Isolating human transcription factor targets by coupling chromatin immunoprecipitation and CpG island microarray analysis
- PMID: 11799066
- PMCID: PMC155318
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.943102
Isolating human transcription factor targets by coupling chromatin immunoprecipitation and CpG island microarray analysis
Abstract
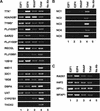
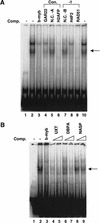
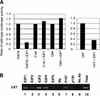
Previously, identification of promoters regulated by mammalian transcription factors has relied upon overexpression studies. Here we present the identification of a large set of promoters that are bound by E2F in physiological conditions. Probing a human CpG microarray with chromatin immunoprecipitated using an antibody to E2F4, we have identified 68 unique target loci; 15% are bidirectional promoters and 25% recruit E2F via a mechanism distinct from the defined consensus site. Interestingly, although E2F has been shown previously to regulate genes involved in cell cycle progression, many of the new E2F target genes encode proteins involved in DNA repair or recombination. We suggest that human CpG microarrays, in combination with chromatin immunoprecipitation, will allow rapid identification of target promoters for many mammalian transcription factors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of novel pRb binding sites using CpG microarrays suggests that E2F recruits pRb to specific genomic sites during S phase.Oncogene. 2003 Mar 13;22(10):1445-60. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206264. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12629508
-
Identification of unknown target genes of human transcription factors using chromatin immunoprecipitation.Methods. 2002 Jan;26(1):37-47. doi: 10.1016/S1046-2023(02)00006-3. Methods. 2002. PMID: 12054903
-
The identification of E2F1-specific target genes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Mar 19;99(6):3890-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.062047499. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11904439 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput screening of chromatin immunoprecipitates using CpG-island microarrays.Methods Enzymol. 2004;376:315-34. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(03)76021-2. Methods Enzymol. 2004. PMID: 14975315 Review. No abstract available.
-
Use of chromatin immunoprecipitation assays in genome-wide location analysis of mammalian transcription factors.Methods Enzymol. 2004;376:304-15. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(03)76020-0. Methods Enzymol. 2004. PMID: 14975314 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Identification of genes directly regulated by the oncogene ZNF217 using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-chip assays.J Biol Chem. 2007 Mar 30;282(13):9703-9712. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611752200. Epub 2007 Jan 26. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17259635 Free PMC article.
-
Exon array CGH: detection of copy-number changes at the resolution of individual exons in the human genome.Am J Hum Genet. 2005 May;76(5):750-62. doi: 10.1086/429588. Epub 2005 Mar 8. Am J Hum Genet. 2005. PMID: 15756638 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the mismatch repair genes PMS2 and MLH1 as p53 target genes by using serial analysis of binding elements.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Mar 29;102(13):4813-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407069102. Epub 2005 Mar 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15781865 Free PMC article.
-
G1/S transcriptional networks modulated by the HOX11/TLX1 oncogene of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Oncogene. 2005 Aug 25;24(36):5561-75. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208727. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15897879 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological genomics identifies estrogen-related receptor alpha as a regulator of renal sodium and potassium homeostasis and the renin-angiotensin pathway.Mol Endocrinol. 2010 Jan;24(1):22-32. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0254. Epub 2009 Nov 9. Mol Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 19901197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyd KE, Farnham PJ. Identification of target genes of oncogenic transcription factors. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1999;222:9–28. - PubMed
-
- Cross SH, Charlton JA, Nan X, Bird AP. Purification of CpG islands using a methylated DNA binding column. Nat Genet. 1994;6:236–244. - PubMed
-
- Hannenhalli S, Levy S. Promoter prediction in the human genome. Bioinformatics. 2001;17:S90–S96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
