Analysis of apoptotic and antiapoptotic signalling pathways induced by Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 12354930
- PMCID: PMC1187257
- DOI: 10.1136/mp.55.5.286
Analysis of apoptotic and antiapoptotic signalling pathways induced by Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
Background and aims: Although it is reported that Helicobacter pylori induces apoptosis on gastric epithelial cells, the mechanism remains unknown. Antiapoptotic effects generated by H pylori have not yet been evaluated.
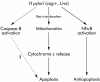
Methods: (1) H pylori strains (type 1 wild, TN2-deltacagE, TN2-deltavacA) were cocultured with MKN45, TMK1, and HeLa cells, and cell viability and apoptosis were assessed by trypan blue exclusion and DNA laddering, respectively. (2) Activation of caspases-3, 7, and 8, cytochrome c release from the mitochondria, and Fas, Fas associated death domain protein (FADD), Bax, Bak, and Bcl-X expression were evaluated by immunoblot analysis. (3) To investigate whether nuclear factor kappa B (NFkappaB) activation induced by cag pathogenicity island (PAI) positive H pylori affects antiapoptosis, MKN45 cells stably expressing super-repressor IkappaBalpha were cocultured with H pylori, and cell viability and caspase activation were evaluated. NFkappaB regulated gene expression was also evaluated by ribonuclease protection assay.
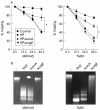
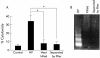
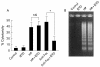
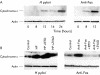
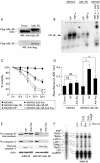
Results: (1) Wild-type and deltavacA mutant H pylori induced apoptosis more potently than the deltacagE mutant. Inhibition of cell contact between H pylori and cancer cells and heat killing H pylori diminished cell death. (2) Caspases-3, 7, and 8 were activated time dependently by H pylori as well as by the agonist anti-Fas. Cytochrome c release from mitochondria was observed and was not inhibited by caspase-8 inhibitor. Although protein expression of Fas, FADD, Bax, Bak, and Bcl-X in the whole cell lysates was not changed by H pylori, Bax was decreased from mitochondria free cytosol suggesting that Bax was translocated into mitochondria. (3) Cell death and the activities of caspases-3 and 8 were promoted in MKN45 cells stably expressing super-repressor IkappaBalpha that inhibits NFkappaB activation. Antiapoptotic proteins c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 were upregulated by the wild-type strains.
Conclusion: cag PAI positive H pylori is capable of inducing apoptotic effects mainly through the mitochondrial pathway. Antiapoptotic effects mediated by NFkappaB activation were also observed.
Figures
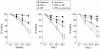

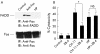
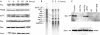
Comment in
-
Helicobacter pylori.Mol Pathol. 2002 Oct;55(5):284-5. doi: 10.1136/mp.55.5.284. Mol Pathol. 2002. PMID: 12354928 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Analysis of apoptotic and antiapoptotic signalling pathways induced by Helicobacter pylori.Gut. 2002 Jun;50(6):771-8. doi: 10.1136/gut.50.6.771. Gut. 2002. PMID: 12010877 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of the caspase family in Helicobacter pylori induced gastric epithelial apoptosis.Helicobacter. 2002 Dec;7(6):367-77. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-5378.2002.00112.x. Helicobacter. 2002. PMID: 12485124
-
Helicobacter pylori induced transactivation of SRE and AP-1 through the ERK signalling pathway in gastric cancer cells.Gut. 2001 Jul;49(1):18-22. doi: 10.1136/gut.49.1.18. Gut. 2001. PMID: 11413105 Free PMC article.
-
Bax translocation and mitochondrial fragmentation induced by Helicobacter pylori.Gut. 2004 Jun;53(6):805-13. doi: 10.1136/gut.2003.024372. Gut. 2004. PMID: 15138206 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori induces antiapoptosis through buclear factor-kappaB activation.J Infect Dis. 2003 Dec 1;188(11):1741-51. doi: 10.1086/379629. Epub 2003 Nov 25. J Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 14639546
Cited by
-
Gastric transcription profile of Helicobacter pylori infection in the rhesus macaque.Infect Immun. 2004 Sep;72(9):5216-26. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.9.5216-5226.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15322016 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori regulates cellular migration and apoptosis by activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling.J Infect Dis. 2009 Mar 1;199(5):641-51. doi: 10.1086/596660. J Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19199544 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling of tumor-initiating stem cells from mouse Krebs-2 carcinoma using a novel marker of poorly differentiated cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 7;8(6):9425-9441. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14116. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28031533 Free PMC article.
-
Role of protease-activated receptor-2 on cell death and DNA fragmentation in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells.J Transl Med. 2010 Sep 16;8:85. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-8-85. J Transl Med. 2010. PMID: 20846373 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori infection induces oxidative stress and programmed cell death in human gastric epithelial cells.Infect Immun. 2007 Aug;75(8):4030-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00172-07. Epub 2007 Jun 11. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17562777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Warren JR, Marshall BJ. Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet 1983;1:1273–5. - PubMed
-
- NIH consensus conference. Helicobacter pylori in peptic ulcer disease. NIH consensus development panel on Helicobacter pylori in peptic ulcer disease. JAMA 1994;272:65–9. - PubMed
-
- Graham DY, Lew GM, Klein PD, et al. Effect of treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection on the long-term recurrence of gastric or duodenal ulcer: a randomized, controlled study. Ann Intern Med 1992; 116:705–8. - PubMed
-
- Parsonnet J, Friedman GD, Vandersteen DP, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. N Engl J Med 1991;325:1127–31. - PubMed
-
- Nomura A, Stemmermann GN, Chyou PH, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric carcinoma among Japanese American in Hawaii. N Engl J Med 1991;325:1132–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
