Tenascin-C modulates matrix contraction via focal adhesion kinase- and Rho-mediated signaling pathways
- PMID: 12388760
- PMCID: PMC129969
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-05-0292
Tenascin-C modulates matrix contraction via focal adhesion kinase- and Rho-mediated signaling pathways
Abstract
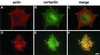
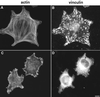
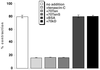
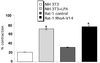
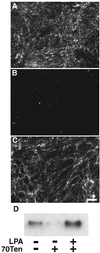
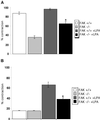
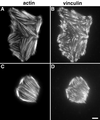
A provisional matrix consisting of fibrin and fibronectin (FN) is deposited at sites of tissue damage and repair. This matrix serves as a scaffold for fibroblast migration into the wound where these cells deposit new matrix to replace lost or damaged tissue and eventually contract the matrix to bring the margins of the wound together. Tenascin-C is expressed transiently during wound repair in tissue adjacent to areas of injury and contacts the provisional matrix in vivo. Using a synthetic model of the provisional matrix, we have found that tenascin-C regulates cell responses to a fibrin-FN matrix through modulation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and RhoA activation. Cells on fibrin-FN+tenascin-C redistribute their actin to the cell cortex, downregulate focal adhesion formation, and do not assemble a FN matrix. Cells surrounded by a fibrin-FN+tenascin-C matrix are unable to induce matrix contraction. The inhibitory effect of tenascin-C is circumvented by downstream activation of RhoA. FAK is also required for matrix contraction and the absence of FAK cannot be overcome by activation of RhoA. These observations show dual requirements for both FAK and RhoA activities during contraction of a fibrin-FN matrix. The effects of tenascin-C combined with its location around the wound bed suggest that this protein regulates fundamental processes of tissue repair by limiting the extent of matrix deposition and contraction to fibrin-FN-rich matrix in the primary wound area.
Figures

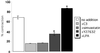

Similar articles
-
Coregulation of fibronectin signaling and matrix contraction by tenascin-C and syndecan-4.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Dec;15(12):5670-7. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-08-0759. Epub 2004 Oct 13. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15483051 Free PMC article.
-
Adenoviral-mediated expression and local deposition of recombinant tenascin-C perturbs cell-dependent matrix contraction.J Surg Res. 2006 Nov;136(1):92-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2006.05.030. Epub 2006 Aug 22. J Surg Res. 2006. PMID: 16926030
-
The fibronectin-binding integrins alpha5beta1 and alphavbeta3 differentially modulate RhoA-GTP loading, organization of cell matrix adhesions, and fibronectin fibrillogenesis.J Cell Biol. 2002 Dec 23;159(6):1071-86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200205014. Epub 2002 Dec 16. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12486108 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of cell-fibronectin matrix interactions during tissue repair.J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2006 Sep;11(1):73-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.jidsymp.5650005. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2006. PMID: 17069013 Review.
-
Modulation of cell-extracellular matrix interactions.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 Oct 23;857:143-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb10114.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. PMID: 9917839 Review.
Cited by
-
ROCK-generated contractility regulates breast epithelial cell differentiation in response to the physical properties of a three-dimensional collagen matrix.J Cell Biol. 2003 Nov 10;163(3):583-95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200305010. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14610060 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin Signaling in Cancer: Mechanotransduction, Stemness, Epithelial Plasticity, and Therapeutic Resistance.Cancer Cell. 2019 Mar 18;35(3):347-367. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.01.007. Cancer Cell. 2019. PMID: 30889378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of cartilage extracellular matrix molecules on cell phenotype and neocartilage formation.Tissue Eng Part A. 2014 Jan;20(1-2):264-74. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2012.0618. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014. PMID: 23962090 Free PMC article.
-
The extracellular matrix: Structure, composition, age-related differences, tools for analysis and applications for tissue engineering.J Tissue Eng. 2014 Dec 20;5:2041731414557112. doi: 10.1177/2041731414557112. eCollection 2014. J Tissue Eng. 2014. PMID: 25610589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of tenascin-C in tissue injury and tumorigenesis.J Cell Commun Signal. 2009 Dec;3(3-4):287-310. doi: 10.1007/s12079-009-0075-1. Epub 2009 Oct 17. J Cell Commun Signal. 2009. PMID: 19838819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amano M, Chihara K, Kimura K, Fukata Y, Nakamura N, Matsuura Y, Kaibuchi K. Formation of actin stress fibers and focal adhesions enhanced by Rho-kinase. Science. 1997;275:1308–1311. - PubMed
-
- Betz P, Nerlich A, Tubel J, Penning R, Eisenmenger W. Localization of tenascin in human skin wounds—an immunohistochemical study. Int J Legal Med. 1993;105:325–328. - PubMed
-
- Bourguignon LY, Zhu H, Shao L, Chen YW. CD44 interaction with c-Src kinase promotes cortactin-mediated cytoskeleton function and hyaluronic acid-dependent ovarian tumor cell migration. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:7327–7336. - PubMed
-
- Bowden ET, Barth M, Thomas D, Glazer RI, Mueller SC. An invasion-related complex of cortactin, paxillin and PKCmu associates with invadopodia at sites of extracellular matrix degradation. Oncogene. 1999;18:4440–4449. - PubMed
-
- Brenner KA, Corbett SA, Schwarzbauer JE. Regulation of fibronectin matrix assembly by activated Ras in transformed cells. Oncogene. 2000;19:3156–3163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

