Bax loss impairs Myc-induced apoptosis and circumvents the selection of p53 mutations during Myc-mediated lymphomagenesis
- PMID: 11604501
- PMCID: PMC99936
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.22.7653-7662.2001
Bax loss impairs Myc-induced apoptosis and circumvents the selection of p53 mutations during Myc-mediated lymphomagenesis
Abstract
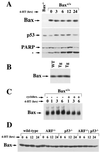
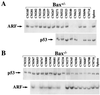
The ARF and p53 tumor suppressors mediate Myc-induced apoptosis and suppress lymphoma development in E mu-myc transgenic mice. Here we report that the proapoptotic Bcl-2 family member Bax also mediates apoptosis triggered by Myc and inhibits Myc-induced lymphomagenesis. Bax-deficient primary pre-B cells are resistant to the apoptotic effects of Myc, and Bax loss accelerates lymphoma development in E mu-myc transgenics in a dose-dependent fashion. Eighty percent of lymphomas arising in wild-type E mu-myc transgenics have alterations in the ARF-Mdm2-p53 tumor suppressor pathway characterized by deletions in ARF, mutations or deletions of p53, and overexpression of Mdm2. The absence of Bax did not alter the frequency of biallelic deletion of ARF in lymphomas arising in E mu-myc transgenic mice or the rate of tumorigenesis in ARF-null mice. Furthermore, Mdm2 was overexpressed at the same frequency in lymphomas irrespective of Bax status, suggesting that Bax resides in a pathway separate from ARF and Mdm2. Strikingly, lymphomas from Bax-null E mu-myc transgenics lacked p53 alterations, whereas 27% of the tumors in Bax(+/-) E mu-myc transgenic mice contained p53 mutations or deletions. Thus, the loss of Bax eliminates the selection of p53 mutations and deletions, but not ARF deletions or Mdm2 overexpression, during Myc-induced tumorigenesis, formally demonstrating that Myc-induced apoptotic signals through ARF/Mdm2 and p53 must bifurcate: p53 signals through Bax, whereas this is not necessarily the case for ARF and Mdm2.
Figures



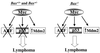
Similar articles
-
Disruption of the ARF-Mdm2-p53 tumor suppressor pathway in Myc-induced lymphomagenesis.Genes Dev. 1999 Oct 15;13(20):2658-69. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.20.2658. Genes Dev. 1999. PMID: 10541552 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of one allele of ARF rescues Mdm2 haploinsufficiency effects on apoptosis and lymphoma development.Oncogene. 2004 Nov 25;23(55):8931-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208052. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15467748
-
Mdm2 haplo-insufficiency profoundly inhibits Myc-induced lymphomagenesis.EMBO J. 2003 Mar 17;22(6):1442-50. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg133. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12628936 Free PMC article.
-
The Myc-nucleophosmin-ARF network: a complex web unveiled.Cell Cycle. 2009 Sep 1;8(17):2703-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.17.9418. Epub 2009 Sep 2. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19652540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MDM2, an introduction.Mol Cancer Res. 2003 Dec;1(14):993-1000. Mol Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14707282 Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of Ras/Mapk pathway signaling inhibits Myc-induced lymphomagenesis.Cell Death Differ. 2012 Jul;19(7):1220-7. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2012.1. Epub 2012 Feb 3. Cell Death Differ. 2012. PMID: 22301919 Free PMC article.
-
MYC degradation under low O2 tension promotes survival by evading hypoxia-induced cell death.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Sep;33(17):3494-504. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00853-12. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23816886 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus in Burkitt's lymphoma: a role for latent membrane protein 2A.Cell Cycle. 2010 Mar 1;9(5):901-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.5.10840. Epub 2010 Mar 3. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20160479 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of p73 promotes dissemination of Myc-induced B cell lymphomas in mice.J Clin Invest. 2010 Jun;120(6):2070-80. doi: 10.1172/JCI40331. Epub 2010 May 17. J Clin Invest. 2010. PMID: 20484818 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of p53 is insufficient to allow B cells and B-cell lymphomas to survive without Dicer.Cancer Res. 2014 Jul 15;74(14):3923-34. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1866. Epub 2014 May 19. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24840646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams J M, Harris A W, Pinkert C A, Corcoran L M, Alexander W S, Cory S, Palmiter R D, Brinster R L. The c-myc oncogene driven by immunoglobulin enhancers induces lymphoid malignancy in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985;318:533–538. - PubMed
-
- Askew D S, Ashmun R A, Simmons B C, Cleveland J L. Constitutive c-myc expression in an IL-3-dependent myeloid cell line suppresses cell cycle arrest and accelerates apoptosis. Oncogene. 1991;6:1915–1922. - PubMed
-
- Brimmell M, Mendiola R, Mangion J, Packham G. BAX frameshift mutations in cell lines derived from human haemopoietic malignancies are associated with resistance to apoptosis and microsatellite instability. Oncogene. 1998;16:1803–1812. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
