The role of neurotrophins in neurotransmitter release
- PMID: 12467374
- PMCID: PMC2810653
- DOI: 10.1177/1073858402238511
The role of neurotrophins in neurotransmitter release
Abstract
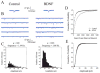
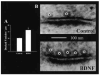
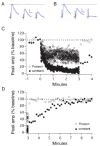
The neurotrophins (NTs) have recently been shown to elicit pronounced effects on quantal neurotransmitter release at both central and peripheral nervous system synapses. Due to their activity-dependent release, as well as the subcellular localization of both protein and receptor, NTs are ideally suited to modify the strength of neuronal connections by "fine-tuning" synaptic activity through direct actions at presynaptic terminals. Here, using BDNF as a prototypical example, the authors provide an update of recent evidence demonstrating that NTs enhance quantal neurotransmitter release at synapses through presynaptic mechanisms. The authors further propose that a potential target for NT actions at presynaptic terminals is the mechanism by which terminals retrieve synaptic vesicles after exocytosis. Depending on the temporal demands placed on synapses during high-frequency synaptic transmission, synapses may use two alternative modes of synaptic vesicle retrieval, the conventional slow endosomal recycling or a faster rapid retrieval at the active zone, referred to as "kiss-and-run." By modulating Ca2+ microdomains associated with voltage-gated Ca2+ channels at active zones, NTs may elicit a switch from the slow to the fast mode of endocytosis of vesicles at presynaptic terminals during high-frequency synaptic transmission, allowing more reliable information transfer and neuronal signaling in the central nervous system.
Figures

Similar articles
-
BDNF enhances quantal neurotransmitter release and increases the number of docked vesicles at the active zones of hippocampal excitatory synapses.J Neurosci. 2001 Jun 15;21(12):4249-58. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-12-04249.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11404410 Free PMC article.
-
The synaptic vesicle cycle.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2004;27:509-47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.26.041002.131412. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15217342 Review.
-
The synaptic vesicle cluster: a source of endocytic proteins during neurotransmitter release.Neuroscience. 2009 Jan 12;158(1):204-10. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.03.035. Epub 2008 Mar 26. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 18440714 Review.
-
Ca(2+) channels and transmitter release at the active zone.Cell Calcium. 2012 Sep-Oct;52(3-4):199-207. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2012.04.011. Epub 2012 Jun 8. Cell Calcium. 2012. PMID: 22682961 Review.
-
Mechanisms, locations, and kinetics of synaptic BDNF secretion: an update.Neurosci Res. 2009 Sep;65(1):11-22. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2009.06.004. Epub 2009 Jun 11. Neurosci Res. 2009. PMID: 19523993
Cited by
-
The actions of BDNF on dendritic spine density and morphology in organotypic slice cultures depend on the presence of serum in culture media.J Neurosci Methods. 2008 Mar 30;169(1):182-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.12.006. Epub 2007 Dec 23. J Neurosci Methods. 2008. PMID: 18242714 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism and therapeutic response to olanzapine in schizophrenia patients.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Sep;231(18):3757-64. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3515-4. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24595507
-
Intracerebroventricular administration of α-ketoisocaproic acid decreases brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor levels in brain of young rats.Metab Brain Dis. 2016 Apr;31(2):377-83. doi: 10.1007/s11011-015-9768-8. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Metab Brain Dis. 2016. PMID: 26586008
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor controls activity-dependent maturation of CA1 synapses by downregulating tonic activation of presynaptic kainate receptors.J Neurosci. 2009 Sep 9;29(36):11294-303. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0560-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19741136 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and trkB signaling in parasympathetic neurons: relevance to regulating alpha7-containing nicotinic receptors and synaptic function.J Neurosci. 2004 May 5;24(18):4340-50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0055-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15128848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott LF, Varela JA, Sen K, Nelson SB. Synaptic depression and cortical gain control. Science. 1997;275:220–4. - PubMed
-
- Abenavoli A, Montagna M, Malgaroli A. Calcium: the common theme in vesicular cycling. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:117–8. - PubMed
-
- Augustine GJ. How does calcium trigger neurotransmitter release? Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2001;11:320–6. - PubMed
-
- Baldelli P, Forni PE, Carbone E. BDNF, NT-3 and NGF induce distinct new Ca2+ channel synthesis in developing hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;12:4017–32. - PubMed
-
- Baldelli P, Magnelli V, Carbone E. Selective up-regulation of P- and R-type Ca2+ channels in rat embryo motoneurons by BDNF. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11:1127–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

