GGAs: roles of the different domains and comparison with AP-1 and clathrin
- PMID: 11694590
- PMCID: PMC60277
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.11.3573
GGAs: roles of the different domains and comparison with AP-1 and clathrin
Abstract
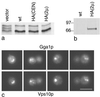
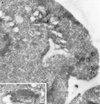
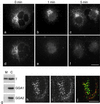
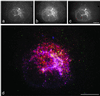
We have previously identified a novel family of proteins called the GGAs (Golgi-localized, gamma-ear-containing, ADP-ribosylation factor-binding proteins). These proteins consist of an NH(2)-terminal VHS domain, followed by a GAT domain, a variable domain, and a gamma-adaptin ear homology domain. Studies from our own laboratory and others, making use of both yeast and mammals cells, indicate that the GGAs facilitate trafficking from the trans-Golgi network to endosomes. Here we have further investigated the function of the GGAs. We find that GGA-deficient yeast are not only defective in vacuolar protein sorting but they are also impaired in their ability to process alpha-factor. Using deletion mutants and chimeras, we show that the VHS domain is required for GGA function and that the VHS domain from Vps27p will not substitute for the GGA VHS domain. In contrast, the gamma-adaptin ear homology domain contributes to GGA function but is not absolutely required, and full function can be restored by replacing the GGA ear domain with the gamma-adaptin ear domain. Deleting the gamma-adaptin gene together with the two GGA genes exacerbates the phenotype in yeast, suggesting that they function on parallel pathways. In mammalian cells, the association of GGAs with the membrane is extremely unstable, which may account for their absence from purified clathrin-coated vesicles. Double- and triple-labeling immunofluorescence experiments indicate that the GGAs and AP-1 are associated with distinct populations of clathrin-coated vesicles budding from the trans-Golgi network. Together with results from other studies, our findings suggest that the GGAs act as monomeric adaptors, with the four domains involved in cargo selection, membrane localization, clathrin binding, and accessory protein recruitment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A family of proteins with gamma-adaptin and VHS domains that facilitate trafficking between the trans-Golgi network and the vacuole/lysosome.J Cell Biol. 2000 Apr 3;149(1):67-80. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.1.67. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10747088 Free PMC article.
-
Structural requirements for function of yeast GGAs in vacuolar protein sorting, alpha-factor maturation, and interactions with clathrin.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Dec;21(23):7981-94. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.23.7981-7994.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11689690 Free PMC article.
-
GGAs: a family of ADP ribosylation factor-binding proteins related to adaptors and associated with the Golgi complex.J Cell Biol. 2000 Apr 3;149(1):81-94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.1.81. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10747089 Free PMC article.
-
The structure and function of GGAs, the traffic controllers at the TGN sorting crossroads.Cell Struct Funct. 2003 Oct;28(5):431-42. doi: 10.1247/csf.28.431. Cell Struct Funct. 2003. PMID: 14745135 Review.
-
Emerging roles of Golgi/endosome-localizing monomeric clathrin adaptors GGAs.Anat Sci Int. 2020 Jan;95(1):12-21. doi: 10.1007/s12565-019-00505-2. Epub 2019 Oct 28. Anat Sci Int. 2020. PMID: 31659673 Review.
Cited by
-
Heterotrimeric G proteins and the single-transmembrane domain IGF-II/M6P receptor: functional interaction and relevance to cell signaling.Mol Neurobiol. 2007 Jun;35(3):329-45. doi: 10.1007/s12035-007-0021-2. Mol Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17917122 Review.
-
Auxilin depletion causes self-assembly of clathrin into membraneless cages in vivo.Traffic. 2008 Aug;9(8):1354-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00764.x. Epub 2008 May 17. Traffic. 2008. PMID: 18489706 Free PMC article.
-
A microscopy-based kinetic analysis of yeast vacuolar protein sorting.Elife. 2020 Jun 25;9:e56844. doi: 10.7554/eLife.56844. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32584255 Free PMC article.
-
Laa1p, a conserved AP-1 accessory protein important for AP-1 localization in yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Jul;17(7):3304-17. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-02-0096. Epub 2006 May 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16687571 Free PMC article.
-
Autoinhibition of the ligand-binding site of GGA1/3 VHS domains by an internal acidic cluster-dileucine motif.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Jun 11;99(12):8072-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.082235699. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12060753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Austin C, Hinners I, Tooze SA. Direct and GTP-dependent interaction of ADP-ribosylation factor 1 with clathrin adaptor protein AP-1 on immature secretory granules. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:21862–21869. - PubMed
-
- Barlowe C, Orci L, Yeung T, Hosobuchi M, Hamamoto S, Salama N, Rexach MF, Ravazzola M, Amherdt M, Schekman R. COPII: a membrane coat formed by Sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994;77:895–907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

