Protein composition of human prespliceosomes isolated by a tobramycin affinity-selection method
- PMID: 12477934
- PMCID: PMC139210
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.262483899
Protein composition of human prespliceosomes isolated by a tobramycin affinity-selection method
Abstract
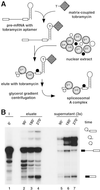
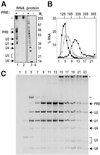
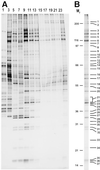
Detailed knowledge of the composition and structure of the spliceosome and its assembly intermediates is a prerequisite for understanding the complex process of pre-mRNA splicing. To this end, we have developed a tobramycin affinity-selection method that is generally applicable for the purification of native RNP complexes. By using this method, we have isolated human prespliceosomes that are ideally suited for both biochemical and structural studies. MS identified >70 prespliceosome-associated proteins, including nearly all known U1 and U2 snRNP proteins, and expected non-snRNP splicing factors. In addition, the DEAD-box protein p68, RNA helicase A, and a number of proteins that appear to perform multiple functions in the cell, such as YB-1 and TLS, were detected. Several previously uncharacterized proteins of unknown function were also identified, suggesting that they play a role in splicing and potentially act during prespliceosome assembly. These data provide insight into the complexity of the splicing machinery at an early stage of its assembly.
Figures
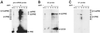
Similar articles
-
Tobramycin affinity tag purification of spliceosomes.Methods Mol Biol. 2004;257:47-64. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-750-5:047. Methods Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 14769995
-
Proteomic analysis of in vivo-assembled pre-mRNA splicing complexes expands the catalog of participating factors.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(12):3928-44. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm347. Epub 2007 May 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17537823 Free PMC article.
-
Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein remodeling during catalytic activation of the spliceosome.Science. 2002 Dec 13;298(5601):2205-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1077783. Epub 2002 Oct 31. Science. 2002. PMID: 12411573
-
The spliceosome: the most complex macromolecular machine in the cell?Bioessays. 2003 Dec;25(12):1147-9. doi: 10.1002/bies.10394. Bioessays. 2003. PMID: 14635248 Review.
-
The spliceosome.Bioessays. 1993 Sep;15(9):595-603. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150905. Bioessays. 1993. PMID: 8240312 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA Binding Motif 5 (RBM5) in the CNS-Moving Beyond Cancer to Harness RNA Splicing to Mitigate the Consequences of Brain Injury.Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 Jul 15;13:126. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00126. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32765218 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoprecipitation of spliceosomal RNAs by antisera to galectin-1 and galectin-3.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(18):5166-74. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl673. Epub 2006 Sep 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16998182 Free PMC article.
-
Functional links between the Prp19-associated complex, U4/U6 biogenesis, and spliceosome recycling.RNA. 2006 May;12(5):765-74. doi: 10.1261/rna.2292106. Epub 2006 Mar 15. RNA. 2006. PMID: 16540691 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of alternative RNA splicing by exon definition and exon sequences in viral and mammalian gene expression.J Biomed Sci. 2004 May-Jun;11(3):278-94. doi: 10.1007/BF02254432. J Biomed Sci. 2004. PMID: 15067211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YB-1 promotes strand separation in vitro of duplex DNA containing either mispaired bases or cisplatin modifications, exhibits endonucleolytic activities and binds several DNA repair proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Jan 12;32(1):316-27. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh170. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 14718551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reed R. & Palandijan, L. (1997) in Eukaryotic mRNA Processing, ed. Krainer, A. R. (IRL, Oxford), pp. 103–129.
-
- Burge C. B., Tuschl, T. & Sharp, P. A. (1999) in The RNA World, eds. Gesteland, R. F., Cech, T. R. & Atkins, J. F. (Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press, Plainview, NY), pp. 525–560.
-
- Das R., Zhou, Z. & Reed, R. (2000) Mol. Cell 5 779-787. - PubMed
-
- Neubauer G., King, A., Rappsilber, J., Calvio, C., Watson, M., Ajuh, P., Sleeman, J., Lamond, A. & Mann, M. (1998) Nat. Genet. 20 46-50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

