Murine retroviruses activate B cells via interaction with toll-like receptor 4
- PMID: 11854525
- PMCID: PMC122356
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.042355399
Murine retroviruses activate B cells via interaction with toll-like receptor 4
Abstract
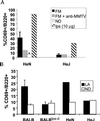
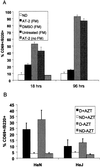
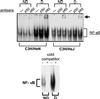
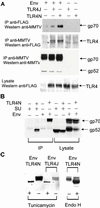
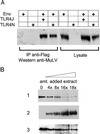
Although most retroviruses require activated cells as their targets for infection, it is not known how this is achieved in vivo. A candidate protein for the activation of B cells by either mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) or murine leukemia virus is the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), a component of the innate immune system. MMTV caused B cell activation in C3H/HeN mice but not in C3H/HeJ or BALB/c (C.C3H Tlr4(lps-d)) congenic mice, both of which have a mutant TLR4 gene. This activation was independent of viral gene expression, because it occurred after treatment of MMTV with ultraviolet light or 2,2'-dithiodipyridine and in azidothymidine-treated mice. Nuclear extracts prepared from the lymphocytes of MMTV-injected C3H/HeN but not C3H/HeJ mice showed increased nuclear factor kappaB activity. Additionally, the MMTV- and Moloney murine leukemia virus envelope proteins coimmunoprecipitated with TLR4 when expressed in 293T cells. The MMTV receptor failed to coimmunoprecipitate with TLR4, suggesting that MMTV/TLR4 interaction is independent of virus attachment and fusion. These results identify retroviral proteins that interact with a mammalian toll receptor and show that direct activation by such viruses may initiate in vivo infection pathways.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endotoxin-induced chemokine expression in murine peritoneal mesothelial cells: the role of toll-like receptor 4.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004 May;15(5):1289-99. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004. PMID: 15100369
-
Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of dendritic cells by a retrovirus.J Virol. 2004 Jan;78(2):576-84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.2.576-584.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14694089 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of macrophages by polysaccharide isolated from the radix of Platycodon grandiflorum.Int Immunopharmacol. 2003 Dec;3(13-14):1873-82. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2003.09.005. Int Immunopharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14636836
-
Can MMTV exploit TLR4?Trends Microbiol. 2002 Jul;10(7):303-5; discussion 305-6. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(02)02385-5. Trends Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12110201 Review.
-
Positional cloning of Lps, and the general role of toll-like receptors in the innate immune response.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2000 Jun;11(2):143-52. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2000. PMID: 10903793 Review.
Cited by
-
Coevolutionary Analysis Implicates Toll-Like Receptor 9 in Papillomavirus Restriction.mBio. 2022 Apr 26;13(2):e0005422. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00054-22. Epub 2022 Mar 21. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35311536 Free PMC article.
-
TANK-binding kinase-1 plays an important role during in vitro and in vivo type I IFN responses to DNA virus infections.J Immunol. 2009 Feb 15;182(4):2248-57. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802466. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19201879 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional changes induced by bovine papillomavirus type 1 in equine fibroblasts.J Virol. 2008 Jul;82(13):6481-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00429-08. Epub 2008 Apr 23. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18434409 Free PMC article.
-
The association of toll-like receptor 4 polymorphism with hepatitis C virus infection in Saudi Arabian patients.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:357062. doi: 10.1155/2014/357062. Epub 2014 Aug 10. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25177689 Free PMC article.
-
Danger of frustrated sensors: Role of Toll-like receptors and NOD-like receptors in aseptic and septic inflammations around total hip replacements.J Orthop Translat. 2017 Jul;10:68-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 Jun 7. J Orthop Translat. 2017. PMID: 29130033 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

