Transcriptional modulation of bacterial gene expression by subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics
- PMID: 12482953
- PMCID: PMC139263
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.252607699
Transcriptional modulation of bacterial gene expression by subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics
Abstract
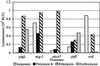
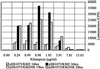
Antibiotics such as erythromycin and rifampicin, at low concentrations, alter global bacterial transcription patterns as measured by the stimulation or inhibition of a variety of promoter-lux reporter constructs in a Salmonella typhimurium library. Analysis of a 6,500-clone library indicated that as many as 5% of the promoters may be affected, comprising genes for a variety of functions, as well as a significant fraction of genes with no known function. Studies of a selection of the reporter clones showed that stimulation varied depending on the nature of the antibiotic, the promoter, and what culture medium was used; the response differed on solid as compared with liquid media. Transcription was markedly reduced in antibiotic-resistant hosts, but the presence of mutations deficient in stress responses such as SOS or universal stress did not prevent antibiotic-induced modulation. The results show that small molecules may have contrasting effects on bacteria depending on their concentration: either the modulation of bacterial metabolism by altering transcription patterns or the inhibition of growth by the inhibition of specific target functions. Both activities could play important roles in the regulation of microbial communities. These studies indicate that the detection of pharmaceutically useful natural product inhibitors could be effectively achieved by measuring activation of transcription at low concentrations in high-throughput assays using appropriate bacterial promoter-reporter constructs.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dual effects of MLS antibiotics: transcriptional modulation and interactions on the ribosome.Chem Biol. 2004 Sep;11(9):1307-16. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.07.010. Chem Biol. 2004. PMID: 15380191
-
Transcription modulation of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium promoters by sub-MIC levels of rifampin.J Bacteriol. 2006 Nov;188(22):7988-91. doi: 10.1128/JB.00791-06. Epub 2006 Sep 15. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16980465 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Salmonella gene expression by subinhibitory concentrations of quinolones.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2011 Jan;64(1):73-8. doi: 10.1038/ja.2010.137. Epub 2010 Nov 24. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2011. PMID: 21102598
-
The world of subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2006 Oct;9(5):445-53. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.08.006. Epub 2006 Aug 30. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16942902 Review.
-
Antibiotic-supersusceptible mutants of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Nov;37(11):2255-60. doi: 10.1128/AAC.37.11.2255. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993. PMID: 8285603 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Effect from low-level exposure of oxytetracycline on abundance of tetracycline resistance genes in arable soils.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015 Sep;22(17):13102-10. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4099-1. Epub 2015 May 1. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25925140
-
Using a sequential regimen to eliminate bacteria at sublethal antibiotic dosages.PLoS Biol. 2015 Apr 8;13(4):e1002104. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002104. eCollection 2015 Apr. PLoS Biol. 2015. PMID: 25853342 Free PMC article.
-
Subinhibitory concentration of ciprofloxacin targets quorum sensing system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa causing inhibition of biofilm formation & reduction of virulence.Indian J Med Res. 2016 May;143(5):643-51. doi: 10.4103/0971-5916.187114. Indian J Med Res. 2016. PMID: 27488009 Free PMC article.
-
Non-invasive determination of conjugative transfer of plasmids bearing antibiotic-resistance genes in biofilm-bound bacteria: effects of substrate loading and antibiotic selection.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Jan;97(1):317-28. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4179-9. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 22669634 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Arcobacter butzleri Infection in a Mucus-Producing Human Intestinal In Vitro Model.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0207122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02071-22. Epub 2023 Jan 9. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36622176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Waksman S. A. (1961) Perspect. Biol. Med. 4, 271-286.
-
- Kell D. B., Kaprelyants, A. S. & Grafen, A. (1995) Trends Ecol. Evol. 10, 126-129. - PubMed
-
- Demain A. L. & Fang, A. (2000) in History of Modern Biotechnology, ed. Fiechter, A. (Springer, Berlin), Vol. 1, pp. 2–39.
-
- Piepersberg W. (2001) in Molecular Medical Microbiology, ed. Sussman, M. (Academic, New York), Vol. 1, pp. 561–585.
-
- Dunny G. M. & Winans, S. C., (1999) Cell–Cell Signaling in Bacteria (Am. Soc. Microbiol., Washington, DC).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

