PVF2, a PDGF/VEGF-like growth factor, induces hemocyte proliferation in Drosophila larvae
- PMID: 12446570
- PMCID: PMC1308320
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvf242
PVF2, a PDGF/VEGF-like growth factor, induces hemocyte proliferation in Drosophila larvae
Abstract
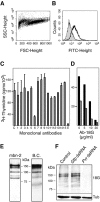
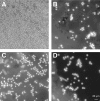
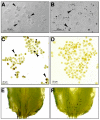
Blood cells play a crucial role in both morphogenetic and immunological processes in Drosophila, yet the factors regulating their proliferation remain largely unknown. In order to address this question, we raised antibodies against a tumorous blood cell line and identified an antigenic determinant that marks the surface of prohemocytes and also circulating plasmatocytes in larvae. This antigen was identified as a Drosophila homolog of the mammalian receptor for platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)/vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The Drosophila receptor controls cell proliferation in vitro. By overexpressing in vivo one of its putative ligands, PVF2, we induced a dramatic increase in circulating hemocytes. These results identify the PDGF/VEGF receptor homolog and one of its ligands as important players in Drosophila hematopoiesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Drosophila platelet-derived growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor-receptor related (Pvr) protein ligands Pvf2 and Pvf3 control hemocyte viability and invasive migration.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 12;288(28):20173-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.483818. Epub 2013 Jun 4. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23737520 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila Perlecan gene trol regulates multiple signaling pathways in different developmental contexts.BMC Dev Biol. 2007 Nov 2;7:121. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-7-121. BMC Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17980035 Free PMC article.
-
The TEAD family transcription factor Scalloped regulates blood progenitor maintenance and proliferation in Drosophila through PDGF/VEGFR receptor (Pvr) signaling.Dev Biol. 2017 May 1;425(1):21-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.03.016. Epub 2017 Mar 18. Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28322737
-
Angiogenesis inhibition in cancer therapy: platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and their receptors: biological functions and role in malignancy.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2010;180:51-81. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-78281-0_5. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20033378 Review.
-
Drosophila immune cell migration and adhesion during embryonic development and larval immune responses.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;36:71-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2015.07.003. Epub 2015 Jul 24. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26210104 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of the Cellular Immune System of Drosophila Requires the Membrane Attack Complex/Perforin-Like Protein Torso-Like.Genetics. 2016 Oct;204(2):675-681. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.185462. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27535927 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related changes in Drosophila midgut are associated with PVF2, a PDGF/VEGF-like growth factor.Aging Cell. 2008 Jun;7(3):318-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2008.00380.x. Epub 2008 Feb 13. Aging Cell. 2008. PMID: 18284659 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila Ras/MAPK signalling regulates innate immune responses in immune and intestinal stem cells.EMBO J. 2011 Mar 16;30(6):1123-36. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.4. Epub 2011 Feb 4. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21297578 Free PMC article.
-
MiniCORVET is a Vps8-containing early endosomal tether in Drosophila.Elife. 2016 Jun 2;5:e14226. doi: 10.7554/eLife.14226. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27253064 Free PMC article.
-
Ancient cytokines, the role of astakines as hematopoietic growth factors.J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 10;285(37):28577-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.138560. Epub 2010 Jun 30. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20592028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown S., Hu N. and Hombria J.C. (2001) Identification of the first invertebrate interleukin JAK/STAT receptor, the Drosophila gene domeless. Curr. Biol., 11, 1700–1705. - PubMed
-
- Cho N.K., Keyes L., Johnson E., Heller J., Ryner L., Karim F. and Krasnow M.A. (2002) Developmental control of blood cell migration by the Drosophila VEGF pathway. Cell, 108, 865–876. - PubMed
-
- Coligan J.E., Kruisbeek A.M., Margulies D.H., Shevach E.M. and Strober W. (1999) Current Protocols in Immunology. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
-
- Dimarcq J.L., Imler J.L., Lanot R., Ezekowitz R.A., Hoffmann J.A., Janeway C.A. and Lagueux M. (1997) Treatment of l(2)mbn Drosophila tumorous blood cells with the steroid hormone ecdysone amplifies the inducibility of antimicrobial peptide gene expression. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol., 27, 877–886. - PubMed
-
- Duchek P., Somogyi K., Jekely G., Beccari S. and Rorth P. (2001) Guidance of cell migration by the Drosophila PDGF/VEGF receptor. Cell, 107, 17–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

