Acid incubation reverses the polarity of intercalated cell transporters, an effect mediated by hensin
- PMID: 11781354
- PMCID: PMC150817
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI13292
Acid incubation reverses the polarity of intercalated cell transporters, an effect mediated by hensin
Abstract
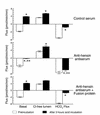
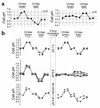
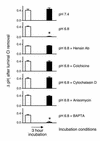
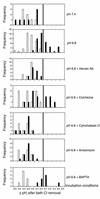
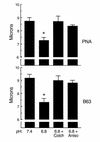
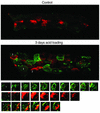
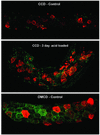
Metabolic acidosis causes a reversal of polarity of HCO(3)(-) flux in the cortical collecting duct (CCD). In CCDs incubated in vitro in acid media, beta-intercalated (HCO(3)(-)-secreting) cells are remodeled to functionally resemble alpha-intercalated (H(+)-secreting) cells. A similar remodeling of beta-intercalated cells, in which the polarity of H(+) pumps and Cl(-)/HCO(3)(-) exchangers is reversed, occurs in cell culture and requires the deposition of polymerized hensin in the ECM. CCDs maintained 3 h at low pH ex vivo display a reversal of HCO(3)(-) flux that is quantitatively similar to an effect previously observed in acid-treated rabbits in vivo. We followed intracellular pH in the same beta-intercalated cells before and after acid incubation and found that apical Cl/HCO(3) exchange was abolished following acid incubation. Some cells also developed basolateral Cl(-)/HCO(3)(-) exchange, indicating a reversal of intercalated cell polarity. This adaptation required intact microtubules and microfilaments, as well as new protein synthesis, and was associated with decreased size of the apical surface of beta-intercalated cells. Addition of anti-hensin antibodies prevented the acid-induced changes in apical and basolateral Cl(-)/HCO(3)(-) exchange observed in the same cells and the corresponding suppression of HCO(3)(-) secretion. Acid loading also promoted hensin deposition in the ECM underneath adapting beta-intercalated cells. Hence, the adaptive conversion of beta-intercalated cells to alpha-intercalated cells during acid incubation depends upon ECM-associated hensin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cyclosporin A produces distal renal tubular acidosis by blocking peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity of cyclophilin.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005 Jan;288(1):F40-7. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00218.2004. Epub 2004 Sep 7. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15353404
-
Phenotypic plasticity and terminal differentiation of the intercalated cell: the hensin pathway.Exp Nephrol. 2000 Mar-Apr;8(2):66-71. doi: 10.1159/000020650. Exp Nephrol. 2000. PMID: 10729744 Review.
-
Galectin-3 expression is induced in renal beta-intercalated cells during metabolic acidosis.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006 Jan;290(1):F148-58. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00244.2005. Epub 2005 Aug 30. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16131647
-
Terminal differentiation in epithelia: the Hensin pathway in intercalated cells.Semin Nephrol. 1999 Sep;19(5):415-20. Semin Nephrol. 1999. PMID: 10511381 Review.
-
Hensin, a new collecting duct protein involved in the in vitro plasticity of intercalated cell polarity.J Clin Invest. 1996 Nov 15;98(10):2324-31. doi: 10.1172/JCI119044. J Clin Invest. 1996. PMID: 8941650 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Topiramate modulates pH of hippocampal CA3 neurons by combined effects on carbonic anhydrase and Cl-/HCO3- exchange.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Jul;142(5):831-42. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705850. Epub 2004 Jun 14. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15197104 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide directly inhibits bicarbonate absorption by the renal outer medullary collecting duct.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 25;10(1):20548. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77363-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33239624 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological role of NBCe2 in the regulation of electrolyte transport in the distal nephron.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015 Sep 15;309(6):F489-91. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00192.2015. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26136555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conversion of ES cells to columnar epithelia by hensin and to squamous epithelia by laminin.J Cell Biol. 2004 Sep 27;166(7):1093-102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200405159. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15452149 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical review: Renal tubular acidosis--a physicochemical approach.Crit Care. 2005;9(6):573-80. doi: 10.1186/cc3802. Epub 2005 Aug 25. Crit Care. 2005. PMID: 16356241 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kaissling B, Kriz W. Structural analysis of the rabbit kidney. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1979; 56:1–121. - PubMed
-
- Madsen KM, Tisher CC. Structural-functional relationships along the distal nephron. Am J Physiol. 1986; 250:F1–F15. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz GJ, Barasch J, Al-Awqati Q. Plasticity of functional epithelial polarity. Nature. 1985; 318:368–371. - PubMed

