A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of MAG-CPT, a water-soluble polymer conjugate of camptothecin
- PMID: 12237769
- PMCID: PMC2364251
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600516
A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of MAG-CPT, a water-soluble polymer conjugate of camptothecin
Abstract
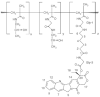
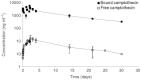
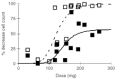
Polymeric drug conjugates are a new and experimental class of drug delivery systems with pharmacokinetic promises. The antineoplastic drug camptothecin was linked to a water-soluble polymeric backbone (MAG-CPT) and administrated as a 30 min infusion over 3 consecutive days every 4 weeks to patients with malignant solid tumours. The objectives of our study were to determine the maximal tolerated dose, the dose-limiting toxicities, and the plasma and urine pharmacokinetics of MAG-CPT, and to document anti-tumour activity. The starting dose was 17 mg m(-2) day(-1). Sixteen patients received 39 courses at seven dose levels. Maximal tolerated dose was at 68 mg m(-2) day(-1) and dose-limiting toxicities consisted of cumulative bladder toxicity. MAG-CPT and free camptothecin were accumulated during days 1-3 and considerable amounts of MAG-CPT could still be retrieved in plasma and urine after 4-5 weeks. The half-lives of bound and free camptothecin were equal indicating that the kinetics of free camptothecin were release rate dependent. In summary, the pharmacokinetics of camptothecin were dramatically changed, showing controlled prolonged exposure of camptothecin. Haematological toxicity was relatively mild, but serious bladder toxicity was encountered which is typical for camptothecin and was found dose limiting.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phase I and pharmacokinetic (PK) study of MAG-CPT (PNU 166148): a polymeric derivative of camptothecin (CPT).Br J Cancer. 2004 Jul 5;91(1):50-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601922. Br J Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15187995 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I study with MAG-camptothecin intravenously administered weekly for 3 weeks in a 4-week cycle in adult patients with solid tumours.Br J Cancer. 2004 Jun 14;90(12):2261-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601811. Br J Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15150611 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of pegylated camptothecin as a 1-hour infusion every 3 weeks in patients with advanced solid malignancies.J Clin Oncol. 2003 Jan 1;21(1):148-57. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.03.143. J Clin Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12506184 Clinical Trial.
-
XMT-1001, a novel polymeric camptothecin pro-drug in clinical development for patients with advanced cancer.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009 Nov 12;61(13):1193-202. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2009.01.007. Epub 2009 Aug 12. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009. PMID: 19682517 Review.
-
CPT-11. The European experience.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996 Dec 13;803:282-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1996.tb26398.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996. PMID: 8993522 Review.
Cited by
-
Interactions of nanomaterials and biological systems: Implications to personalized nanomedicine.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012 Oct;64(13):1363-84. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.08.005. Epub 2012 Aug 17. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012. PMID: 22917779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DE-310, a macromolecular prodrug of the topoisomerase-I-inhibitor exatecan (DX-8951), in patients with operable solid tumors.Invest New Drugs. 2005 Aug;23(4):339-47. doi: 10.1007/s10637-005-1442-2. Invest New Drugs. 2005. PMID: 16012793 Clinical Trial.
-
Cancer therapies utilizing the camptothecins: a review of the in vivo literature.Mol Pharm. 2010 Apr 5;7(2):307-49. doi: 10.1021/mp900243b. Mol Pharm. 2010. PMID: 20108971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase I and pharmacokinetic (PK) study of MAG-CPT (PNU 166148): a polymeric derivative of camptothecin (CPT).Br J Cancer. 2004 Jul 5;91(1):50-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601922. Br J Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15187995 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Recent Advances in Using Natural Antibacterial Additives in Bioactive Wound Dressings.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 14;15(2):644. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020644. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839966 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- CaiolfaVRZamaiMFiorinoAFrigerioEPellizzoniCd'ArgyRGhiglieriACastelliMGFaraoMPesentiEGigliMAngelucciFSuaratoA2000Polymer-bound camptothecin: initial biodistribution and antitumour activity studies J Control Release 65105119 - PubMed
-
- ChabotGG1997Clinical pharmacokinetics of irinotecan Clin Pharmacokinet 33245259 - PubMed
-
- ConoverCDGreenwaldRBPendriAGilbertCWShumKL1998Camptothecin delivery systems: enhanced efficacy and tumor accumulation of camptothecin following its conjugation to polyethyulene glycol via a glycine linker Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 42407414 - PubMed
-
- ConoverCDGreenwaldRBPendriASumK1999Camptothecin delivery systems: the utility of amino acid spacers for the conjugation of camptothecin with polyethylene glycol to create prodrugs Anti-cancer Drug Design 14499506 - PubMed
-
- HoughtonPJCheshirePJHallmanIIJDLutzLFriedmanHSDanksMKHoughtonJA1995Efficacy of topoisomerase I inhibitors, topotecan and irinotecan, administered at low dose levels in protracted schedules to mice bearing xenografts of human tumours Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 36393403 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

