A complex of the IL-1 homologue IL-1F7b and IL-18-binding protein reduces IL-18 activity
- PMID: 12381835
- PMCID: PMC129755
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.212519099
A complex of the IL-1 homologue IL-1F7b and IL-18-binding protein reduces IL-18 activity
Abstract
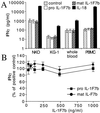
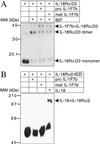
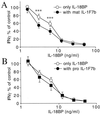
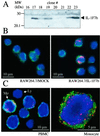
IL-1F7 was discovered in expressed sequence tag databases as a member of the increasing family of proteins sharing sequence homology to IL-1alpha/beta, IL-1Ra, and IL-18. In the present study using immunohistochemical staining, IL-1F7 was localized in human peripheral monocytic cells, suggesting its role in immune regulation. Recombinant human IL-1F7b was shown to bind to the IL-18Ralpha but without IL-18 agonistic or antagonistic function. Using chemical cross-linking, we observed that, unlike IL-18, IL-1F7b fails to recruit the IL-18Rbeta chain to form a functionally active, ternary complex with the IL-18Ralpha chain. IL-1F7b shares two conserved amino acids with IL-18 (Glu-35 and Lys-124), which participate in the interaction of IL-18 with the IL-18Ralpha chain as well as the IL-18-binding protein (IL-18BP), a secreted protein that neutralizes IL-18 activity. In testing whether IL-1F7b interacts with IL-18BP, we unexpectedly observed that IL-1F7b enhanced the ability of IL-18BP to inhibit IL-18-induced IFNgamma by 25-30% in a human natural killer cell line. This effect was observed primarily at limiting concentrations of IL-18BP (3.12-12.5 ng/ml) and at a 50- to 100-fold molar excess of IL-1F7b. Similar results were obtained by using isolated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. To study the molecular basis of this effect we performed binding studies of IL-1F7b and IL-18BP. After cross-linking, a high molecular weight complex consisting of IL-1F7b and IL-18BP was observed on SDS/PAGE. We propose that after binding to IL-18BP, IL-1F7b forms a complex with IL-18Rbeta, depriving the beta-chain of forming a functional receptor complex with IL-18Ralpha and thus inhibiting IL-18 activity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The combination of soluble IL-18Ralpha and IL-18Rbeta chains inhibits IL-18-induced IFN-gamma.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002 May;22(5):593-601. doi: 10.1089/10799900252982070. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002. PMID: 12060498
-
Interleukin-1F7B (IL-1H4/IL-1F7) is processed by caspase-1 and mature IL-1F7B binds to the IL-18 receptor but does not induce IFN-gamma production.Cytokine. 2002 Apr 21;18(2):61-71. doi: 10.1006/cyto.2002.0873. Cytokine. 2002. PMID: 12096920
-
Interleukin-1 homologues IL-1F7b and IL-18 contain functional mRNA instability elements within the coding region responsive to lipopolysaccharide.Biochem J. 2004 Jul 15;381(Pt 2):503-10. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040217. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15046617 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 18 and interleukin 18 binding protein: possible role in immunosuppression of chronic renal failure.Blood Purif. 2003;21(3):258-70. doi: 10.1159/000070699. Blood Purif. 2003. PMID: 12784053 Review.
-
Interleukin-18.Methods. 1999 Sep;19(1):121-32. doi: 10.1006/meth.1999.0837. Methods. 1999. PMID: 10525448 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-37 expression and its potential role in oral leukoplakia and oral squamous cell carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2016 May 26;6:26757. doi: 10.1038/srep26757. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27225603 Free PMC article.
-
The evaluation of plasma and leukocytic IL-37 expression in early inflammation in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction after PCI.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:626934. doi: 10.1155/2015/626934. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 25960620 Free PMC article.
-
Mast Cell Cytokines in Acute and Chronic Gingival Tissue Inflammation: Role of IL-33 and IL-37.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 31;23(21):13242. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113242. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-18: a therapeutic target in rheumatoid arthritis?Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(1):38-41. doi: 10.1186/ar1497. Epub 2004 Dec 17. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. PMID: 15642152 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the IL-1 family members in skin inflammation.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2010 Nov;11(11):1211-20. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2010. PMID: 21157640 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dinarello C A. Blood. 1996;87:2095–2147. - PubMed
-
- Nakanishi K, Yoshimoto T, Tsutsui H, Okamura H. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:423–474. - PubMed
-
- Barton J L, Herbst R, Bosisio D, Higgins L, Nicklin M J. Eur J Immunol. 2000;30:3299–3308. - PubMed
-
- Busfield S J, Comrack C A, Yu G, Chickering T W, Smutko J S, Zhou H, Leiby K R, Holmgren L M, Gearing D P, Pan Y. Genomics. 2000;66:213–216. - PubMed
-
- Debets R, Timans J C, Homey B, Zurawski S, Sana T R, Lo S, Wagner J, Edwards G, Clifford T, Menon S, et al. J Immunol. 2001;167:1440–1446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

