Use of recombinant envelope proteins for serological diagnosis of Dengue virus infection in an immunochromatographic assay
- PMID: 11687456
- PMCID: PMC96242
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.8.6.1150-1155.2001
Use of recombinant envelope proteins for serological diagnosis of Dengue virus infection in an immunochromatographic assay
Abstract
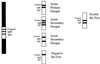
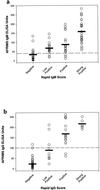
An immunochromatographic test that incorporates recombinant antigens (Dengue Duo Rapid Strip Test; PanBio, Brisbane, Australia) has recently become commercially available. This assay is performed in 15 min and detects both immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG in a capture format. The four recombinant proteins used represent the N-terminal 80% of the viral envelope glycoproteins of dengue viruses 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of the recombinant-antigen-based assay were 90 and 86%, respectively. The similar diagnostic performance of these antigens to that of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays using whole dengue virus suggests that they mimic whole dengue viruses in primary structure and epitope conformation. These results suggest that recombinant proteins can be used in diagnostic assays for dengue to overcome safety issues associated with the use of whole virus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of recombinant dengue viral envelope B domain protein antigens for the detection of dengue complex-specific antibodies.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1998 Feb;58(2):144-51. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1998.58.144. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1998. PMID: 9502595
-
Comparison of PanBio dengue duo enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and MRL dengue fever virus immunoglobulin M capture ELISA for diagnosis of dengue virus infections in Southeast Asia.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1999 Sep;6(5):705-12. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.6.5.705-712.1999. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10473522 Free PMC article.
-
A custom-designed recombinant multiepitope protein as a dengue diagnostic reagent.Protein Expr Purif. 2005 May;41(1):136-47. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2005.01.009. Protein Expr Purif. 2005. PMID: 15802231
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of rapid immunochromatographic assays for the detection of dengue virus IgM antibodies during acute infection.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2006 Aug;100(8):775-84. doi: 10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.10.018. Epub 2006 Mar 23. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2006. PMID: 16551470 Review.
-
Peptide Based Viral Detection Systems for Effective Diagnosis of Common Viral Infections in India.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017;18(9):939-945. doi: 10.2174/1389203717666160724205226. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017. PMID: 27455967 Review.
Cited by
-
Immuno-dominant dengue NS1 peptides as antigens for production of monoclonal antibodies.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Oct 21;9:935456. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.935456. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36339720 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes with hypertension as risk factors for adult dengue hemorrhagic fever in a predominantly dengue serotype 2 epidemic: a case control study.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6(5):e1641. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001641. Epub 2012 May 1. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012. PMID: 22563519 Free PMC article.
-
Dengue Mosaic Vaccines Enhance Cellular Immunity and Expand the Breadth of Neutralizing Antibody Against All Four Serotypes of Dengue Viruses in Mice.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 20;10:1429. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01429. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31281322 Free PMC article.
-
Early appearance of neutralizing immunoglobulin G3 antibodies is associated with chikungunya virus clearance and long-term clinical protection.J Infect Dis. 2012 Apr 1;205(7):1147-54. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis033. Epub 2012 Mar 1. J Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22389226 Free PMC article.
-
The different tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19 - A review in Brazil so far.JBRA Assist Reprod. 2020 Jul 14;24(3):340-346. doi: 10.5935/1518-0557.20200046. Online ahead of print. JBRA Assist Reprod. 2020. PMID: 32491306 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bundo K, Igarashi A. Antibody capture ELISA for detection of immunoglobulin M antibodies in sera from Japanese encephalitis and dengue haemorrhagic fever patients. J Virol Methods. 1985;11:15–22. - PubMed
-
- Burke D S, Nisalak A, Hoke C H., Jr Field trial of a Japanese encephalitis diagnostic kit. J Med Virol. 1986;18:41–49. - PubMed
-
- Cardosa M J, Zuraini I. Comparison of an IgM capture ELISA with a dot enzyme immunoassay for laboratory diagnosis of dengue virus infections. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1991;22:337–340. - PubMed
-
- Cardosa M J, Bahavudin F, Hamid S, Hooi T P, Nimmanitya S. A nitrocellulose membrane based IgM capture enzyme immunoassay for etiological diagnosis of dengue virus infection. Clin Diagn Virol. 1995;3:343–350. - PubMed
-
- Churdboonchart V, Bhamarapravati N, Peampramprecha S, Sirinavin S. Antibodies against dengue viral proteins in primary and secondary dengue hemorrhagic fever. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1991;44:481–493. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical