P21-activated kinase-1 phosphorylates and transactivates estrogen receptor-alpha and promotes hyperplasia in mammary epithelium
- PMID: 12374744
- PMCID: PMC129075
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf543
P21-activated kinase-1 phosphorylates and transactivates estrogen receptor-alpha and promotes hyperplasia in mammary epithelium
Abstract
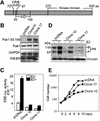
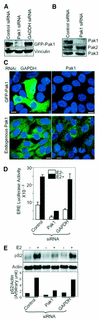
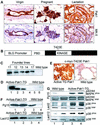
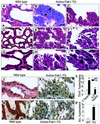
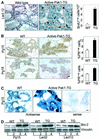
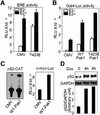
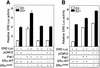
Stimulation of p21-activated kinase-1 (Pak1) induces cytoskeleton reorganization and signaling pathways in mammary cancer cells. Here, we show that inhibition of Pak1 kinase activity by a dominant-negative fragment or by short interference RNA markedly reduced the estrogen receptor-alpha (ER) transactivation functions. To understand the role of Pak1 in mammary glands, we developed a murine model expressing constitutively active Thr423 glutamic acid Pak1 driven by the beta-lactoglobulin promoter. We show that mammary glands from these mice developed widespread hyperplasia associated with apocrine metaplasia and lobuloalveolar hyperdevelopment during lactation. Mammary tissues with active Pak1 also exhibited an increased activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and stimulated transactivation functions of the ER and expression of endogenous ER target genes. Furthermore, Pak1 directly phosphorylated the activation function-2 domain of the ER at the N-terminal residue Ser305, and its mutation to Ala (S305A) abolished the Pak1-mediated phosphorylation and transactivation functions of the ER, while its mutation to glutamic acid (S305E) promoted transactivation activity of ER. These findings reveal a novel role for the Pak1-ER pathway in promoting hyperplasia in mammary epithelium.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Essential functions of p21-activated kinase 1 in morphogenesis and differentiation of mammary glands.J Cell Biol. 2003 May 12;161(3):583-92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200212066. Epub 2003 May 5. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12732616 Free PMC article.
-
p21-activated kinase-1 signaling mediates cyclin D1 expression in mammary epithelial and cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jan 9;279(2):1422-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M309937200. Epub 2003 Oct 6. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14530270
-
Estrogen regulation of Pak1 and FKHR pathways in breast cancer cells.FEBS Lett. 2003 Jan 30;535(1-3):6-10. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03846-2. FEBS Lett. 2003. PMID: 12560069
-
Sliding p21-activated kinase 1 to nucleus impacts tamoxifen sensitivity.Biomed Pharmacother. 2007 Aug;61(7):408-11. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2007.05.006. Epub 2007 Jun 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2007. PMID: 17604944 Review.
-
The hyperplastic phenotype in PR-A and PR-B transgenic mice: lessons on the role of estrogen and progesterone receptors in the mouse mammary gland and breast cancer.Vitam Horm. 2013;93:185-201. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-416673-8.00012-5. Vitam Horm. 2013. PMID: 23810007 Review.
Cited by
-
PKA-induced resistance to tamoxifen is associated with an altered orientation of ERalpha towards co-activator SRC-1.EMBO J. 2007 Aug 8;26(15):3534-44. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601791. Epub 2007 Jul 12. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17627277 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Chlamydia trachomatis entry into nonphagocytic cells.Infect Immun. 2007 Aug;75(8):3925-34. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00106-07. Epub 2007 May 14. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17502389 Free PMC article.
-
PAK1 as a therapeutic target.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010 Jul;14(7):703-25. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2010.492779. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010. PMID: 20507214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tyrosyl phosphorylated serine-threonine kinase PAK1 is a novel regulator of prolactin-dependent breast cancer cell motility and invasion.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;846:97-137. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-12114-7_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 25472536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic advances in BIG3-PHB2 inhibition targeting the crosstalk between estrogen and growth factors in breast cancer.Cancer Sci. 2015 May;106(5):550-8. doi: 10.1111/cas.12654. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 25736224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam L., Vadlamudi,R., Kondapaka,S.B., Chernoff,J., Mendelsohn,J. and Kumar,R. (1998) Heregulin regulates cytoskeletal reorganization and cell migration through the p21-activated kinase-1 via phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. J. Biol. Chem., 273, 28238–28246. - PubMed
-
- Adam L., Vadlamudi,R., Mandal,M., Chernoff,J. and Kumar,R. (2000) Regulation of microfilament reorganization and invasiveness of breast cancer cells by p21-activated kinase-1 K299R. J. Biol. Chem., 275, 12041–12050. - PubMed
-
- Ali S., Lutz,Y., Bellocq,J.P., Chenard-Neu,M.P., Rouyer,N. and Metzger,D. (1993) Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies recognising defined regions of the human oestrogen receptor. Hybridoma, 12, 391–405. - PubMed
-
- Alimandi M., Romano,A., Curia,M.C., Muraro,R., Fedi,P., Aaronson,S.A., Di Fiore,P.P. and Kraus,M.H. (1995) Cooperative signaling of ErbB3 and ErbB2 in neoplastic transformation and human mammary carcinomas. Oncogene, 10, 1813–1821. - PubMed
-
- Bagheri-Yarmand R., Mandal,M., Taludker,A.H., Wang,R.A., Vadlamudi,R.K., Kung,H.J. and Kumar,R. (2001) Etk/bmx tyrosine kinase activates pak1 and regulates tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 29403–29409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

