Cell cycle-dependent nuclear export of Cdh1p may contribute to the inactivation of APC/C(Cdh1)
- PMID: 12456658
- PMCID: PMC136938
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf634
Cell cycle-dependent nuclear export of Cdh1p may contribute to the inactivation of APC/C(Cdh1)
Abstract
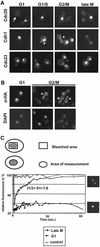
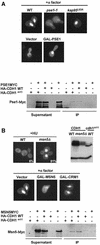
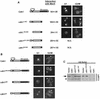
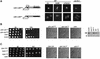
Cdh1p is a substrate-specific subunit of the anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C), which functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase to degrade the mitotic cyclin Clb2p and other substrates during the G(1) phase of the cell cycle. Cdh1p is phosphorylated and thereby inactivated at the G(1)/S transition predominantly by Cdc28p-Clb5p. Here we show that Cdh1p is nuclear during the G(1) phase of the cell cycle, but redistributes to the cytoplasm between S phase and the end of mitosis. Nuclear export of Cdh1p is regulated by phosphorylation and requires active Cdc28p kinase. Cdh1p binds to the importin Pse1p and the exportin Msn5p, which is necessary and sufficient to promote efficient export of Cdh1p in vivo. Although msn5delta cells are viable, they are sensitive to Cdh1p overexpression. Likewise, a mutant form of Cdh1p, which is constitutively nuclear, prevents accumulation of Clb2p and leads to cell cycle arrest when overexpressed in wild-type cells. Taken together, these results suggest that phosphorylation-dependent nuclear export of Cdh1p by Msn5p contributes to efficient inactivation of APC/C(Cdh1).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activity of the APC(Cdh1) form of the anaphase-promoting complex persists until S phase and prevents the premature expression of Cdc20p.J Cell Biol. 2001 Jul 9;154(1):85-94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200102007. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11448992 Free PMC article.
-
Hsl1p, a Swe1p inhibitor, is degraded via the anaphase-promoting complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Jul;20(13):4614-25. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.13.4614-4625.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10848588 Free PMC article.
-
Mitotic regulation of the APC activator proteins CDC20 and CDH1.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 May;11(5):1555-69. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.5.1555. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10793135 Free PMC article.
-
The anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C): cell-cycle-dependent and -independent functions.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Feb;38(Pt 1):65-71. doi: 10.1042/BST0380065. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20074037 Review.
-
Mechanisms and regulation of the degradation of cyclin B.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999 Sep 29;354(1389):1571-5; discussion 1575-6. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1999.0500. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999. PMID: 10582242 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the cellular mechanism of the yeast ubiquitin ligase APC/C-Cdh1 from the analysis of in vivo degrons.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Mar 1;26(5):843-58. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-09-1342. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25540434 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of the functional distinction between Cln1 and Cln2 cyclins.Cell Cycle. 2012 Aug 15;11(16):3117-31. doi: 10.4161/cc.21505. Epub 2012 Aug 14. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22889732 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient nuclear transport of structurally disturbed cargo: mutations in a cargo protein switch its cognate karyopherin.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 9;6(2):e16846. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016846. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21347375 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of Cdh1 by synergistic action of Cdk1 and polo kinase is necessary for proper assembly of the mitotic spindle.Nat Cell Biol. 2008 Jun;10(6):665-75. doi: 10.1038/ncb1729. Epub 2008 May 25. Nat Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18500339 Free PMC article.
-
Dual control by Cdk1 phosphorylation of the budding yeast APC/C ubiquitin ligase activator Cdh1.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Jul 15;27(14):2198-212. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-11-0787. Epub 2016 May 25. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27226481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amon A., Irniger,S. and Nasmyth,K. (1994) Closing the cell cycle circle in yeast: G2 cyclin proteolysis initiated at mitosis persists until the activation of G1 cyclins in the next cycle. Cell, 77, 1037–1050. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F.M., Brent,R., Kingston,R.E., Moore,D.D., Seidman,J.G., Smith,J.A. and Struhl,K. (1991) Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Greene Publishing Associates and Wiley-Interscience, New York, NY.
-
- Baumer M., Kunzler,M., Steigemann,P., Braus,G.H. and Irniger,S. (2000) Yeast Ran-binding protein Yrb1p is required for efficient proteolysis of cell cycle regulatory proteins Pds1p and Sic1p. J. Biol. Chem., 275, 38929–38937. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

