Differential sorting and fate of endocytosed GPI-anchored proteins
- PMID: 12145200
- PMCID: PMC126144
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf398
Differential sorting and fate of endocytosed GPI-anchored proteins
Abstract
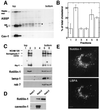
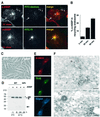
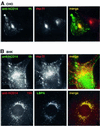
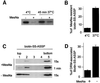
In this paper, we studied the fate of endocytosed glycosylphosphatidyl inositol anchored proteins (GPI- APs) in mammalian cells, using aerolysin, a bacterial toxin that binds to the GPI anchor, as a probe. We find that GPI-APs are transported down the endocytic pathway to reducing late endosomes in BHK cells, using biochemical, morphological and functional approaches. We also find that this transport correlates with the association to raft-like membranes and thus that lipid rafts are present in late endosomes (in addition to the Golgi and the plasma membrane). In marked contrast, endocytosed GPI-APs reach the recycling endosome in CHO cells and this transport correlates with a decreased raft association. GPI-APs are, however, diverted from the recycling endosome and routed to late endosomes in CHO cells, when their raft association is increased by clustering seven or less GPI-APs with an aerolysin mutant. We conclude that the different endocytic routes followed by GPI-APs in different cell types depend on the residence time of GPI-APs in lipid rafts, and hence that raft partitioning regulates GPI-APs sorting in the endocytic pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of the roles of ordered lipid microdomains in post-endocytic trafficking of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins in mammalian fibroblasts.Traffic. 2011 Aug;12(8):1012-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01206.x. Epub 2011 Jun 22. Traffic. 2011. PMID: 21696526
-
GPI anchoring leads to sphingolipid-dependent retention of endocytosed proteins in the recycling endosomal compartment.EMBO J. 2001 Apr 2;20(7):1583-92. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.7.1583. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11285223 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingomyelin chain length influences the distribution of GPI-anchored proteins in rafts in supported lipid bilayers.Mol Membr Biol. 2007 May-Jun;24(3):233-42. doi: 10.1080/09687860601127770. Mol Membr Biol. 2007. PMID: 17520480
-
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins: Membrane organization and transport.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Apr;1858(4):632-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.12.018. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26706096 Review.
-
The GPI-anchor and protein sorting.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001 Dec;58(14):1969-87. doi: 10.1007/PL00000831. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001. PMID: 11814051 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Subcellular targeting strategies for drug design and delivery.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010 Jan;9(1):29-42. doi: 10.1038/nrd2897. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010. PMID: 20043027 Review.
-
Initial steps of Shigella infection depend on the cholesterol/sphingolipid raft-mediated CD44-IpaB interaction.EMBO J. 2002 Sep 2;21(17):4449-57. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf457. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 12198147 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the V-ATPase along the endocytic pathway occurs through reversible subunit association and membrane localization.PLoS One. 2008 Jul 23;3(7):e2758. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002758. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18648502 Free PMC article.
-
A Raft-derived, Pak1-regulated entry participates in alpha2beta1 integrin-dependent sorting to caveosomes.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Jul;19(7):2857-69. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-10-1094. Epub 2008 Apr 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18448666 Free PMC article.
-
Chip-Based Sensing of the Intercellular Transfer of Cell Surface Proteins: Regulation by the Metabolic State.Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 13;9(10):1452. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101452. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34680568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrami L., Fivaz,M. and van der Goot,F.G. (2000) Adventures of a pore-forming toxin at the target cell surface. Trends Microbiol., 8, 168–172. - PubMed
-
- Abrami L., Fivaz,M., Kobayashi,T., Kinoshita,T., Parton,R.G. and van der Goot,F.G. (2001) Cross-talk between caveolae and glycosylphosphatidylinositol-rich domains. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 30729–30736. - PubMed
-
- Abrami L., Velluz,M.C., Hong,Y., Ohishi,K., Mehlert,A., Ferguson,M., Kinoshita,T. and Gisou van der Goot,F. (2002) The glycan core of GPI-anchored proteins modulates aerolysin binding but is not sufficient: the polypeptide moiety is required for the toxin-receptor interaction. FEBS Lett., 512, 249–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

