ribosomes: Another Glance to the Past.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 13;25(16):8806. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168806. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201491 Free PMC article.
-
Protein content of minimal and ancestral ribosome.RNA. 2005 Sep;11(9):1400-6. doi: 10.1261/rna.2180205. Epub 2005 Jul 25. RNA. 2005. PMID: 16043494 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic distribution of DNA-binding transcription factors in bacteria and archaea.Comput Biol Chem. 2004 Dec;28(5-6):341-50. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2004.09.004. Comput Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15556475
-
Atomic structures of the eukaryotic ribosome.Trends Biochem Sci. 2012 May;37(5):189-98. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2012.02.007. Epub 2012 Mar 20. Trends Biochem Sci. 2012. PMID: 22436288 Review.
Cited by
-
Early bioenergetic evolution.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 Jun 10;368(1622):20130088. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0088. Print 2013 Jul 19. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23754820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ProteoVision: web server for advanced visualization of ribosomal proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jul 2;49(W1):W578-W588. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab351. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33999189 Free PMC article.
-
A pursuit of lineage-specific and niche-specific proteome features in the world of archaea.BMC Genomics. 2012 Jun 12;13:236. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-236. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22691113 Free PMC article.
-
The Last Universal Common Ancestor of Ribosome-Encoding Organisms: Portrait of LUCA.J Mol Evol. 2024 Oct;92(5):550-583. doi: 10.1007/s00239-024-10186-9. Epub 2024 Aug 19. J Mol Evol. 2024. PMID: 39158619 Review.
-
YRA1 autoregulation requires nuclear export and cytoplasmic Edc3p-mediated degradation of its pre-mRNA.Mol Cell. 2007 Feb 23;25(4):559-73. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.01.012. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17317628 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wimberly B.T., Brodersen,D.E., Clemons,W.M.,Jr, Morgan-Warren,R.J., Carter,A.P., Vonrhein,C., Hartsch,T. and Ramakrishnan,V. (2000) Structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit. Nature, 407, 327–339. - PubMed
-
- Schluenzen F., Tocilj,A., Zarivach,R., Harms,J., Gluehmann,M., Janell,D., Bashan,A., Bartels,H., Agmon,I., Franceschi,F. et al. (2000) Structure of functionally activated small ribosomal subunit at 3.3 angstroms resolution. Cell, 102, 615–623. - PubMed
-
- Harms J., Schluenzen,F., Zarivach,R., Bashan,A., Gat,S., Agmon,I., Bartels,H., Franceschi,F. and Yonath,A. (2001) High resolution structure of the large ribosomal subunit from a mesophilic eubacterium. Cell, 107, 679–688. - PubMed
-
- Ban N., Nissen,P., Hansen,J., Moore,P.B. and Steitz,T.A. (2000) The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 Å resolution. Science, 289, 905–920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

