Open reading frame 50 protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus directly activates the viral PAN and K12 genes by binding to related response elements
- PMID: 11884541
- PMCID: PMC136055
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.7.3168-3178.2002
Open reading frame 50 protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus directly activates the viral PAN and K12 genes by binding to related response elements
Abstract
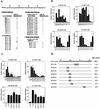
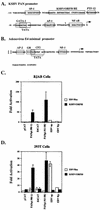
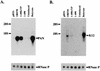
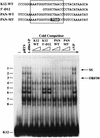
Open reading frame (ORF) 50 protein is capable of activating the entire lytic cycle of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), but its mechanism of action is not well characterized. Here we demonstrate that ORF 50 protein activates two KSHV lytic cycle genes, PAN (polyadenylated nuclear RNA) and K12, by binding to closely related response elements located approximately 60 to 100 nucleotides (nt) upstream of the start of transcription of the two genes. The 25-nt sequence 5' AAATGGGTGGCTAACCTGTCCAAAA from the PAN promoter (PANp) confers a response to ORF 50 protein in both epithelial cells and B cells in the absence of other KSHV proteins. The responsive region of DNA can be transferred to a heterologous minimal promoter. Extensive point mutagenesis showed that a span of at least 20 nt is essential for a response to ORF 50 protein. However, a minimum of six positions within this region were ambiguous. The related 26-nt responsive element in the K12 promoter (K12p), 5' GGAAATGGGTGGCTAACCCCTACATA, shares 20 nt (underlined) with the comparable region of PANp. The divergence is primarily at the 3' end. The DNA binding domain of ORF 50 protein, encompassing amino acids 1 to 490, fused to a heterologous activation domain from herpes simplex virus VP16 [ORF 50(1-490)+VP] can mediate activation of reporter constructs bearing these response elements. Most importantly, ORF 50(1-490)+VP can induce PAN RNA and K12 transcripts in transfected cells. ORF 50(1-490)+VP expressed in human cells binds specifically to duplex oligonucleotides containing the responsive regions from PANp and K12p. These DNA-protein complexes were supershifted by antibody to VP16. ORF 50(1-490) without a VP16 tag also bound to the response element. There was a strong correlation between DNA binding by ORF 50 and transcriptional activation. Mutations within PANp and K12p that impaired transactivation by ORF 50 or ORF 50(1-490)+VP also abolished DNA binding. Only one of eight related complexes formed on PANp and K12p oligonucleotides was due to ORF 50(1-490)+VP. The other complexes were due to cellular proteins. Two KSHV lytic-cycle promoters are activated by a similar mechanism that involves direct recognition of a homologous response element by the DNA binding domain of ORF 50 protein in the context of related cellular proteins.
Figures
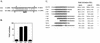
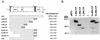
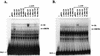
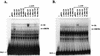

Similar articles
-
Sp3 Transcription Factor Cooperates with the Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus ORF50 Protein To Synergistically Activate Specific Viral and Cellular Gene Promoters.J Virol. 2020 Aug 31;94(18):e01143-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01143-20. Print 2020 Aug 31. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32641483 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) in activation of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) lytic-cycle replication-associated protein (RAP) promoter in cooperation with the KSHV replication and transcription activator (RTA) and RAP.J Virol. 2003 Jan;77(1):600-23. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.1.600-623.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12477864 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus viral interferon regulatory factor gene.J Virol. 2000 Sep;74(18):8623-34. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.18.8623-8634.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10954564 Free PMC article.
-
gamma-2 Herpes virus post-transcriptional gene regulation.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006 Feb;12(2):110-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01317.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006. PMID: 16441447 Review.
-
Transcriptional activation by viral regulatory proteins.Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):435-9. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90171-q. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991. PMID: 1663668 Review.
Cited by
-
Direct interactions of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8 ORF50/Rta protein with the cellular protein octamer-1 and DNA are critical for specifying transactivation of a delayed-early promoter and stimulating viral reactivation.J Virol. 2007 Aug;81(16):8451-67. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00265-07. Epub 2007 May 30. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17537858 Free PMC article.
-
KSHV episomes reveal dynamic chromatin loop formation with domain-specific gene regulation.Nat Commun. 2018 Jan 4;9(1):49. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02089-9. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29302027 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular transcription factor Oct-1 interacts with the Epstein-Barr virus BRLF1 protein to promote disruption of viral latency.J Virol. 2011 Sep;85(17):8940-53. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00569-11. Epub 2011 Jun 22. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21697476 Free PMC article.
-
The RBP-Jκ binding sites within the RTA promoter regulate KSHV latent infection and cell proliferation.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Jan;8(1):e1002479. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002479. Epub 2012 Jan 12. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22253595 Free PMC article.
-
Principal role of TRAP/mediator and SWI/SNF complexes in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus RTA-mediated lytic reactivation.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Mar;23(6):2055-67. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.6.2055-2067.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12612078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamson, A. L., D. Darr, E. Holley-Guthrie, R. A. Johnson, A. Mauser, J. Swenson, and S. Kenney. 2000. Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early proteins BZLF1 and BRLF1 activate the ATF2 transcription factor by increasing the levels of phosphorylated p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinases. J. Virol. 74:1224-1233. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan, S. R., C. Bloomer, and B. Chandran. 1998. Identification and characterization of human herpesvirus-8 lytic cycle-associated ORF 59 protein and the encoding cDNA by monoclonal antibody. Virology 240:118-126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

