Runx2 (Cbfa1, AML-3) interacts with histone deacetylase 6 and represses the p21(CIP1/WAF1) promoter
- PMID: 12391164
- PMCID: PMC134736
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.22.7982-7992.2002
Runx2 (Cbfa1, AML-3) interacts with histone deacetylase 6 and represses the p21(CIP1/WAF1) promoter
Abstract
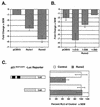
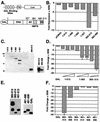
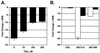
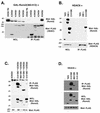
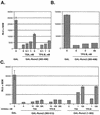
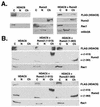
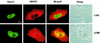
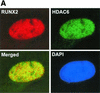
Runx2 (Cbfa1, AML-3) is multifunctional transcription factor that is essential for osteoblast development. Runx2 binds specific DNA sequences and interacts with transcriptional coactivators and corepressors to either activate or repress transcription of tissue-specific genes. In this study, the p21(CIP/WAF1) promoter was identified as a repressible target of Runx2. A carboxy-terminal repression domain distinct from the well-characterized TLE/Groucho-binding domain contributed to Runx2-mediated p21 repression. This carboxy-terminal domain was sufficient to repress a heterologous GAL reporter. The repressive activity of this domain was sensitive to the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A but not to trapoxin B. HDAC6, which is insensitive to trapoxin B, specifically interacted with the carboxy terminus of Runx2. The HDAC6 interaction domain of Runx2 was mapped to a region overlapping the nuclear matrix-targeting signal. The Runx2 carboxy terminus was necessary for recruitment of HDAC6 from the cytoplasm to chromatin. HDAC6 also colocalized and coimmunoprecipitated with the nuclear matrix-associated protein Runx2 in osteoblasts. Finally, we show that HDAC6 is expressed in differentiating osteoblasts and that the Runx2 carboxy terminus is necessary for maximal repression of the p21 promoter in preosteoblasts. These data identify Runx2 as the first transcription factor to interact with HDAC6 and suggest that HDAC6 may bind to Runx2 in differentiating osteoblasts to regulate tissue-specific gene expression.
Figures
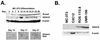


Similar articles
-
Histone deacetylase 3 interacts with runx2 to repress the osteocalcin promoter and regulate osteoblast differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 1;279(40):41998-2007. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403702200. Epub 2004 Aug 2. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15292260
-
Histone deacetylase 7 associates with Runx2 and represses its activity during osteoblast maturation in a deacetylation-independent manner.J Bone Miner Res. 2008 Mar;23(3):361-72. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.071104. J Bone Miner Res. 2008. PMID: 17997710 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21(WAF1/Cip1) gene by Zac1 through the antagonistic regulators p53 and histone deacetylase 1 in HeLa Cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2008 Jul;6(7):1204-14. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0123. Mol Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18644983
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor activates the p21/WAF1/Cip1 gene promoter through the Sp1 sites.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;886:195-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb09415.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10667218 Review.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors: signalling towards p21cip1/waf1.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(7-8):1367-74. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2007.03.001. Epub 2007 Mar 7. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17412634 Review.
Cited by
-
HDAC6: A unique HDAC family member as a cancer target.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022 Oct;45(5):779-829. doi: 10.1007/s13402-022-00704-6. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022. PMID: 36036883 Review.
-
Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) is an essential modifier of glucocorticoid-induced hepatic gluconeogenesis.Diabetes. 2012 Feb;61(2):513-23. doi: 10.2337/db11-0313. Epub 2011 Dec 30. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22210316 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC8, A Potential Therapeutic Target, Regulates Proliferation and Differentiation of Bone Marrow Stromal Cells in Fibrous Dysplasia.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019 Feb;8(2):148-161. doi: 10.1002/sctm.18-0057. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 30426726 Free PMC article.
-
Runx-dependent expression of PKC is critical for cell survival in the sea urchin embryo.BMC Biol. 2005 Aug 2;3:18. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-3-18. BMC Biol. 2005. PMID: 16076398 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc2: a monopotent or pluripotent CDK?Cell Prolif. 2011 Jun;44(3):205-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2011.00753.x. Cell Prolif. 2011. PMID: 21535261 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amann, J. M., J. Nip, D. K. Strom, B. Lutterbach, H. Harada, N. Lenny, J. R. Downing, S. Meyers, and S. W. Hiebert. 2001. ETO, a target of t(8;21) in acute leukemia, makes distinct contacts with multiple histone deacetylases and binds mSin3A through its oligomerization domain. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21:6470-6483. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berger, J., J. Hauber, R. Hauber, R. Geiger, and B. R. Cullen. 1988. Secreted placental alkaline phosphatase: a powerful new quantitative indicator of gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Gene. 66:1-10. - PubMed
-
- Bertos, N. R., A. H. Wang, and X. J. Yang. 2001. Class II histone deacetylases: structure, function, and regulation. Biochem. Cell Biol. 79:243-252. - PubMed
-
- Blyth, K., A. Terry, N. Mackay, F. Vaillant, M. Bell, E. R. Cameron, J. C. Neil, and M. Stewart. 2001. Runx2: a novel oncogenic effector revealed by in vivo complementation and retroviral tagging. Oncogene 20:295-302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
