Inhibition of all-TRANS-retinoic acid metabolism by R116010 induces antitumour activity
- PMID: 11870544
- PMCID: PMC2375285
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600056
Inhibition of all-TRANS-retinoic acid metabolism by R116010 induces antitumour activity
Abstract
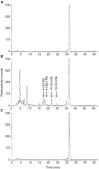
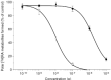
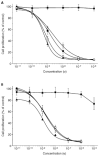
All-trans-retinoic acid is a potent inhibitor of cell proliferation and inducer of differentiation. However, the clinical use of all-trans-retinoic acid in the treatment of cancer is significantly hampered by its toxicity and the prompt emergence of resistance, believed to be caused by increased all-trans-retinoic acid metabolism. Inhibitors of all-trans-retinoic acid metabolism may therefore prove valuable in the treatment of cancer. In this study, we characterize R116010 as a new anticancer drug that is a potent inhibitor of all-trans-retinoic acid metabolism. In vitro, R116010 potently inhibits all-trans-retinoic acid metabolism in intact T47D cells with an IC(50)-value of 8.7 nM. In addition, R116010 is a selective inhibitor as indicated by its inhibition profile for several other cytochrome P450-mediated reactions. In T47D cell proliferation assays, R116010 by itself has no effect on cell proliferation. However, in combination with all-trans-retinoic acid, R116010 enhances the all-trans-retinoic acid-mediated antiproliferative activity in a concentration-dependent manner. In vivo, the growth of murine oestrogen-independent TA3-Ha mammary tumours is significantly inhibited by R116010 at doses as low as 0.16 mg kg(-1). In conclusion, R116010 is a highly potent and selective inhibitor of all-trans-retinoic acid metabolism, which is able to enhance the biological activity of all-trans-retinoic acid, thereby exhibiting antitumour activity. R116010 represents a novel and promising anticancer drug with an unique mechanism of action.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Increasing the intracellular availability of all-trans retinoic acid in neuroblastoma cells.Br J Cancer. 2005 Feb 28;92(4):696-704. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602398. Br J Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15714209 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular targeting of retinoic acid metabolism in neuroblastoma: the role of the CYP26 inhibitor R116010 in vitro and in vivo.Br J Cancer. 2007 Jun 4;96(11):1675-83. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603779. Epub 2007 May 8. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17486130 Free PMC article.
-
Novel retinoic acid metabolism blocking agents endowed with multiple biological activities are efficient growth inhibitors of human breast and prostate cancer cells in vitro and a human breast tumor xenograft in nude mice.J Med Chem. 2004 Dec 30;47(27):6716-29. doi: 10.1021/jm0401457. J Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15615521
-
Cytochrome p450 retinoic acid 4-hydroxylase inhibitors: potential agents for cancer therapy.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2002 Jun;2(3):261-9. doi: 10.2174/1389557023406223. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2002. PMID: 12370067 Review.
-
The cloning and characterization of a novel cytochrome P450 family, CYP26, with specificity toward retinoic acid.Nutr Rev. 1998 Mar;56(3):84-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1998.tb01699.x. Nutr Rev. 1998. PMID: 9564181 Review.
Cited by
-
Improved Homology Model of the Human all-trans Retinoic Acid Metabolizing Enzyme CYP26A1.Molecules. 2016 Mar 15;21(3):351. doi: 10.3390/molecules21030351. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 26999080 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency of All-Trans Retinoic Acid on Gastric Cancer: A Narrative Literature Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 29;19(11):3388. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113388. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30380687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytochrome P450s in the regulation of cellular retinoic acid metabolism.Annu Rev Nutr. 2011 Aug 21;31:65-87. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-072610-145127. Annu Rev Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21529158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in the Application of 2-Aminobenzothiazole to the Multicomponent Synthesis of Heterocycles.ChemistryOpen. 2024 Nov;13(11):e202400185. doi: 10.1002/open.202400185. Epub 2024 Sep 9. ChemistryOpen. 2024. PMID: 39246248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Retinoic Acid-Metabolizing Cytochrome P450s, CYP26, in Inflammation and Cancer.Adv Pharmacol. 2015;74:373-412. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2015.04.006. Epub 2015 May 27. Adv Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26233912 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- AchkarCCBentelJMBoylanJFScherHIGudasLMillerJrWH1994Differences in the pharmacokinetic properties of orally administered all-trans-retinoic acid and 9-cis-retinoic acid in the plasma of nude mice Drug Metab Dispos 22451458 - PubMed
-
- BruynseelsJDe CosterRVan RooyPWoutersWCoeneM-CSnoeckERaeymaekersAFreyneESanzGVanden BusscheGVanden BosscheHWillemsensGJanssenPAJ1990R75251, a new inhibitor of steroid biosynthesis Prostate 16345357 - PubMed
-
- DijkmanGAVan MoorselaarRJAVan GinckelRVan StratumPWoutersLDebruyneFMJSchalkenJADe CosterR1994Antitumoral effects of liarozole in androgen-dependent and -independnet R3327-Dunning prostate adenocarcinomas J Urol 151217222 - PubMed
-
- GarrabrantTAEndDW1995A rapid assay for measuring the metabolism of [3H]-retinoic acid in cell cultures J Pharmacol Toxicol Meth 34219223 - PubMed
-
- HanISChoiJ-H1996Highly specific cytochrome P450-like enzymes for all-trans-retinoic acid in T47D human breast cancer cells J Clin Endocrinol Metab 8120692075 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

