EGF-R signaling through Fyn kinase disrupts the function of integrin alpha6beta4 at hemidesmosomes: role in epithelial cell migration and carcinoma invasion
- PMID: 11684709
- PMCID: PMC2150849
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200105017
EGF-R signaling through Fyn kinase disrupts the function of integrin alpha6beta4 at hemidesmosomes: role in epithelial cell migration and carcinoma invasion
Abstract
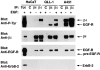
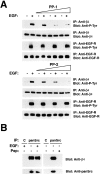
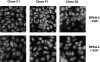
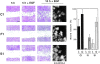
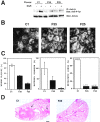
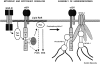
We have examined the mechanism and functional significance of hemidesmosome disassembly during normal epithelial cell migration and squamous carcinoma invasion. Our findings indicate that a fraction of EGF receptor (EGF-R) combines with the hemidesmosomal integrin alpha6beta4 in both normal and neoplastic keratinocytes. Activation of the EGF-R causes tyrosine phosphorylation of the beta4 cytoplasmic domain and disruption of hemidesmosomes. The Src family kinase inhibitors PP1 and PP2 prevent tyrosine phosphorylation of beta4 and disassembly of hemidesmosomes without interfering with the activation of EGF-R. Coimmunoprecipitation experiments indicate that Fyn and, to a lesser extent, Yes combine with alpha6beta4. By contrast, Src and Lck do not associate with alpha6beta4 to a significant extent. A dominant negative form of Fyn, but not Src, prevents tyrosine phosphorylation of beta4 and disassembly of hemidesmosomes. These observations suggest that the EGF-R causes disassembly of hemidesmosomes by activating Fyn, which in turn phosphorylates the beta4 cytoplasmic domain. Neoplastic cells expressing dominant negative Fyn display increased hemidesmosomes and migrate poorly in vitro in response to EGF. Furthermore, dominant negative Fyn decreases the ability of squamous carcinoma cells to invade through Matrigel in vitro and to form lung metastases following intravenous injection in nude mice. These results suggest that disruption of hemidesmosomes mediated by Fyn is a prerequisite for normal keratinocyte migration and squamous carcinoma invasion.
Figures



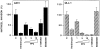
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase Cdelta-mediated phosphorylation of alpha6beta4 is associated with reduced integrin localization to the hemidesmosome and decreased keratinocyte attachment.Cancer Res. 2001 Jun 1;61(11):4591-8. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11389095
-
Interaction of syndecan and alpha6beta4 integrin cytoplasmic domains: regulation of ErbB2-mediated integrin activation.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 30;285(18):13569-79. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.102137. Epub 2010 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20181947 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase C-dependent mobilization of the alpha6beta4 integrin from hemidesmosomes and its association with actin-rich cell protrusions drive the chemotactic migration of carcinoma cells.J Cell Biol. 1999 Sep 6;146(5):1147-60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.146.5.1147. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10477766 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of hemidesmosome disassembly by growth factor receptors.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008 Oct;20(5):589-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.05.001. Epub 2008 Jun 24. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18583123 Review.
-
The alpha 6 beta 4 integrin and epithelial cell migration.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001 Oct;13(5):541-5. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00249-0. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11544021 Review.
Cited by
-
β4 Integrin signaling induces expansion of prostate tumor progenitors.J Clin Invest. 2013 Feb;123(2):682-99. doi: 10.1172/JCI60720. Epub 2013 Jan 25. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23348745 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent mutations in epigenetic regulators, RHOA and FYN kinase in peripheral T cell lymphomas.Nat Genet. 2014 Feb;46(2):166-70. doi: 10.1038/ng.2873. Epub 2014 Jan 12. Nat Genet. 2014. PMID: 24413734 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin α6β4 in colorectal cancer.World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2010 Apr 15;1(1):3-11. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v1.i1.3. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2010. PMID: 21607137 Free PMC article.
-
An EGFR/Src-dependent β4 integrin/FAK complex contributes to malignancy of breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 9;5:16408. doi: 10.1038/srep16408. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26549523 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin β4 in EMT: an implication of renal diseases.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 May 15;8(5):6967-76. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26221233 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alland, L., S.M. Peseckis, R.E. Atherton, L. Berthiaume, and M.D. Resh. 1994. Dual myristylation and palmitylation of Src family member p59fyn affects subcellular localization. J. Biol. Chem. 269:16701–16705. - PubMed
-
- Biscardi, J.S., D.A. Tice, and S.J. Parsons. 1999. c-Src, receptor tyrosine kinases, and human cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 76:61–119. - PubMed
-
- Borradori, L., and A. Sonnenberg. 1999. Structure and function of hemidesmosomes: more than simple adhesion complexes. J. Invest. Dermatol. 112:411–418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

