The Arabidopsis mutant cev1 links cell wall signaling to jasmonate and ethylene responses
- PMID: 12119374
- PMCID: PMC150706
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.002022
The Arabidopsis mutant cev1 links cell wall signaling to jasmonate and ethylene responses
Erratum in
- Plant Cell 2002 Aug;14(8):1981
Abstract
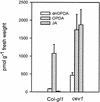
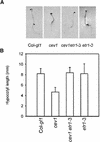
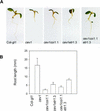
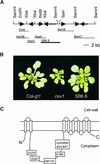
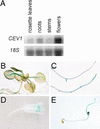
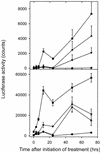
Biotic and abiotic stresses stimulate the synthesis of jasmonates and ethylene, which, in turn, induce the expression of genes involved in stress response and enhance defense responses. The cev1 mutant has constitutive expression of stress response genes and has enhanced resistance to fungal pathogens. Here, we show that cev1 plants have increased production of jasmonate and ethylene and that its phenotype is suppressed by mutations that interrupt jasmonate and ethylene signaling. Genetic mapping, complementation analysis, and sequence analysis revealed that CEV1 is the cellulose synthase CeSA3. CEV1 was expressed predominantly in root tissues, and cev1 roots contained less cellulose than wild-type roots. Significantly, the cev1 mutant phenotype could be reproduced by treating wild-type plants with cellulose biosynthesis inhibitors, and the cellulose synthase mutant rsw1 also had constitutive expression of VSP. We propose that the cell wall can signal stress responses in plants.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Arabidopsis mutant cev1 has constitutively active jasmonate and ethylene signal pathways and enhanced resistance to pathogens.Plant Cell. 2001 May;13(5):1025-33. doi: 10.1105/tpc.13.5.1025. Plant Cell. 2001. PMID: 11340179 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced cellulose synthesis invokes lignification and defense responses in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant J. 2003 May;34(3):351-62. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2003.01729.x. Plant J. 2003. PMID: 12713541
-
Ethylene and jasmonic acid signaling affect the NPR1-independent expression of defense genes without impacting resistance to Pseudomonas syringae and Peronospora parasitica in the Arabidopsis ssi1 mutant.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2003 Jul;16(7):588-99. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2003.16.7.588. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2003. PMID: 12848424
-
Jasmonate-related mutants of Arabidopsis as tools for studying stress signaling.Planta. 2002 Feb;214(4):497-504. doi: 10.1007/s00425-001-0688-y. Planta. 2002. PMID: 11925032 Review.
-
Ethylene biosynthesis and signaling networks.Plant Cell. 2002;14 Suppl(Suppl):S131-51. doi: 10.1105/tpc.001768. Plant Cell. 2002. PMID: 12045274 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Jasmonates: biosynthesis, perception, signal transduction and action in plant stress response, growth and development. An update to the 2007 review in Annals of Botany.Ann Bot. 2013 Jun;111(6):1021-58. doi: 10.1093/aob/mct067. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Ann Bot. 2013. PMID: 23558912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cosuppression of eukaryotic release factor 1-1 in Arabidopsis affects cell elongation and radial cell division.Plant Physiol. 2005 Sep;139(1):115-26. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.062695. Epub 2005 Aug 19. Plant Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16113224 Free PMC article.
-
Cellulose binding domains of a Phytophthora cell wall protein are novel pathogen-associated molecular patterns.Plant Cell. 2006 Jul;18(7):1766-77. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.038687. Epub 2006 Jun 9. Plant Cell. 2006. PMID: 16766692 Free PMC article.
-
Oxylipins produced by the 9-lipoxygenase pathway in Arabidopsis regulate lateral root development and defense responses through a specific signaling cascade.Plant Cell. 2007 Mar;19(3):831-46. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.046052. Epub 2007 Mar 16. Plant Cell. 2007. PMID: 17369372 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of cinnamoyl-coenzyme A reductase in poplar: multiple-level phenotyping reveals effects on cell wall polymer metabolism and structure.Plant Cell. 2007 Nov;19(11):3669-91. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.054148. Epub 2007 Nov 16. Plant Cell. 2007. PMID: 18024569 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arioli, T., et al. (1998). Molecular analysis of cellulose biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Science 279, 717–720. - PubMed
-
- Bell, C.J., and Ecker, J.R. (1994). Assignment of 30 microsatellite loci to the linkage map of Arabidopsis. Genomics 19, 137–144. - PubMed
-
- Berger, S., Bell, E., Sadka, A., and Mullet, J.E. (1995). Arabidopsis thaliana AtVSP is homologous to soybean VSPA and VSPB, genes encoding vegetative storage protein acid phosphatases, and is regulated similarly by methyl jasmonate, wounding, sugars, light, and phosphate. Plant Mol. Biol. 27, 933–942. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

