Loss of mRor1 enhances the heart and skeletal abnormalities in mRor2-deficient mice: redundant and pleiotropic functions of mRor1 and mRor2 receptor tyrosine kinases
- PMID: 11713269
- PMCID: PMC99997
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.24.8329-8335.2001
Loss of mRor1 enhances the heart and skeletal abnormalities in mRor2-deficient mice: redundant and pleiotropic functions of mRor1 and mRor2 receptor tyrosine kinases
Abstract
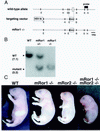
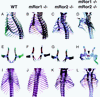
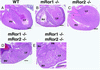
The mammalian Ror family of receptor tyrosine kinases consists of two structurally related proteins, Ror1 and Ror2. We have shown that mRor2-deficient mice exhibit widespread skeletal abnormalities, ventricular septal defects in the heart, and respiratory dysfunction, leading to neonatal lethality (S. Takeuchi, K. Takeda, I. Oishi, M. Nomi, M. Ikeya, K. Itoh, S. Tamura, T. Ueda, T. Hatta, H. Otani, T. Terashima, S. Takada, H. Yamamura, S. Akira, and Y. Minami, Genes Cells 5:71-78, 2000). Here we show that mRor1-deficient mice have no apparent skeletal or cardiac abnormalities, yet they also die soon after birth due to respiratory dysfunction. Interestingly, mRor1/mRor2 double mutant mice show markedly enhanced skeletal abnormalities compared with mRor2 mutant mice. Furthermore, double mutant mice also exhibit defects not observed in mRor2 mutant mice, including a sternal defect, dysplasia of the symphysis of the pubic bone, and complete transposition of the great arteries. These results indicate that mRor1 and mRor2 interact genetically in skeletal and cardiac development.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Spatio-temporally regulated expression of receptor tyrosine kinases, mRor1, mRor2, during mouse development: implications in development and function of the nervous system.Genes Cells. 1999 Jan;4(1):41-56. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.1999.00234.x. Genes Cells. 1999. PMID: 10231392
-
Mouse Ror2 receptor tyrosine kinase is required for the heart development and limb formation.Genes Cells. 2000 Jan;5(1):71-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.2000.00300.x. Genes Cells. 2000. PMID: 10651906
-
Expression and function of the Ror-family receptor tyrosine kinases during development: lessons from genetic analyses of nematodes, mice, and humans.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2003 Feb;23(1):1-15. doi: 10.1081/rrs-120018757. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2003. PMID: 12680586 Review.
-
Mice lacking the orphan receptor ror1 have distinct skeletal abnormalities and are growth retarded.Dev Dyn. 2010 Aug;239(8):2266-77. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22362. Dev Dyn. 2010. PMID: 20593419
-
Thoracic skeletal defects and cardiac malformations: a common epigenetic link?Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2006 Dec;78(4):354-70. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.20084. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2006. PMID: 17315248 Review.
Cited by
-
microRNA regulation of Wnt signaling pathways in development and disease.Cell Signal. 2015 Jul;27(7):1380-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Cell Signal. 2015. PMID: 25843779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt5a-Ror-Dishevelled signaling constitutes a core developmental pathway that controls tissue morphogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Mar 13;109(11):4044-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1200421109. Epub 2012 Feb 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22343533 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor tyrosine kinase profiling of ischemic heart identifies ROR1 as a potential therapeutic target.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018 Oct 20;18(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12872-018-0933-y. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018. PMID: 30342492 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-ROR1 CAR-T cells: Architecture and performance.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 17;10:1121020. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1121020. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36873868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ror1-Ror2 complexes modulate synapse formation in hippocampal neurons.Neuroscience. 2010 Feb 17;165(4):1261-74. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.11.056. Epub 2009 Dec 1. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 19958813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afzal A R, Rajab A, Fenske C D, Oldridge M, Elanko N, Ternes-Pereira E, Tüysüz B, Murday V A, Patton M A, Wilkie A O M, Jeffery S. Recessive Robinow syndrome, allelic to dominant brachydactyly type B, is caused by mutation of Ror2. Nat Genet. 2000;25:419–422. - PubMed
-
- Clouthier D E, Hosoda K, Richardson J A, Williams S C, Yanagisawa H, Kuwaki T, Kumada M, Hammer R E, Yanagisawa M. Cranial and cardiac neural crest defects in endothelin-A receptor-deficient mice. Development. 1998;125:813–824. - PubMed
-
- Colin L B. Cardiac pathology. In: Becker A E, Anderson R H, editors. Paediatric pathology. New York, N.Y: Springer-Verlag; 1981. pp. 87–145.
-
- Davis A P, Witte D P, Hsieh-Li H M, Potter S S, Capecchi M R. Absence of radius and ulna in mice lacking hoxa-11 and hoxd-11. Nature. 1995;375:791–795. - PubMed
-
- DeChiara T M, Kimble R B, Poueymirou W T, Rojas J, Masiakowski P, Valenzuela D M, Yancopoulos G D. Ror2, encoding a receptor-like tyrosine kinase, is required for cartilage and growth plate development. Nat Genet. 2000;24:271–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
