A transcription factor regulatory circuit in differentiated pancreatic cells
- PMID: 11717395
- PMCID: PMC64707
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.241349398
A transcription factor regulatory circuit in differentiated pancreatic cells
Abstract
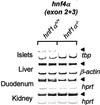
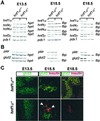
Mutations in the human genes encoding hepatocyte nuclear factors (HNF) 1alpha, 1beta, 4alpha, and IPF1(PDX1/IDX1/STF1) result in pancreatic beta cell dysfunction and diabetes mellitus. In hepatocytes, hnf4alpha controls the transcription of hnf1alpha, suggesting that this same interaction may operate in beta cells and thus account for the common diabetic phenotype. We show that, in pancreatic islet and exocrine cells, hnf4alpha expression unexpectedly depends on hnf1alpha. This effect is tissue-specific and mediated through direct occupation by hnf1alpha of an alternate promoter located 45.6 kb from the previously characterized hnf4alpha promoter. Hnf1alpha also exerts direct control of pancreatic-specific expression of hnf4gamma and hnf3gamma. Hnf1alpha dependence of hnf4alpha, hnf4gamma, hnf3gamma, and two previously characterized distal targets (glut2 and pklr) is established only after differentiated cells arise during pancreatic embryonic development. These studies define an unexpected hierarchical regulatory relationship between two genes involved in human monogenic diabetes in the cells, which are relevant to its pathophysiology. Furthermore, they indicate that hnf1alpha is an essential component of a transcription factor circuit whose role may be to maintain differentiated functions of pancreatic cells.
Figures



Comment in
-
Dissecting the transcriptional network of pancreatic islets during development and differentiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Dec 4;98(25):14189-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.251558998. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11734636 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Genetic evidence that HNF-1alpha-dependent transcriptional control of HNF-4alpha is essential for human pancreatic beta cell function.J Clin Invest. 2002 Sep;110(6):827-33. doi: 10.1172/JCI15085. J Clin Invest. 2002. PMID: 12235114 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular biology. HNFs--linking the liver and pancreatic islets in diabetes.Science. 2004 Feb 27;303(5662):1311-2. doi: 10.1126/science.1095486. Science. 2004. PMID: 14988544 No abstract available.
-
Mutations in hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha (HNF4alpha) gene associated with diabetes result in greater loss of HNF4alpha function in pancreatic beta-cells than in nonpancreatic beta-cells and in reduced activation of the apolipoprotein CIII promoter in hepatic cells.J Mol Med (Berl). 2002 Jul;80(7):423-30. doi: 10.1007/s00109-002-0340-8. Epub 2002 May 8. J Mol Med (Berl). 2002. PMID: 12110948
-
The role of transcription factors in maturity-onset diabetes of the young.Mol Genet Metab. 2002 Sep-Oct;77(1-2):35-43. doi: 10.1016/s1096-7192(02)00150-6. Mol Genet Metab. 2002. PMID: 12359128 Review.
-
Different genes, different diabetes: lessons from maturity-onset diabetes of the young.Ann Med. 2002;34(3):207-16. Ann Med. 2002. PMID: 12173691 Review.
Cited by
-
Variants influencing age at diagnosis of HNF1A-MODY.Mol Med. 2022 Sep 14;28(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00542-0. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36104811 Free PMC article.
-
Liver fat storage is controlled by HNF4α through induction of lipophagy and is reversed by a potent HNF4α agonist.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jun 11;12(6):603. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03862-x. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34117215 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha involvement in liver and intestinal inflammatory networks.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jan 7;20(1):22-30. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.22. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24415854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulation of Transcription Factor Networks Unveils Different Pathways in Human Papillomavirus 16-Positive Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Adenocarcinoma of the Uterine Cervix.Front Oncol. 2021 May 19;11:626187. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.626187. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34094909 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila HNF4 nuclear receptor promotes glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and mitochondrial function in adults.Elife. 2016 May 17;5:e11183. doi: 10.7554/eLife.11183. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27185732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deeney J T, Prentki M, Corkey B E. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2000;11:267–275. - PubMed
-
- Sander M, Sussel L, Conners J, Scheel D, Kalamaras J, Dela C F, Schwitzgebel V, Hayes-Jordan A, German M. Development (Cambridge, UK) 2000;127:5533–5540. - PubMed
-
- Edlund H. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999;11:663–668. - PubMed
-
- Froguel P, Velho G. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1999;10:142–146. - PubMed
-
- Yamagata K, Oda N, Kaisaki P J, Menzel S, Furuta H, Vaxillaire M, Southam L, Cox R D, Lathrop G M, Boriraj V V, et al. Nature (London) 1996;384:455–458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

