Functional interaction between the pp71 protein of human cytomegalovirus and the PML-interacting protein human Daxx
- PMID: 11992005
- PMCID: PMC137040
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.11.5769-5783.2002
Functional interaction between the pp71 protein of human cytomegalovirus and the PML-interacting protein human Daxx
Abstract
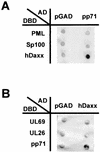
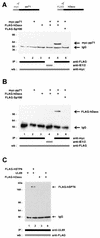
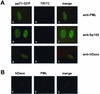
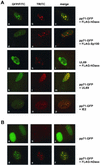
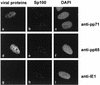
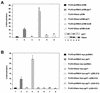
The tegument protein pp71 (UL82) of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) has previously been shown to transactivate the major immediate-early enhancer-promoter of HCMV. Furthermore, this protein is able to enhance the infectivity of viral DNA and to accelerate the infection cycle, suggesting an important regulatory function during viral replication. To gain insight into the underlying mechanisms that are used by pp71 to exert these pleiotropic effects, we sought for cellular factors interacting with pp71 in a yeast two-hybrid screen. Here, we report the isolation of the human Daxx (hDaxx) protein as a specific interaction partner of HCMV pp71. hDaxx, which was initially described as an adapter protein involved in apoptosis regulation, has recently been identified as a nuclear protein that interacts and colocalizes with PML in the nuclear domain ND10. In order to assess whether pp71 can also be detected in ND10 structures, a vector expressing pp71 in fusion with the green fluorescent protein was used for transfection of human fibroblasts. This revealed a colocalization of pp71 with the ND10 proteins PML and Sp100. In addition, cotransfection of a hDaxx expression vector resulted in an enhanced recruitment of pp71 to ND10. Targeting of pp71 to nuclear dots could also be observed in infected human fibroblasts in the absence of de novo viral protein synthesis. Moreover, cotransfection experiments revealed that pp71-mediated transactivation of the major immediate-early enhancer-promoter was synergistically enhanced in the presence of hDaxx. These results suggest an important role of hDaxx for pp71 protein function.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Daxx-mediated accumulation of human cytomegalovirus tegument protein pp71 at ND10 facilitates initiation of viral infection at these nuclear domains.J Virol. 2002 Aug;76(15):7705-12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.15.7705-7712.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12097584 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus protein pp71 displaces the chromatin-associated factor ATRX from nuclear domain 10 at early stages of infection.J Virol. 2008 Dec;82(24):12543-54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01215-08. Epub 2008 Oct 15. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18922870 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulation of the Replication of ICP0-Null Mutant Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and pp71-Deficient Human Cytomegalovirus by Epstein-Barr Virus Tegument Protein BNRF1.J Virol. 2016 Oct 14;90(21):9664-9673. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01224-16. Print 2016 Nov 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27535048 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic cellular defense mechanisms targeting human cytomegalovirus.Virus Res. 2011 May;157(2):128-33. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.10.002. Epub 2010 Oct 8. Virus Res. 2011. PMID: 20934469 Review.
-
Expanding the Known Functional Repertoire of the Human Cytomegalovirus pp71 Protein.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Mar 12;10:95. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00095. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32226778 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell analysis of Daxx and ATRX-dependent transcriptional repression.J Cell Sci. 2012 Nov 15;125(Pt 22):5489-501. doi: 10.1242/jcs.110148. Epub 2012 Sep 12. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22976303 Free PMC article.
-
Virion factors that target Daxx to overcome intrinsic immunity.J Virol. 2013 Oct;87(19):10412-22. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00425-13. Epub 2013 Jul 17. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23864634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional activation of the adenoviral genome is mediated by capsid protein VI.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Feb;8(2):e1002549. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002549. Epub 2012 Feb 23. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22427750 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Determinants and the Regulation of Human Cytomegalovirus Latency and Reactivation.Viruses. 2018 Aug 20;10(8):444. doi: 10.3390/v10080444. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30127257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Enters the Primary CD34+ Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells Where It Establishes Latency by Macropinocytosis.J Virol. 2019 Jul 17;93(15):e00452-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00452-19. Print 2019 Aug 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31118259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn, J. H., E. J. Brignole III, and G. S. Hayward. 1998. Disruption of PML subnuclear domains by the acidic IE1 protein of human cytomegalovirus is mediated through interaction with PML and may modulate a RING finger-dependent cryptic transactivator function of PML. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18:4899-4913. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahn, J. H., and G. S. Hayward. 2000. Disruption of PML-associated nuclear bodies by IE1 correlates with efficient early stages of viral gene expression and DNA replication in human cytomegalovirus infection. Virology 274:39-55. - PubMed
-
- Ahn, J. H., W. J. Jang, and G. S. Hayward. 1999. The human cytomegalovirus IE2 and UL112-113 proteins accumulate in viral DNA replication compartments that initiate from the periphery of promyelocytic leukemia protein-associated nuclear bodies (PODs or ND10). J. Virol. 73:10458-10471. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alford, C. A., and W. J. Britt. 1990. Cytomegalovirus, p. 1981-2010. In B. N. Fields, D. M. Knipe, and P. M. Howley (ed.), Virology. Raven Press, Ltd., New York, N.Y.
-
- Andreoni, M., M. Faircloth, L. Vugler, and W. J. Britt. 1989. A rapid microneutralization assay for the measurement of neutralizing antibody reactive with human cytomegalovirus. J. Virol. Methods 23:157-167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

