In vivo and in vitro interaction between human transcription factor MOK2 and nuclear lamin A/C
- PMID: 12409453
- PMCID: PMC135794
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkf587
In vivo and in vitro interaction between human transcription factor MOK2 and nuclear lamin A/C
Abstract
The human and murine MOK2 proteins are factors able to recognize both DNA and RNA through their zinc finger motifs. This dual affinity of MOK2 suggests that MOK2 might be involved in transcription and post-transcriptional regulation of MOK2 target genes. The IRBP gene contains two MOK2-binding elements, a complete 18 bp MOK2-binding site located in intron 2 and the essential core MOK2-binding site (8 bp of conserved 3'-half-site) located in the IRBP promoter. We have demonstrated that MOK2 can bind to the 8 bp present in the IRBP promoter and repress transcription from this promoter by competing with the CRX activator for DNA binding. In this study, we identify a novel interaction between lamin A/C and hsMOK2 by using the yeast two-hybrid system. The interaction, which was confirmed by GST pull-down assays and co-immunolocalization studies in vivo, requires the N-terminal acidic domain of hsMOK2 and the coiled 2 domain of lamin A/C. Furthermore, we show that a fraction of hsMOK2 protein is associated with the nuclear matrix. We therefore suggest that hsMOK2 interactions with lamin A/C and the nuclear matrix may be important for its ability to repress transcription.
Figures


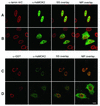
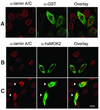

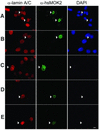
Similar articles
-
Mislocalization of human transcription factor MOK2 in the presence of pathogenic mutations of lamin A/C.Biol Cell. 2008 Jan;100(1):51-61. doi: 10.1042/BC20070053. Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 17760566
-
Phosphorylation-dependent binding of human transcription factor MOK2 to lamin A/C.FEBS J. 2009 Jun;276(11):3137-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07032.x. Epub 2009 Apr 23. FEBS J. 2009. PMID: 19490114
-
The zinc finger transcription factor, MOK2, negatively modulates expression of the interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein gene, IRBP.J Biol Chem. 2001 Apr 13;276(15):11963-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M011036200. Epub 2001 Jan 18. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11278819
-
Human and mouse MOK2 proteins are associated with nuclear ribonucleoprotein components and bind specifically to RNA and DNA through their zinc finger domains.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Apr;17(4):2116-26. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.4.2116. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9121460 Free PMC article.
-
Human and mouse Krüppel-like (MOK2) orthologue genes encode two different zinc finger proteins.J Mol Evol. 1995 Dec;41(6):784-94. doi: 10.1007/BF00173158. J Mol Evol. 1995. PMID: 8587123
Cited by
-
Ameliorating pathogenesis by removing an exon containing a missense mutation: a potential exon-skipping therapy for laminopathies.Gene Ther. 2015 Jun;22(6):503-15. doi: 10.1038/gt.2015.8. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Gene Ther. 2015. PMID: 25832542
-
Lamin A/C and Emerin depletion impacts chromatin organization and dynamics in the interphase nucleus.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019 May 22;20(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12860-019-0192-5. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31117946 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear lamins: major factors in the structural organization and function of the nucleus and chromatin.Genes Dev. 2008 Apr 1;22(7):832-53. doi: 10.1101/gad.1652708. Genes Dev. 2008. PMID: 18381888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Attenuated hypertrophic response to pressure overload in a lamin A/C haploinsufficiency mouse.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010 Jun;48(6):1290-7. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.10.024. Epub 2009 Nov 12. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 19913544 Free PMC article.
-
Interphase phosphorylation of lamin A.J Cell Sci. 2014 Jun 15;127(Pt 12):2683-96. doi: 10.1242/jcs.141820. Epub 2014 Apr 16. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24741066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ernoult-Lange M., Arranz,V., Leconiat,M., Berger,R. and Kress,M. (1995) Human and mouse Kruppel-like (MOK2) orthologue genes encode two different zinc finger proteins. J. Mol. Evol., 41, 784–794. - PubMed
-
- Fong S.L. and Bridges,C.D. (1990) Interstitial retinol-binding protein: purification, characterization, molecular cloning and sequence. Methods Enzymol., 189, 207–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

