Characterization of human metapneumoviruses isolated from patients in North America
- PMID: 12023774
- PMCID: PMC7109943
- DOI: 10.1086/340518
Characterization of human metapneumoviruses isolated from patients in North America
Abstract
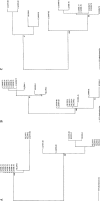
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) was recently identified in The Netherlands and was linked to acute respiratory tract illness. In this study, 11 isolates from 10 patients with respiratory disease from Quebec, Canada, were tested by a reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction based on the fusion protein gene. Identified sequences were consistent with HMPV. The patients were 2 months to 87 years of age (median age, 58 years) and presented with acute respiratory tract illness during the winter season. Sequence studies of the nucleocapsid, fusion, and polymerase genes identified 2 main lineages of HMPV and cocirculation of both lineages during the same year. These findings support a previous finding that HMPV is a human respiratory pathogen that merits further study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic diversity and molecular evolution of the major human metapneumovirus surface glycoproteins over a decade.J Clin Virol. 2013 Nov;58(3):541-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2013.08.029. Epub 2013 Sep 4. J Clin Virol. 2013. PMID: 24041471
-
Human metapneumovirus infection in young children hospitalized with acute respiratory tract disease: virologic and clinical features.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2008 May;27(5):406-12. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e318162a164. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2008. PMID: 18382388
-
Human metapneumovirus infection in the Canadian population.J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Oct;41(10):4642-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.10.4642-4646.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14532196 Free PMC article.
-
[Human metapneumovirus].Uirusu. 2006 Dec;56(2):173-81. doi: 10.2222/jsv.56.173. Uirusu. 2006. PMID: 17446666 Review. Japanese.
-
Human metapneumovirus: a newly emerging respiratory pathogen.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2003 Jun;16(3):255-8. doi: 10.1097/00001432-200306000-00012. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 12821817 Review.
Cited by
-
Interferon Epsilon-Mediated Antiviral Activity Against Human Metapneumovirus and Respiratory Syncytial Virus.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Oct 21;12(10):1198. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12101198. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39460364 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of human metapneumovirus in Taiwan from 2013 to 2023.Arch Virol. 2024 Oct 23;169(11):229. doi: 10.1007/s00705-024-06147-8. Arch Virol. 2024. PMID: 39441325 Free PMC article.
-
Probenecid Inhibits Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) Replication In Vitro and in BALB/c Mice.Viruses. 2024 Jul 6;16(7):1087. doi: 10.3390/v16071087. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39066249 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacious human metapneumovirus vaccine based on AI-guided engineering of a closed prefusion trimer.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 25;15(1):6270. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50659-5. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39054318 Free PMC article.
-
Zoonotic Origins of Human Metapneumovirus: A Journey from Birds to Humans.Viruses. 2022 Mar 25;14(4):677. doi: 10.3390/v14040677. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35458407 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Collins MS, Gough RE. Characterization of a virus associated with turkey rhinotracheitis. J Gen Virol. 1988;69:909–16. - PubMed
-
- Aebi U, Pollard TD. A glow discharge unit to render electron microscope grids and other surfaces hydrophilic. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1987;7:29–33. - PubMed
-
- Luftig R. An accurate measurement of the catalase crystal and its use as an internal marker for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967;20:91–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

