Targeting of human DNA polymerase iota to the replication machinery via interaction with PCNA
- PMID: 11724965
- PMCID: PMC64669
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.261560798
Targeting of human DNA polymerase iota to the replication machinery via interaction with PCNA
Abstract
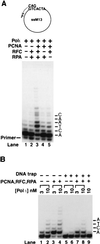
Human DNA polymerase iota (hPoliota) promotes translesion synthesis by inserting nucleotides opposite highly distorting or noninstructional DNA lesions. Here, we provide evidence for the physical interaction of hPoliota with proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), and show that PCNA, together with replication factor C (RFC) and replication protein A (RPA), stimulates the DNA synthetic activity of hPoliota. In the presence of these protein factors, on undamaged DNA, the efficiency (V(max)/K(m)) of correct nucleotide incorporation by hPoliota is increased approximately 80-150-fold, and this increase in efficiency results from a reduction in the apparent K(m) for the nucleotide. PCNA, RFC, and RPA also stimulate nucleotide incorporation opposite the 3'-T of the (6) thymine-thymine (T-T) photoproduct and opposite an abasic site. The interaction of hPoliota with PCNA implies that the targeting of this polymerase to the replication machinery stalled at a lesion site is achieved via this association.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A single domain in human DNA polymerase iota mediates interaction with PCNA: implications for translesion DNA synthesis.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Feb;25(3):1183-90. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.3.1183-1190.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15657443 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulation of DNA synthesis activity of human DNA polymerase kappa by PCNA.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Feb;22(3):784-91. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.3.784-791.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11784855 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction with PCNA is essential for yeast DNA polymerase eta function.Mol Cell. 2001 Aug;8(2):407-15. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00319-7. Mol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11545742
-
'PIPs' in DNA polymerase: PCNA interaction affairs.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Dec 18;48(6):2811-2822. doi: 10.1042/BST20200678. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 33196097 Review.
-
Functions of Multiple Clamp and Clamp-Loader Complexes in Eukaryotic DNA Replication.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1042:135-162. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-6955-0_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29357057 Review.
Cited by
-
The Fanconi anemia pathway in replication stress and DNA crosslink repair.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Dec;69(23):3963-74. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1051-0. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22744751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PUB-NChIP--"in vivo biotinylation" approach to study chromatin in proximity to a protein of interest.Genome Res. 2013 Feb;23(2):331-40. doi: 10.1101/gr.134874.111. Epub 2012 Oct 4. Genome Res. 2013. PMID: 23038767 Free PMC article.
-
A single domain in human DNA polymerase iota mediates interaction with PCNA: implications for translesion DNA synthesis.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Feb;25(3):1183-90. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.3.1183-1190.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15657443 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of PCNA-binding and ubiquitin-binding domains in human DNA polymerase eta in translesion DNA synthesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Nov 18;105(46):17724-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809844105. Epub 2008 Nov 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 19001268 Free PMC article.
-
Translesion DNA polymerases in eukaryotes: what makes them tick?Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Jun;52(3):274-303. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2017.1291576. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28279077 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

