Release of hypocretin (orexin) during waking and sleep states
- PMID: 12097478
- PMCID: PMC6758234
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-13-05282.2002
Release of hypocretin (orexin) during waking and sleep states
Abstract
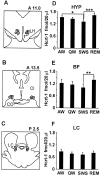
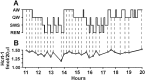
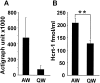
Hypocretin (Hcrt or orexin) somas are located in the hypothalamus and project widely to forebrain and brainstem regions, densely innervating monoaminergic and cholinergic cells. Loss of Hcrt function results in the sleep disorder narcolepsy. However, the normal pattern of Hcrt release across the sleep-wake cycle is unknown. We monitored Hcrt-1 release in the basal forebrain, perifornical hypothalamus, and locus ceruleus (LC) across the sleep-wake cycle using microdialysis in freely moving cats and a sensitive solid phase radioimmunoassay. We found that the peptide concentration in dialysates from the hypothalamus was significantly higher during active waking (AW) than during slow-wave sleep (SWS). Moreover, Hcrt-1 release was significantly higher during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep than during SWS in the hypothalamus and basal forebrain. We did not detect a significant difference in release across sleep-waking states in the LC, perhaps because recovered levels of the peptide were lower at this site. Because there was a trend toward higher levels of Hcrt-1 release during AW compared with quiet waking (QW) in our 10 min dialysis samples, we compared Hcrt-1 levels in CSF in 2 hr AW and QW periods. Hcrt-1 release into CSF was 67% higher during AW than during QW. Elevated levels of Hcrt during REM sleep and AW are consistent with a role for Hcrt in the central programming of motor activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The diurnal rhythm of hypocretin in young and old F344 rats.Sleep. 2004 Aug 1;27(5):851-6. doi: 10.1093/sleep/27.5.851. Sleep. 2004. PMID: 15453542 Free PMC article.
-
Hypocretin-1 modulates rapid eye movement sleep through activation of locus coeruleus neurons.J Neurosci. 2000 Oct 15;20(20):7760-5. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-20-07760.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11027239 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of hypocretin (orexin) neuronal loss on sleep and extracellular adenosine levels in the rat basal forebrain.Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Sep;28(6):1191-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06424.x. Epub 2008 Sep 9. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18783368 Free PMC article.
-
Hypocretin (orexin): role in normal behavior and neuropathology.Annu Rev Psychol. 2004;55:125-48. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.55.090902.141545. Annu Rev Psychol. 2004. PMID: 14744212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of hypocretins (orexins) in sleep regulation and narcolepsy.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2002;25:283-313. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.25.112701.142826. Epub 2002 Mar 20. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12052911 Review.
Cited by
-
A towering genome: Experimentally validated adaptations to high blood pressure and extreme stature in the giraffe.Sci Adv. 2021 Mar 17;7(12):eabe9459. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abe9459. Print 2021 Mar. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 33731352 Free PMC article.
-
The anatomical, cellular and synaptic basis of motor atonia during rapid eye movement sleep.J Physiol. 2016 Oct 1;594(19):5391-414. doi: 10.1113/JP271324. Epub 2016 Jul 3. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27060683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MCH-containing neurons in the hypothalamus of the cat: searching for a role in the control of sleep and wakefulness.Brain Res. 2006 Nov 13;1119(1):101-14. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.08.100. Epub 2006 Oct 9. Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 17027934 Free PMC article.
-
The injection of hypocretin-1 into the nucleus pontis oralis induces either active sleep or wakefulness depending on the behavioral state when it is administered.Sleep. 2010 Sep;33(9):1236-43. doi: 10.1093/sleep/33.9.1236. Sleep. 2010. PMID: 20857871 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin-A inputs onto visuomotor cell groups in the monkey brainstem.Neuroscience. 2009 Dec 1;164(2):629-40. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.08.039. Epub 2009 Aug 22. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19703526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrahamson EE, Moore RY. Topographical organization of efferent projections arising from hypocretin containing neuron populations located in the lateral hypothalamus. Soc Neurosci Abstr. 1999;25:1886.
-
- Bachmann GA, Grill J. Exercise in the postmenopausal woman. Geriatrics 42 1987. 75 77, 81–85. - PubMed
-
- Brown RE, Sergeeva O, Eriksson KS, Haas HL. Orexin A excites serotonergic neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus of the rat. Neuropharmacology. 2001;40:457–459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
