Release of hepatocyte growth factor from mechanically stretched skeletal muscle satellite cells and role of pH and nitric oxide
- PMID: 12181355
- PMCID: PMC117951
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-01-0062
Release of hepatocyte growth factor from mechanically stretched skeletal muscle satellite cells and role of pH and nitric oxide
Abstract
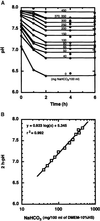
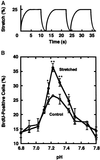
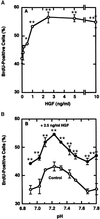
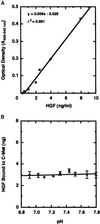
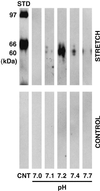
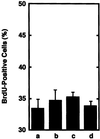
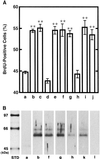
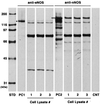
Application of mechanical stretch to cultured adult rat muscle satellite cells results in release of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and accelerated entry into the cell cycle. Stretch activation of cultured rat muscle satellite cells was observed only when medium pH was between 7.1 and 7.5, even though activation of satellite cells was accelerated by exogenous HGF over a pH range from 6.9 to 7.8. Furthermore, HGF was only released in stretched cultures when the pH of the medium was between 7.1 and 7.4. Conditioned medium from stretched satellite cell cultures stimulated activation of unstretched satellite cells, and the addition of anti-HGF neutralizing antibodies to stretch-conditioned medium inhibited the stretch activation response. Conditioned medium from satellite cells that were stretched in the presence of nitric-oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride did not accelerate activation of unstretched control satellite cells, and HGF was not released into the medium. Conditioned medium from unstretched cells that were treated with a nitric oxide donor, sodium nitroprusside dihydrate, was able to accelerate the activation of satellite cells in vitro, and HGF was found in the conditioned medium. Immunoblot analysis indicated that both neuronal and endothelial NOS isoforms were present in satellite cell cultures. Furthermore, assays of NOS activity in stretched satellite cell cultures demonstrated that NOS is stimulated when satellite cells are stretched in vitro. These experiments indicate that stretch triggers an intracellular cascade of events, including nitric oxide synthesis, which results in HGF release and satellite cell activation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A role for calcium-calmodulin in regulating nitric oxide production during skeletal muscle satellite cell activation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009 Apr;296(4):C922-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00471.2008. Epub 2009 Jan 21. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19158401
-
Satellite cell activation in stretched skeletal muscle and the role of nitric oxide and hepatocyte growth factor.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006 Jun;290(6):C1487-94. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00513.2005. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16684931
-
Matrix metalloproteinases are involved in mechanical stretch-induced activation of skeletal muscle satellite cells.Muscle Nerve. 2006 Sep;34(3):313-9. doi: 10.1002/mus.20601. Muscle Nerve. 2006. PMID: 16810685
-
Mechano-biology of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and regeneration: possible mechanism of stretch-induced activation of resident myogenic stem cells.Anim Sci J. 2010 Feb;81(1):11-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1740-0929.2009.00712.x. Anim Sci J. 2010. PMID: 20163667 Review.
-
Skeletal muscle satellite cell cultures.Methods Cell Biol. 1997;52:155-76. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60378-7. Methods Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9379949 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Biomimetic scaffolds for regeneration of volumetric muscle loss in skeletal muscle injuries.Acta Biomater. 2015 Oct;25:2-15. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2015.07.038. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Acta Biomater. 2015. PMID: 26219862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanotransduction in skeletal muscle.Front Biosci. 2007 Jan 1;12:174-91. doi: 10.2741/2057. Front Biosci. 2007. PMID: 17127292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanical strain activates a program of genes functionally involved in paracrine signaling of angiogenesis.Physiol Genomics. 2008 Dec 12;36(1):1-14. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.90291.2008. Epub 2008 Oct 14. Physiol Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18854370 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular circuitry of stem cell fate in skeletal muscle regeneration, ageing and disease.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 May;17(5):267-79. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.7. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26956195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aging of the immune system and impaired muscle regeneration: A failure of immunomodulation of adult myogenesis.Exp Gerontol. 2021 Mar;145:111200. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2020.111200. Epub 2020 Dec 24. Exp Gerontol. 2021. PMID: 33359378 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allen RE, Sheehan SM, Tayler RG, Kendall TL, Rice GM. Hepatocyte growth factor activates quiescent skeletal muscle satellite cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1995;165:307–312. - PubMed
-
- Allen RE, Temm-Grove CJ, Sheehan SM, Rice G. Skeletal muscle satellite cell cultures. Methods Cell Biol. 1998;52:155–176. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, J.E., and Pilipowicz, O. (2002). Activation of muscle satellite cells in single fiber cultures. Nitric Oxide (in press). - PubMed
-
- Barouch LA, et al. Nitric oxide regulates the heart by spatial confinement of nitric oxide synthase isoforms. Nature. 2002;416:337–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

