Human monoclonal antibodies specific for conformation-sensitive epitopes of V3 neutralize human immunodeficiency virus type 1 primary isolates from various clades
- PMID: 12186887
- PMCID: PMC136433
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.18.9035-9045.2002
Human monoclonal antibodies specific for conformation-sensitive epitopes of V3 neutralize human immunodeficiency virus type 1 primary isolates from various clades
Abstract
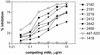
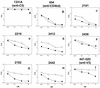
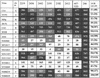
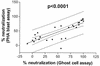
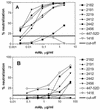
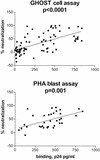
The epitopes of the V3 domain of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 glycoprotein have complex structures consisting of linear and conformational antigenic determinants. Anti-V3 antibodies (Abs) recognize both types of elements, but Abs which preferentially react to the conformational aspect of the epitopes may have more potent neutralizing activity against HIV-1, as recently suggested. To test this hypothesis, human anti-V3 monoclonal Abs (MAbs) were selected using a V3 fusion protein (V3-FP) which retains the conformation of the third variable region. The V3-FP consists of the V3(JR-CSF) sequence inserted into a truncated form of murine leukemia virus gp70. Six human MAbs which recognize epitopes at the crown of the V3 loop were selected with the V3-FP. They were found to react more strongly with molecules displaying conformationally intact V3 than with linear V3 peptides. In a virus capture assay, these MAbs showed cross-clade binding to native, intact virions of clades A, B, C, D, and F. No binding was found to isolates from subtype E. The neutralizing activity of MAbs against primary isolates was determined in three assays: the GHOST cell assay, a phytohemagglutinin-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cell assay, and a luciferase assay. While these new MAbs displayed various degrees of activity, the pattern of cross-clade neutralization of clades A, B, and F was most pronounced. The neutralization of clades C and D viruses was weak and sporadic, and neutralization of clade E by these MAbs was not detected. Analysis by linear regression showed a highly significant correlation (P < 0.0001) between the strength of binding of these anti-V3 MAbs to intact virions and the percent neutralization. These studies demonstrate that human MAbs to conformation-sensitive epitopes of V3 display cross-clade reactivity in both binding to native, intact virions and neutralization of primary isolates.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The v3 loop is accessible on the surface of most human immunodeficiency virus type 1 primary isolates and serves as a neutralization epitope.J Virol. 2004 Mar;78(5):2394-404. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.5.2394-2404.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14963135 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved and exposed epitopes on intact, native, primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions of group M.J Virol. 2000 Aug;74(15):7096-107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.15.7096-7107.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10888650 Free PMC article.
-
Human monoclonal antibodies to the V3 loop of HIV-1 with intra- and interclade cross-reactivity.J Immunol. 1997 Nov 15;159(10):5114-22. J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9366441
-
HIV-1 neutralization directed to epitopes other than linear V3 determinants.AIDS. 1991;5 Suppl 2:S135-43. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199101001-00019. AIDS. 1991. PMID: 1726953 Review. No abstract available.
-
The implications of antigenic diversity for vaccine development.Immunol Lett. 1999 Mar;66(1-3):159-64. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2478(98)00176-x. Immunol Lett. 1999. PMID: 10203049 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation of monoclonal antibodies with predetermined conformational epitope specificity.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38943. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038943. Epub 2012 Jun 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22737224 Free PMC article.
-
Complex-type N-glycan recognition by potent broadly neutralizing HIV antibodies.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Nov 20;109(47):E3268-77. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217207109. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23115339 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-clinical evaluation of a 213Bi-labeled 2556 antibody to HIV-1 gp41 glycoprotein in HIV-1 mouse models as a reagent for HIV eradication.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e31866. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031866. Epub 2012 Mar 9. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22427811 Free PMC article.
-
The V1/V2 domain of gp120 is a global regulator of the sensitivity of primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates to neutralization by antibodies commonly induced upon infection.J Virol. 2004 May;78(10):5205-15. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.10.5205-5215.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15113902 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro restoration of Th17 response during HIV infection with an antiretroviral drug and Th17 differentiation cytokines.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2012 Aug;28(8):823-34. doi: 10.1089/AID.2011.0184. Epub 2011 Dec 1. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2012. PMID: 22011036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arendrup, M., A. Sonnerborg, B. Svennerholm, L. Akerblom, C. Nielsen, H. Clausen, S. Olofsson, J. O. Nielsen, and J.-E. S. Hansen. 1993. Neutralizing antibody response during human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection: type and group specificity and viral escape. J. Gen. Virol. 74:855-863. - PubMed
-
- Beddows, S. A., S. Louisirirotchanakul, R. Cheingsong-Popov, P. J. Easterbrook, P. Simmonds, and J. N. Weber. 1998. Neutralization of primary and T-cell line adapted isolates of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1: role of V3 specific antibodies. J. Gen. Virol. 79:77-82. - PubMed
-
- Bolmstedt, A., S. Olofsson, E. Sjogren-Jansson, S. Jeansson, I. Sjoblom, L. Akerblom, J.-E. S. Hansen, and S.-L. Hu. 1992. Carbohydrate determinant NeuAc-GalB(1-4) of N-linked glycans modulates the antigenic activity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 glycoprotein gp120. J. Gen. Virol. 73:3099-3105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

