The role of cytochrome c in caspase activation in Drosophila melanogaster cells
- PMID: 11901173
- PMCID: PMC2173478
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200111107
The role of cytochrome c in caspase activation in Drosophila melanogaster cells
Abstract
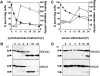
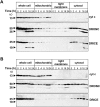
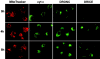
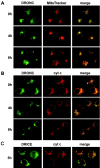
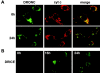
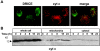
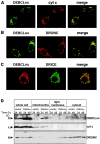
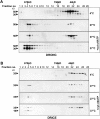
The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria is necessary for the formation of the Apaf-1 apoptosome and subsequent activation of caspase-9 in mammalian cells. However, the role of cytochrome c in caspase activation in Drosophila cells is not well understood. We demonstrate here that cytochrome c remains associated with mitochondria during apoptosis of Drosophila cells and that the initiator caspase DRONC and effector caspase DRICE are activated after various death stimuli without any significant release of cytochrome c in the cytosol. Ectopic expression of the proapoptotic Bcl-2 protein, DEBCL, also fails to show any cytochrome c release from mitochondria. A significant proportion of cellular DRONC and DRICE appears to localize near mitochondria, suggesting that an apoptosome may form in the vicinity of mitochondria in the absence of cytochrome c release. In vitro, DRONC was recruited to a >700-kD complex, similar to the mammalian apoptosome in cell extracts supplemented with cytochrome c and dATP. These results suggest that caspase activation in insects follows a more primitive mechanism that may be the precursor to the caspase activation pathways in mammals.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The two cytochrome c species, DC3 and DC4, are not required for caspase activation and apoptosis in Drosophila cells.J Cell Biol. 2004 Nov 8;167(3):405-10. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200408054. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15533997 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the apoptosome: mechanistic insights into activation of an initiator caspase from Drosophila.Genes Dev. 2015 Feb 1;29(3):277-87. doi: 10.1101/gad.255877.114. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 25644603 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-beta(1) induces apoptosis in rat FaO hepatoma cells via cytochrome c release and oligomerization of Apaf-1 to form a approximately 700-kd apoptosome caspase-processing complex.Hepatology. 2000 Oct;32(4 Pt 1):750-60. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2000.18329. Hepatology. 2000. PMID: 11003619
-
The fly caspases.Cell Death Differ. 2000 Nov;7(11):1039-44. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400756. Cell Death Differ. 2000. PMID: 11139276 Review.
-
Apaf-1/cytochrome c apoptosome: an essential initiator of caspase activation or just a sideshow?Cell Death Differ. 2003 Jan;10(1):16-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401166. Cell Death Differ. 2003. PMID: 12655291 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The mitochondria-mediate apoptosis of Lepidopteran cells induced by azadirachtin.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58499. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058499. Epub 2013 Mar 13. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23516491 Free PMC article.
-
Just So Stories about the Evolution of Apoptosis.Curr Biol. 2016 Jul 11;26(13):R620-R627. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.05.023. Curr Biol. 2016. PMID: 27404257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of Cell Death in Drosophila Tissues.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1419:131-44. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3581-9_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27108437 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial fusion is regulated by Reaper to modulate Drosophila programmed cell death.Cell Death Differ. 2011 Oct;18(10):1640-50. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.26. Epub 2011 Apr 8. Cell Death Differ. 2011. PMID: 21475305 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila IAP antagonists form multimeric complexes to promote cell death.J Cell Biol. 2010 Sep 20;190(6):1039-52. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201004086. Epub 2010 Sep 13. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20837774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baehrecke, E.H. 2000. Steroid regulation of programmed cell death during Drosophila development. Cell Death Differ. 7:1057–1062. - PubMed
-
- Brachmann, C.B., O.W. Jassim, B.D. Wachsmuth, and R.L. Cagan. 2000. The Drosophila bcl-2 family member dBorg-1 functions in the apoptotic response to UV-irradiation. Curr. Biol. 10:547–550. - PubMed
-
- Cain, K., D.G. Brown, C. Langlais, and G.M. Cohen. 1999. Caspase activation involves the formation of the aposome, a large (∼700kDa) caspase-activating complex. J. Biol. Chem. 274:22686–22692. - PubMed
-
- Cain, K., S.B. Bratton, C. Langlais, G. Walker, D.G. Brown, X.-M. Sun, and G.M. Cohen. 2000. Apaf-1 oligomerises into biologically active ∼700-kDa and inactive ∼1.4MDa apoptosome complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 275:6067–6070. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

